死锁检测实现
一、背景
在工作项目使用多进程、多线程过程中,因争夺资源而造成一种资源竞态,所以需加锁处理。如下图所示,线程A想获取线程B的锁,线程B想获取线程C的锁,线程 C 想获取线程D的锁, 线程D想获取线程A的锁,从而构建了一个资源获取环,当进程或者线程申请的锁处于相互交叉锁住的情况,就会出现死锁,它们将无法继续运行。
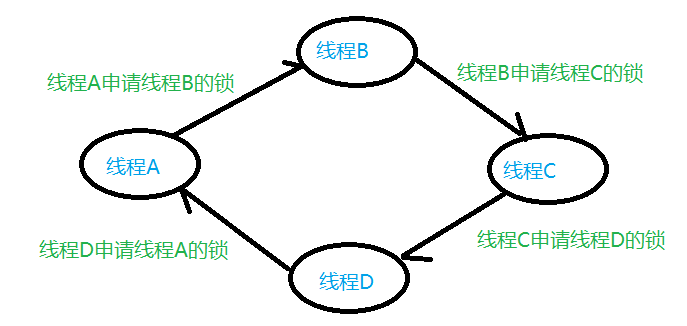
死锁的存在是因为有资源获取环的存在,所以只要能检测出资源获取环,就等同于检测出死锁的存在。
二、原理
在不改变项目源代码的情况下,采用图算法来检测环的存在,使用有向图来存储;如线程A获取线程B已占用的锁(表示线程B获取锁成功),则为线程A指向线程B;启动一个线程定时对图进行检测是否有环的存在。
(1)数据结构
//数据/点 struct node{ uint64 thread_id;//线程ID uint64 lock_id;//锁ID int degress; }; //数据和数据结构分开 struct vertex{ struct node *d; struct vertex *next; }; struct graph{ struct vertex list[THREAD_MAX];//存储图的所有节点 int num;//已经使用了多少个 struct node locklist[THREAD_MAX]; int lockidx; pthread_mutex_t mutex;//预留:线程安全考虑,在对图修改时加锁 };
(2)图的操作
a.创建图节点
//创建图节点 struct vertex *create_vertex(struct node *d){ struct vertex *tex = (struct vertex*)calloc(1,sizeof(struct vertex)); if(tex == NULL) return NULL; tex->d = d; tex->next = NULL; return tex; }
b.查找节点
//查找节点,是否存在 int search_vertex(struct node *d){ int i; for (i = 0; i < tg->num; i++) { if (tg->list[i].d->thread_id == d->thread_id) { return i; } } return -1; }
c.添加节点
//添加节点,只是把添加的节点放到list中,还没有确定各节点间的指向,必须通过add_edge添加边来确定 void add_vertex(struct node *d){ if (search_vertex(d) == -1) { tg->list[tg->num].d = d;//添加到list中 tg->list[tg->num].next = NULL; tg->num++;//节点数累加 } }
d.添加边,指定方向
//添加边,指定方向,谁指向谁 void add_edge(struct node *from, struct node *to){ add_vertex(from); add_vertex(to); struct vertex *v = &tg->list[search_vertex(from)]; while (v->next != NULL) { v = v->next; } v->next = create_vertex(to); }
e.检测节点间是否有边
//检测节点from和to间是否有边连接 int verifty_edge(struct node *from, struct node *to){ if(tg->num == 0) return 0; int idx = search_vertex(from); if(idx == -1) return 0; struct vertex *v = &(tg->list[idx]); while(v != NULL){ if(v->d->thread_id == to->thread_id) return 1; v = v->next; } return 0; }
f.删除边
//删除边 void remove_edge(struct node *from, struct node *to){ int idxi = search_vertex(from); int idxj = search_vertex(to); if(idxi != -1 && idxj !=-1){ struct vertex *v = &tg->list[idxi]; struct vertex *remove; while(v->next != NULL){ if(v->next->d->thread_id == to->thread_id){//找到要删除的节点 remove = v->next; v->next = v->next->next; free(remove); break; } v = v->next; } } }
(3)图遍历
本文采用图遍历中最为常用的深度优先搜索进行遍历,代码如下。
//dfs深度遍历 int dfs(int idx){ struct vertex *v = &tg->list[idx]; if(visited[idx] == 1){//有环 path[k++] = idx; print_deadlock(); deadlock = 1; return 0; } visited[idx] =1;//被遍历到了,赋值为1,保证同一个节点只能遍历一次 path[k++] = idx; while(v->next !=NULL){ dfs(search_vertex(v->next->d)); k--; v = v->next; } return 1; } //遍历图,任意从图的一个节点出发,对每一个节点进行dfs遍历 int search_for_cycle(int idx){ struct vertex *v = &tg->list[idx]; visited[idx] = 1; k = 0; path[k++] = idx; while(v->next != NULL){ int i = 0; for (; i < tg->num; i++) { if(i == idx){ continue; } visited[i] = 0; } for(i = 1; i <= THREAD_MAX; i++){ path[i] = -1; } k = 1; dfs(search_vertex(v->next->d)); v = v->next; } }
(4)启动检测
启动线程定时检测图是否有环,代码如下。
//从第0个节点开始dfs void check_dead_lock(){ int i = 0; deadlock = 0; for(;i < tg->num; i++){ if(deadlock == 1) break; search_for_cycle(i); } if(deadlock == 0){ printf("no deadlock\n"); } } //检测锁线程func static void *thread_func(void *args){ while(1){ sleep(5); check_dead_lock(); } } //启动检测锁线程 void start_check(){ tg = (struct graph*)malloc(sizeof(struct graph)); tg->num = 0; tg->lockidx = 0; pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thread_func,NULL); }
(5)钩子hook
为了不改变项目原代码,使用hook在应用程序调用系统加锁、解锁API时进行劫持,使其实际调用的是应用程序定义的加锁、解锁API;再进行加锁、解锁前,我们先去理解3个状态,加锁前、加锁后、解锁后,即:lock_before、lock_after、unlock_after,通过这三个函数与图构建起来,具体实现如下。
