gh-ost使用问题记录
因为 pt-osc 对数据库性能影响较大,且容易造成死锁问题,目前我们在线更改表结构都使用 gh-ost 工具进行修改,这里记录一下使用 gh-ost 过程中的问题,以作记录;首先先复习一下gh-ost的基本实现,gh-ost的基本实现原理如下图所示:
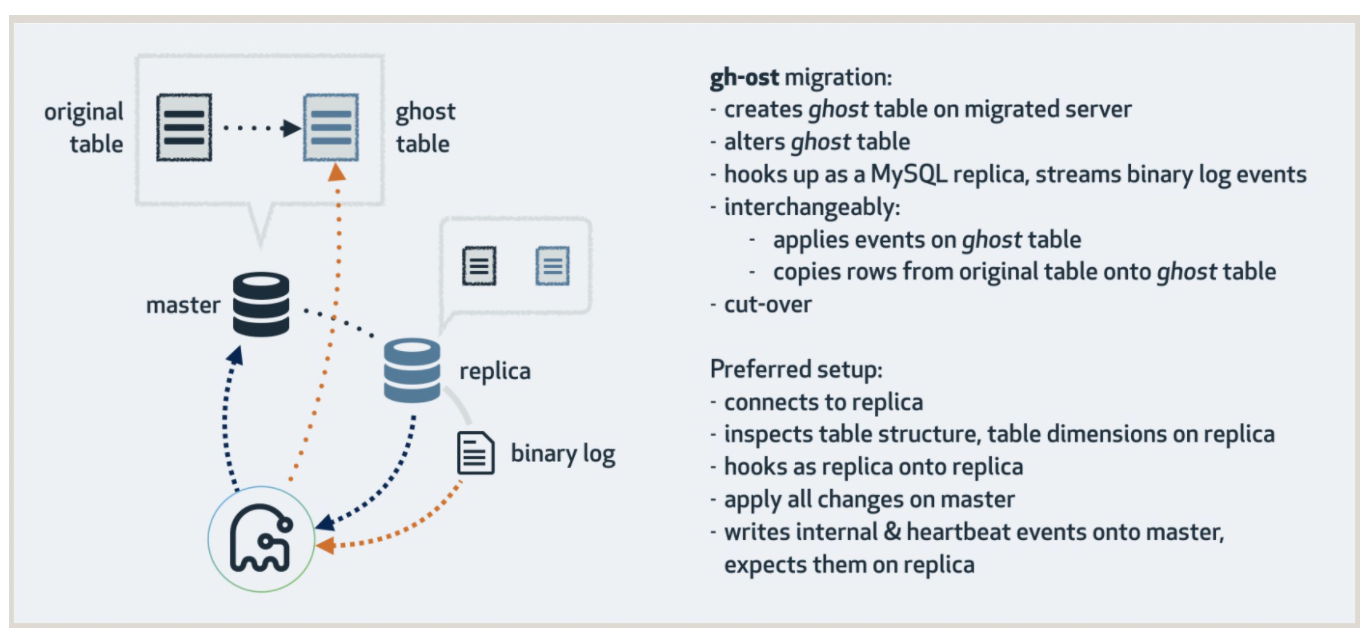
根据源码,核心步骤如下:
1. initiateStreaming: 初始化 binlog events streaming
2. initiateApplier: 初始化 applier
3. addDMLEventsListener: 添加对指定表的binlog event过滤
4. ReadMigrationRangeValues: 获取对应表唯一索引的 min & max 值
5. executeWriteFuncs: 通过applier向ghost表写入数据, binlog event 相比 copy rows具有更高优先级
6. iterateChunks: 根据 min & max的值, 批量插入数据到 ghost 表
7. cutOver: rename & drop新旧表
问题一:gh-ost导致最新一次写操作丢失
原因分析:
在 initiateStreaming 的过程中通过 show master status 获取主节点当前的 binlog name & pos & Executed_Gtid_Set,然后通过 binlog name & pos 和当前的数据库节点建立复制通道,而后在 ReadMigrationRangeValues 的过程中通过 select min(unique_key) 和 select max(unique_key) 快照读的方式获取原表数据的范围。
问题就出在这里,根据事务的提交流程,如果sync_binlog != 1,那么 binlog name & pos 是在binlog flush阶段之后进行更新;如果 sync_binlog = 1,那么 binlog name & pos 是在 binlog sync 阶段之后进行更新,这时事务还没有在 Innodb 中完成 commit。因此,最新的一次事务对于 select min() & max() 这样的快照读是不可见的,最终造成了写操作的丢失。
如何修复:
这里有两种解决办法:1. 虽然 binlog name & pos 的信息是在 Innodb memory commit 之前进行更新,但是show master status 的 Executed_Gtid_Set 是在 Innodb memory commit 完成之后进行更新的,因此 gh-ost 可以使用 Executed_Gtid_Set 来与数据库节点建立复制通道来解决这个问题。
2. 在 ReadMigrationRangeValues 的过程中使用 select min() & max() lock in share mode 当前读来解决这个问题;
问题二:添加唯一索引时有可能导致数据丢失:
在使用 gh-ost 做 “add column field1 int not null, add unique index uniq_idx_field1(field1)” 或 “add column field1 int not null default 0, add unique index uniq_idx_field1(field1)” 这样的操作时,会导致整张表只剩下一条数据;
在执行 “add unique index uniq_idx_field1(field1)” 这样的操作时,如果表中的 field1字段存在重复数据,会导致第 2~n 条重复数据丢失。
