《Java基础知识》Java 浅拷贝与深拷贝
前言
在学习ArrayList的时候,发现ArrayList继承了Cloneable接口,于是就想着需要了解一下该接口是什么作用。
浅拷贝
我们先写一段代码,来看看什么是浅拷贝
public class DogSchool { public String address; public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } }
public class Dog implements Cloneable{ public int age; public String name; public DogSchool dogSchool; public Dog(int age, String name){ this.age = age; this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public DogSchool getDogSchool() { return dogSchool; } public void setDogSchool(DogSchool dogSchool) { this.dogSchool = dogSchool; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
public class CloneTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException { /*************** 设置好原对象信息 *****************/ Dog dogSource = new Dog(12,"li"); DogSchool dogSchool = new DogSchool(); dogSchool.setAddress("hangzhou"); dogSource.setDogSchool(dogSchool); /*************** 进行对象拷贝,并且修改原对象的值 *****************/ Dog dogTarget = (Dog) dogSource.clone(); dogSource.getDogSchool().setAddress("shanghai"); dogSource.setAge(14); System.out.println("dogSource.age:"+dogSource.getAge()); System.out.println("dogSource.dogSchool.address:"+dogSource.getDogSchool().getAddress()); System.out.println("dogTarget.age:"+dogTarget.getAge()); System.out.println("dogTarget.dogSchool.address:"+dogTarget.getDogSchool().getAddress()); System.out.println("dogTarget.dog:"+dogSource.getDogSchool()); System.out.println("dogTarget.dog:"+dogTarget.getDogSchool()); } }
运行结果:
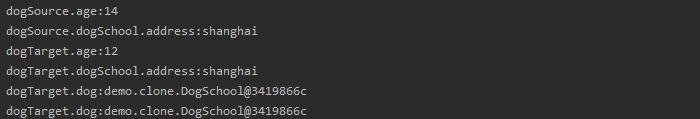
从结果看,我们的年龄age拷贝之后对原对象赋值没有影响到复制出来的对象,但是引用对象里面的属性值被修改之后却影响了复制出来的对象。结论:在浅拷贝下,基本类型是独立的,拷贝前后互不干扰;引用类型是不独立的,拷贝前后互干扰;String类型也是独立的,拷贝前后互不干扰。浅拷贝是拷贝了栈里面的信息。
这边对String为什么在浅拷贝下,也能不受影响的原因说明一下,因为String虽然是引用类型,但是String是被final修饰,导致他是不能被修改的,当你修改String的值,是在常量池里面,又产生一个新的字符串常量,然后引用地址指向新的字符串常量地址。
深拷贝
在上面代码的基础上,我们修改一下拷贝的逻辑,只需要修改Dog 类和 DogSchool 类。
DogSchool 加上支持拷贝的接口,并且实现接口
public class DogSchool implements Cloneable{ public String address; public String getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(String address) { this.address = address; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { return super.clone(); } }
Dog 类里面修改一下拷贝逻辑:
public class Dog implements Cloneable{ public int age; public String name; public DogSchool dogSchool; public Dog(int age, String name){ this.age = age; this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public DogSchool getDogSchool() { return dogSchool; } public void setDogSchool(DogSchool dogSchool) { this.dogSchool = dogSchool; } @Override public Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException { Dog dog = (Dog)super.clone(); dog.setDogSchool((DogSchool) this.dogSchool.clone()); return dog; } }
运行结果:

从浅拷贝我们可以看到只有引用类型会出现指向内存地址是同一个的情况,所以我们处理一下引用类型即可。就达到了深拷贝的效果。
总结
上述拷贝是比较简单和易操作的,同时注意一下他的特性,我们的拷贝还有通过序列化实现的拷贝。
This moment will nap, you will have a dream; But this moment study,you will interpret a dream.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号