//1.没有被其他线程占用,不用处理 //2.有被其它线程占用,就要把边构建起来 // 添加边 void lock_before(uint64 thread_id, uint64 lockid){ int idx = 0; for(;idx < tg->lockidx;idx++){ if(tg->locklist[idx].lock_id == lockid){ struct node from; from.thread_id = thread_id; add_vertex(&from); struct node to; to.thread_id = tg->locklist[idx].thread_id; tg->locklist[idx].degress++; add_vertex(&to); if(!verifty_edge(&from, &to)){ add_edge(&from, &to);//添加边 } } } }
//1.没有被其它线程占用 //先加入一个节点add_edge //2.有被占用 //是进不来lock_after的 // //等unlock_after 释放后 // mtx没有主人 void lock_after(uint64 threadid, uint64 lockid) { int idx = 0; if(-1 == (idx = search_lock(lockid))){ int eidx = search_empty_lock(); tg->locklist[eidx].thread_id = threadid; tg->locklist[eidx].lock_id = lockid; inc(&tg->lockidx, 1); }else{ struct node from; from.thread_id = threadid; struct node to; to.thread_id = tg->locklist[idx].thread_id; tg->locklist[idx].degress--; if(verifty_edge(&from, &to)){ remove_edge(&from, &to);//不在死锁检测的圈里面了,所以删除边 } tg->locklist[idx].thread_id = threadid; } }
void unlock_after(uint64 threadid, uint64 lockid) { int idx = search_lock(lockid); if(tg->locklist[idx].degress == 0){ tg->locklist[idx].thread_id = 0; tg->locklist[idx].lock_id = 0; } }
honk钩子主要实现pthread_mutex_lock、pthread_mutex_unlock的劫持,具体实现如下。
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex){ pthread_t selfid = pthread_self(); lock_before(selfid, (uint64)mutex); pthread_mutex_lock_f(mutex);//执行系统加锁的入口函数 lock_after(selfid, (uint64)mutex); } int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t * mutex){ pthread_t selfid = pthread_self(); pthread_mutex_unlock_f(mutex);//执行系统解锁的入口函数 unlock_after(selfid, (uint64)mutex); } static int init_hook(){ pthread_mutex_lock_f = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT,"pthread_mutex_lock"); pthread_mutex_unlock_f = dlsym(RTLD_NEXT,"pthread_mutex_unlock"); }
(6)Demo
//测试样例 pthread_mutex_t mtx1 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_mutex_t mtx2 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_mutex_t mtx3 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; pthread_mutex_t mtx4 = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER; void *th_func1(void *arg) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx1); sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx2); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx2); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx1); } void *th_func2(void *arg) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx2); sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx3); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx3); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx2); } void *th_func3(void *arg) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx3); sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx1); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx1); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx3); } void *th_func4(void *arg) { pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx2); sleep(1); pthread_mutex_lock(&mtx3); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx3); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mtx2); } int main(){ init_hook();//初始化hook start_check();//启动检测死锁线程 pthread_t t1,t2,t3,t4; pthread_create(&t1,NULL,th_func1,NULL); pthread_create(&t2,NULL,th_func2,NULL); pthread_create(&t3,NULL,th_func3,NULL); pthread_create(&t4,NULL,th_func4,NULL); pthread_join(t1,NULL); pthread_join(t2,NULL); pthread_join(t3,NULL); pthread_join(t4,NULL); return 0; }