相比之下,pt-osc 工具提供的 --check-unique-key-change 参数可以在出现以上情况时进行 warning 退出,有补救的可能。
问题三:高并发写入时gh-ost无法结束:
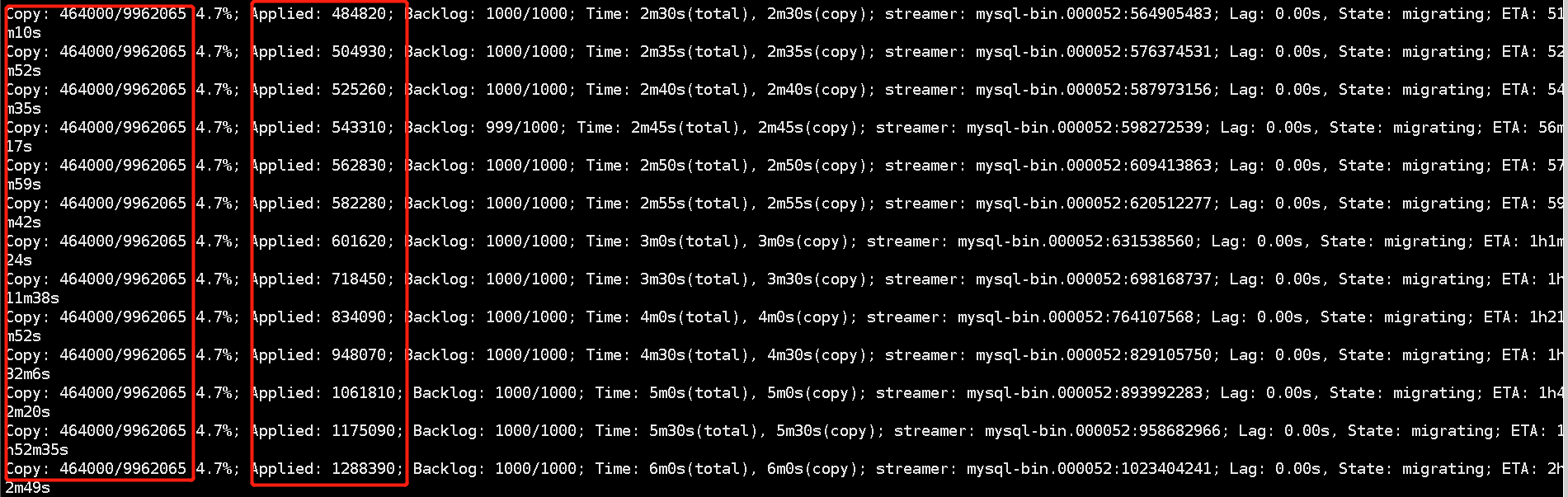
如截图所示,Applied一直在增大,而 Copy保持不变。这是因为在通过 Applier 向 ghost 表中写数据时,binlog events apply 相比rows copy 具有更高的优先级;同时,由于 gh-ost 是通过监听 mysql binlog的方式获取增量写操作,对源MySQL节点的侵入较小;因此,在MySQL实例高并发写入时,gh-ost会忙于 apply binlog events而无法结束。
扩展一:gh-ost的cutover过程:
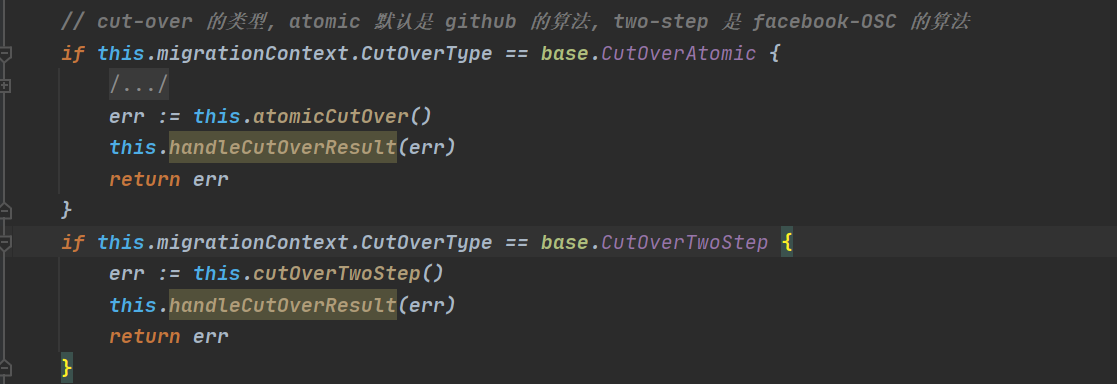
如上图所示,根据gh-ost -cut-over参数的不同会选择不同的 cur-over 算法,默认是github的 atomic算法,也可以选择 facebook的 OSC算法。
atomic算法// atomicCutOver
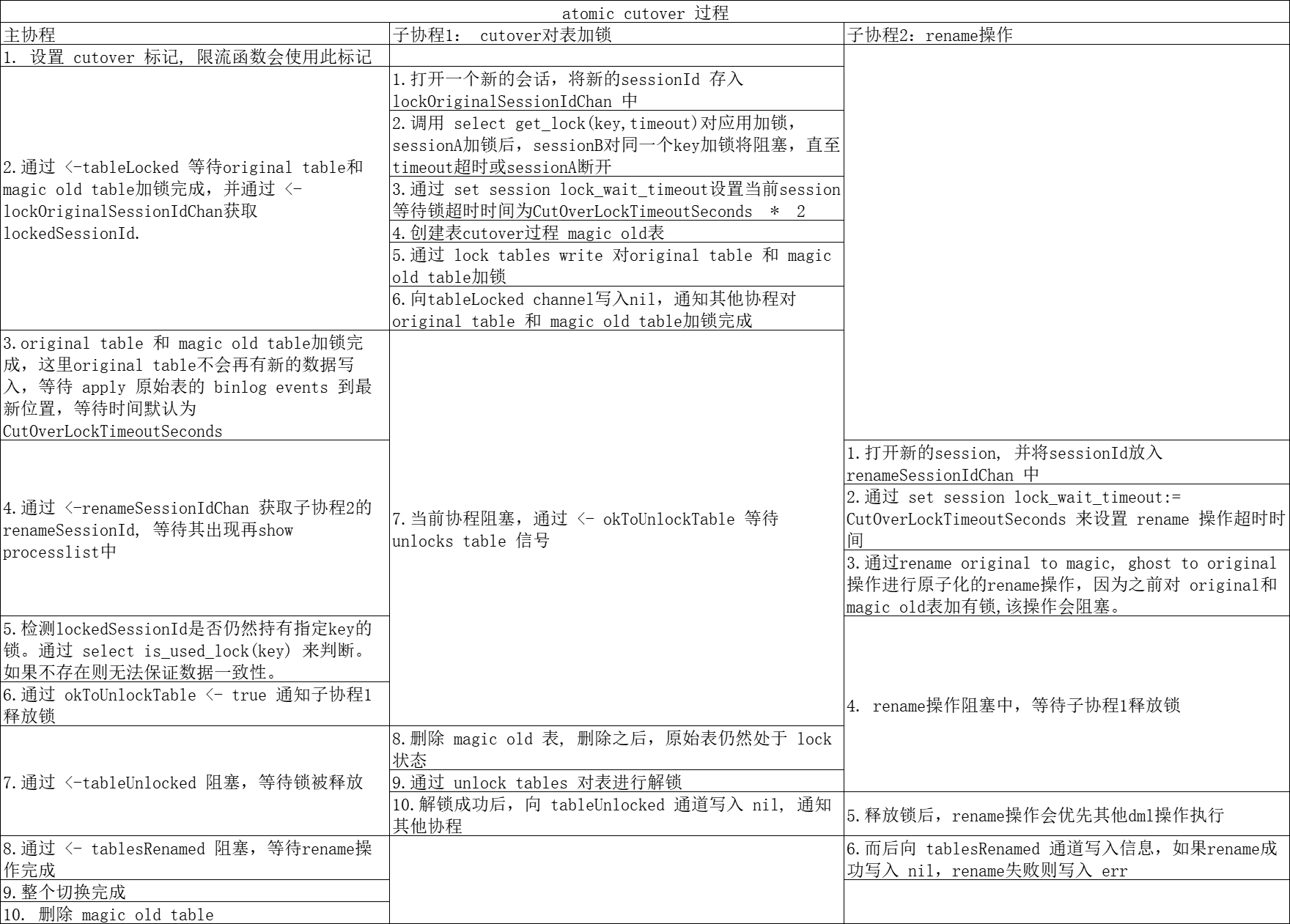
这里为什么需要 magic_old表呢?
是为了防止lockSessionId被意外关闭后,可以阻塞rename操作。lockSessionId被意外关闭后,original table可以被写入,会造成数据不一致。至于为何要对 magic_old表加锁,我个人认为是防止magic_old表被意外删除。
源码实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 | func (this *Migrator) atomicCutOver() (err error) { // 设置 cutover 标记, 限流函数会使用此标记 atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.InCutOverCriticalSectionFlag, 1) defer atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.InCutOverCriticalSectionFlag, 0) // 通知释放锁的通道 okToUnlockTable := make(chan bool, 4) // 最后删除 magic old table defer func() { okToUnlockTable <- true this.applier.DropAtomicCutOverSentryTableIfExists() }() // atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.AllEventsUpToLockProcessedInjectedFlag, 0) // 存储会话ID lockOriginalSessionIdChan := make(chan int64, 2) // 表锁定后通知通道 tableLocked := make(chan error, 2) // 表锁释放后通知通道 tableUnlocked := make(chan error, 2) go func() { /* * 在 cutover 阶段对表加锁, 共分为以下几步: * 1. 打开一个新的会话,将会话ID存入 lockOriginalSessionIdChan 中 2. 