React制作吸顶功能总结
总结一下最近用react写项目时,遇到的一些坑,恩,真的还蛮坑的,主要是设置状态的时候特别不好控制,下面我们一起来看下,这里自己做了几个demo,分别看下,
主页面代码如下:
class Head extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
contentClass:"conditionArea"
};
this.windowOnScroll();
let isScrollTop = true;
};
windowOnScroll(){
let _this = this;
window.onscroll = function(){
//获取滚动条滚动的距离
let h = document.body.scrollTop;
console.log(h);
if(h > 74){
console.log('111');
_this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea conditionArea_fixed"
});
}else{
_this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea"
});
}
}
};
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<div className="set_head_fixed">
<span className="set_text">我是头部</span>
</div>
<div id="conditionArea" className={this.state.contentClass}>
<div className="content_name">
<span>置顶块</span>
</div>
</div>
<div className="set_displayContent">
<p>内容区域</p>
</div>
</div>
);
}
};
function APP (){
return (
<div className="head_top ">
<Head title="头部" />
</div>
)
};
ReactDOM.render(
<APP />,
document.getElementById('demo')
);
1:头部与吸顶的块,一起移动的问题
问题:鼠标滚动到顶部时候,状态一直在更改,我们来看下效果图:

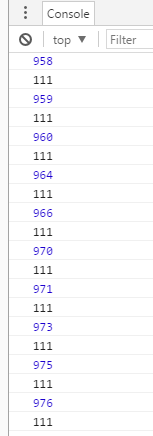
看吧,很明显,这是一个bug,有问题,那我们继续改,为什么状态一直在更改呢,这里我们可以用一个变量来进行控制,逻辑大概是,当滚轮达到顶部时
将其置为false,那它的状态就只会更改一次了。我们来看下核心代码,其它代码不再贴了。
if(h > 74){
if(isScrollTop){
console.log('111');
isScrollTop = false;
_this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea conditionArea_fixed"
});
}else{
console.log("333");
_this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea"
});
}
}
我们来看下控制台打印出来的结果:为什么会出现这么多3呢?首先,有两种情况,一种用户向上滑动,然后向下滑动,另外就是,向上滑动-向下滑动-向上滑动操作
因此,当小于74px的时候,我们同样要控制它的状态。
 控制后的结果
控制后的结果 
ok,我们状态控制好啦,代码如下:
if(h > 74){
if(isScrollTop){
console.log('111');
isScrollTop = false;
_this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea conditionArea_fixed"
});
}
}else{
if(!isScrollTop){
console.log("333");
isScrollTop = true;
this.setState({
contentClass:"conditionArea"
});
}
}
2:头部固定,吸顶的块移动

与上面的区别是定位的问题,这里要注意一下,无论上面哪种,吸顶的块都应该是由position:absolute 变为 position : fixed,经博主检测,使用position : relative会出现问题
在微信打开,qq浏览器,UC浏览器,百度浏览器打开均会出现卡顿,反应慢的问题,后来我就用了absolute进行定位,问题就好啦,另外,注意解决fixed的兼容性问题,setState的
做法有问题,setState是异步的,没办法做到立马将效果展示出来,必要时候直接操作DOM元素来解决问题。
css样式如下:
body {
display: block;
margin: 0px;
padding: 0px;
color: #fff;
}
.set_head_fixed{
border:1px solid red;
width:100%;
height:74px;
background-color: #54B6E3;
color: #fff;
text-align: center;
position: relative;
}
.set_text{
margin-top: 5px;
}
.conditionArea{
width: 100%;
height: 80px;
background-color:#66C6AD;
border: 1px solid blue;
text-align: center;
position: absolute;
}
.conditionArea_fixed{
position: fixed;
top: 0px;
z-index: 44;
}
.set_displayContent{
position: relative;
margin: 60px 10px;
height: 1700px;
background: #fc9720;
border-radius: 8px;
}
其实,感觉,利用变量来控制状态是非常好的办法,关键是要知道什么时候去控制它,调用它。
3:关于setState函数
特点:
1:是异步函数。
2: this.setState 还没有被调用;
3: 批量执行 State 转变时让 DOM 渲染更快(相对比一个一个的setState的来的快)。
同步更新方法:
1:直接操作DOM
2: 在componentWillUpdate生命周期或者componentDidUpdate生命周期的回调函数去执行我们的操作。
componentDidMount(){
//执行操作
};
3:回调函数
this.setState({},()=>{
//执行操作
});








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号