离散化
题目描述
假定有一个无限长的数轴,数轴上每个坐标上的数都是0。
现在,我们首先进行 n 次操作,每次操作将某一位置x上的数加c。
接下来,进行 m 次询问,每个询问包含两个整数l和r,你需要求出在区间[l, r]之间的所有数的和。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数n和m。
接下来 n 行,每行包含两个整数x和c。
再接下里 m 行,每行包含两个整数l和r。
输出格式
共m行,每行输出一个询问中所求的区间内数字和。
数据范围
−109≤x≤109,
1≤n,m≤105,
−109≤l≤r≤109,
−10000≤c≤10000
输入样例:
3 3
1 2
3 6
7 5
1 3
4 6
7 8
输出样例:
8
0
5
算法 (离散化+二分查找求映射+前缀和) O((n+2∗m)log(n+2∗m))
分析
首先什么是离散化,离散化的本质,是映射,将间隔很大的点,映射到相邻的数组元素中。减少对空间的需求,也减少计算量。通俗的说,离散化是在不改变数据相对大小的条件下,对数据进行相应的缩小。例如:原数据:1,999,100000,15;处理后:1,3,4,2;那么本题为什么要离散化呢,数轴坐标范围过大且有负数,不能直接用数组下标存储.
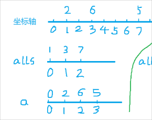
离散化的难点在于如何映射,本题用alls数组存数轴位置,这样数轴位置就映射到了all是数组的下标,那么我们怎么存原来数轴位置上面的数呢,这时我们开辟一个新的数组a,把alls下标+1映射到a数组下标,这样a数组存的数就是原来数轴上面的数了,加一是因为要求前缀和。具体可以看下面这个图,分析每个数组存的是值还是位置
c++代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 300010;//前缀和的因素,加上了2*m个点
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
vector<int> alls;//存储待离散的位置,而不是位置上的数
vector<PII> add, query;
int a[N], s[N];//a[N]是映射到的新数组
int n, m;
vector<int> :: iterator unique(vector<int> &a)
{
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i ++)
if(!i || a[i] != a[i - 1])
a[j ++] = a[i];
return a.begin() + j; //返回的是重复元素的首地址
}
int find(int x)
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1;// 因为要求前缀和,映射到的数组下标从1开始,而alls是从0开始的,所有加一
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
while(n --)
{
int x, c;
cin >> x >> c;
alls.push_back(x);
add.push_back({x, c});
}
while(m --)
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
alls.push_back(l);
alls.push_back(r);
query.push_back({l, r});
}
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());//排序
alls.erase(unique(alls), alls.end());//去重,unqiue函数是c++ 11的,不支持c++ 11, 可以自己手写
for(auto item : add)//auto c ++ 11 等价于 for(vector<PII>::iterator it=add.begin();it!=add.end();it++)
{
int x = find(item.first);
a[x] += item.second;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= alls.size(); i ++ ) s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
for(auto item : query)
{
int l = find(item.first), r = find(item.second);
cout << s[r] - s[l - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}