调用 get_lock(key, timeout) 对应用进行加锁。需要一个字符串key和加锁超时等待时间,sessionA 调用 get_lock 对key加锁, sessionB也调用 get_lock 对相同的key加锁会等待,直到超时或 sessionA 断开。 3. 通过 set session lock_wait_timeout 设置表切换锁超时时间为CutOverLockTimeoutSeconds * 2, 默认为 6s,CutOverLockTimeoutSeconds可以人为指定。 4. 创建 cutover 过程中的 magic old表 5. 通过 lock tables write 对原始表和 magic old 表加 write锁 6. 向 tableLocked 通道中写入nil, 通知其他协程对原表和 magic old表加锁完成,可以开始后续工作 7. 当前协程阻塞,通过 <- okToUnlockTable 等待 unlocks table 信号 8. 删除 magic old 表, 删除之后,原始表仍然处于 lock 状态 9. 通过 unlock tables 对表进行解锁 10. 解锁成功后,向 tableUnlocked 通道写入 nil, 通知其他协程 */ if err := this.applier.AtomicCutOverMagicLock(lockOriginalSessionIdChan, tableLocked, okToUnlockTable, tableUnlocked); err != nil { log.Errore(err) } }() // 这里阻塞等待原始表和 magic old 表加锁完成 if err := <-tableLocked; err != nil { return log.Errore(err) } // 获取加锁的 sessionId lockOriginalSessionId := <-lockOriginalSessionIdChan log.Infof("Session locking original & magic tables is %+v", lockOriginalSessionId) // At this point we know the original table is locked. // We know any newly incoming DML on original table is blocked. // 这里,原始表已被锁定,原始表不会产生新的 binlog event。我们需要等待 apply 原始表的 binlog events 到最新位置,等待 // 时间默认为 CutOverLockTimeoutSeconds(3s, 可以人为指定) if err := this.waitForEventsUpToLock(); err != nil { return log.Errore(err) } // Step 2 // We now attempt an atomic RENAME on original & ghost tables, and expect it to block. this.migrationContext.RenameTablesStartTime = time.Now() // rename 操作是否被阻塞标志 var tableRenameKnownToHaveFailed int64 // 存储 rename 会话ID renameSessionIdChan := make(chan int64, 2) // rename 成功或失败后消息通知通道 tablesRenamed := make(chan error, 2) // 异步的进行 rename 操作 go func() { /** * rename 表操作 1. 打开新的 session,并将 sessionId 存入 renameSessionIdChan 中 2. 通过 set session lock_wait_timeout:= CutOverLockTimeoutSeconds 来设置 rename 操作超时时间 3. 通过 rename originalTable to magic_oldTable, ghost_table to originalTable 来进行rename操作,因为在之前对 originalTable 和 magic_oldTable 加有锁,正常情况下会阻塞 4. 而后向 tablesRenamed 通道写入信息,如果rename成功写入 nil,rename失败则写入 err */ if err := this.applier.AtomicCutoverRename(renameSessionIdChan, tablesRenamed); err != nil { // Abort! Release the lock // 终止,释放锁 atomic.StoreInt64(&tableRenameKnownToHaveFailed, 1) okToUnlockTable <- true } }() // 这里获取 rename sessionId renameSessionId := <-renameSessionIdChan log.Infof("Session renaming tables is %+v", renameSessionId) waitForRename := func() error { if atomic.LoadInt64(&tableRenameKnownToHaveFailed) == 1 { // We return `nil` here so as to avoid the `retry`. The RENAME has failed, // it won't show up in PROCESSLIST, no point in waiting // 当 rename 操作失败时, 返回 nil避免重试。 return nil } return this.applier.ExpectProcess(renameSessionId, "metadata lock", "rename") } // Wait for the RENAME to appear in PROCESSLIST // 等待 rename 操作出现在 processlist 中 if err := this.retryOperation(waitForRename, true); err != nil { // Abort! Release the lock // 终止! 释放锁 okToUnlockTable <- true return err } // tableRenameKnownToHaveFailed = 0 表示 rename 操作被阻塞,符合预期 if atomic.LoadInt64(&tableRenameKnownToHaveFailed) == 0 { log.Infof("Found atomic RENAME to be blocking, as expected. Double checking the lock is still in place (though I don't strictly have to)") } // 探测对 original table 和 magic old table 加锁的线程还继续存在, 如果不存在则无法保证数据一致性 if err := this.applier.ExpectUsedLock(lockOriginalSessionId); err != nil { // Abort operation. Just make sure to drop the magic table. return log.Errore(err) } log.Infof("Connection holding lock on original table still exists") // Now that we've found the RENAME blocking, AND the locking connection still alive, // we know it is safe to proceed to release the lock // 这里 rename 操作被阻塞,并且加锁的连接仍然有效,继续释放锁是能保证数据安全的,这里通知释放锁 okToUnlockTable <- true // BAM! magic table dropped, original table lock is released // -> RENAME released -> queries on original are unblocked. // 阻塞等待锁被释放 if err := <-tableUnlocked; err != nil { return log.Errore(err) } // 阻塞等待 rename 操作完成 (锁被释放后rename操作会优先其他dml操作执行) if err := <-tablesRenamed; err != nil { return log.Errore(err) } this.migrationContext.RenameTablesEndTime = time.Now() // ooh nice! We're actually truly and thankfully done // 整个切换完成 lockAndRenameDuration := this.migrationContext.RenameTablesEndTime.Sub(this.migrationContext.LockTablesStartTime) log.Infof("Lock & rename duration: %s. During this time, queries on %s were blocked", lockAndRenameDuration, sql.EscapeName(this.migrationContext.OriginalTableName)) return nil} |
facebook OSC算法// cutOverTwoStep
cutOverTwoStep很巧妙地利用MySQL不同 session 下 alter table x rename to x1; 和 rename table x1 to x; 不同的锁机制进行 cutover,值得深入研究。
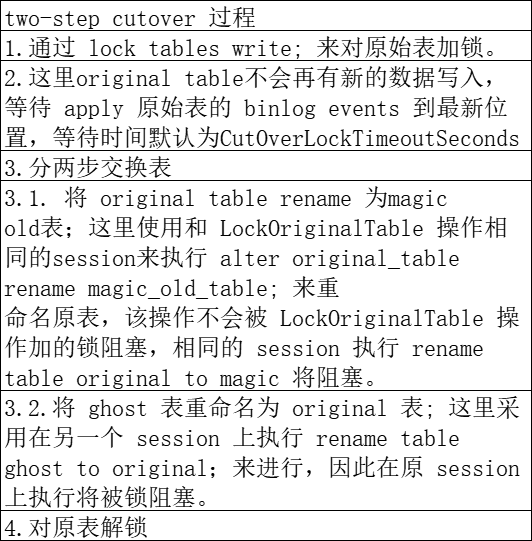
源码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | /* * cutOverTwoStep() 将阻塞原始表,等待原始表上的binlog events全部应用到 ghost 表,然后进行非原子的表rename操作,original->old, then new->original; * 在rename过程中,原始表不存在,查询操作将失败。*/func (this *Migrator) cutOverTwoStep() (err error) { atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.InCutOverCriticalSectionFlag, 1) defer atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.InCutOverCriticalSectionFlag, 0) atomic.StoreInt64(&this.migrationContext.AllEventsUpToLockProcessedInjectedFlag, 0) // 首先通过 lock tables write; 对原始表加锁 if err := this.retryOperation(this.applier.LockOriginalTable); err != nil { return err } // 等待原始表上的 binlog events 全部应用到 ghost 表 if err := this.retryOperation(this.waitForEventsUpToLock); err != nil { return err } // 1. 这里使用和 LockOriginalTable 操作相同的session来执行 alter original_table rename magic_old_table; 来重 // 命名原表,该操作不会被 LockOriginalTable 操作加的锁阻塞,相同的 session 执行 rename table original to magic 将阻塞。 // 2. 将 ghost 表重命名为 original 表; 这里采用在另一个 session 上执行 rename table ghost to original;来进行,因此在 // 原 session 上执行将被锁阻塞。 if err := this.retryOperation(this.applier.SwapTablesQuickAndBumpy); err != nil { return err } // 对原表解锁 if err := this.retryOperation(this.applier.UnlockTables); err != nil { return err } lockAndRenameDuration := this.migrationContext.RenameTablesEndTime.Sub(this.migrationContext.LockTablesStartTime) renameDuration := this.migrationContext.RenameTablesEndTime.Sub(this.migrationContext.RenameTablesStartTime) log.Debugf("Lock & rename duration: %s (rename only: %s). During this time, queries on %s were locked or failing", lockAndRenameDuration, renameDuration, sql.EscapeName(this.migrationContext.OriginalTableName)) return nil} |




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!