《Java基础知识》Java 反射详解
定义
JAVA反射机制是在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能够调用它的任意方法和属性;这种动态获取信息以及动态调用对象方法的功能称为java语言的反射机制。
用途
在日常的第三方应用开发过程中,经常会遇到某个类的某个成员变量、方法或是属性是私有的或是只对系统应用开放,这时候就可以利用Java的反射机制通过反射来获取所需的私有成员或是方法。当然,也不是所有的都适合反射,之前就遇到一个案例,通过反射得到的结果与预期不符。阅读源码发现,经过层层调用后在最终返回结果的地方对应用的权限进行了校验,对于没有权限的应用返回值是没有意义的缺省值,否则返回实际值起到保护用户的隐私目的。
案例:(重要)
public class Demo1 { //创建一个自己本身的公共变量 public static demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Demo1 demo1; private static final boolean flag = true ; //将其私有化,保证不能通过New的方式创建。 private Demo1(){} //创建get方法,用于告知使用者,不能被new,不能被获取。 public static Demo1 getDemo1() throws Exception{ if(flag){ throw new Exception("抱歉,该类不通过new 的方式创建!"); } return demo1; } public void print(){ System.out.println("恭喜成功获取Demo1!"); } //通过静态代码块创建实体类。 static { demo1 = new Demo1(); } }
public class Demo2 { //创建一个自己本身的私有变量 private static demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Demo2 demo2; private static final boolean flag = true ; //将其私有化,保证不能通过New的方式创建。 private Demo2(){} //创建get方法,用于告知使用者,不能被new,不能被获取。 public static Demo2 getDemo2() throws Exception{ if(flag){ throw new Exception("抱歉,该类不通过new 的方式创建!"); } return demo2; } public void print(){ System.out.println("恭喜成功获取Demo2!"); } //通过静态代码块创建实体类。 static { demo2 = new Demo2(); } }
public class Reflect { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo1 demo1 = null; Demo2 demo2 = null; try { //发现new ,编译报错。 //demo1 = new Demo1(); //demo2 = new Demo2(); //发现get方法也获取不到,执行会报异常。 demo1 = Demo1.getDemo1(); demo2 = Demo2.getDemo2(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:

通过上述代码,我们知道通过普通方法是无法获取到Demo1 和 Demo2。但是看Demo1 和 Demo2的写法,在静态代码块中是new了对象的。说明肯定有办法可以获取到实例。
这里说的方法就是反射。
import java.lang.reflect.Field; public class Reflect { public static void main(String[] args) { Demo1 demo1 = null; Demo2 demo2 = null; try { //首先通过Field,获取需要的类,Field包在jdk的反射包中:java.lang.reflect Field field1 = Demo1.class.getDeclaredField("demo1"); //获取之后,强制转换成Demo1。 demo1 = (Demo1)field1.get(null); demo1.print(); //然后我们再来创建一个Demo2. Field field2 = Demo2.class.getDeclaredField("demo2"); //私有方法需要将:field2.setAccessible(true) ,才能获取到实例类 field2.setAccessible(true); demo2 = (Demo2)field2.get(null); demo2.print(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:

通过上述代码,我们通过反射,获取到Demo1和Demo2的公共属性和私有属性,成功获取到对象。
讲讲反射原理:
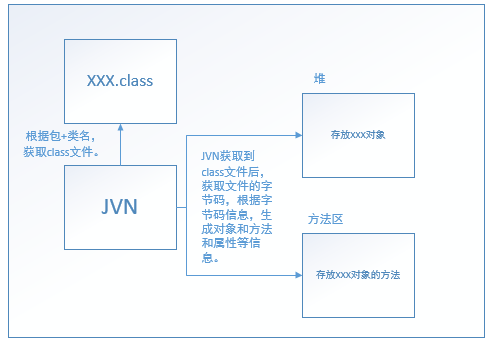
通过到class所在目录下,执行javap -c Book.class,可以查看字节码。可以看到一些公共的方法,私有的看不到,不过不影响JVN获取。
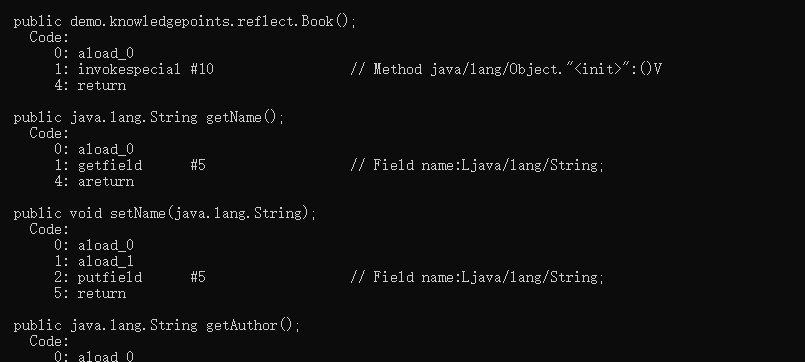
下面介绍一下反射的基础类和方法
| 类名 | 用途 |
| Class类 | 代表类的实体,在运行的Java应用程序中表示类和接口 |
| Field类 | 代表类的成员变量(成员变量也称为类的属性) |
| Method类 | 代表类的方法 |
| Constructor类 | 代表类的构造方法 |
以下是常见方法的使用案例:
package demo.knowledgepoints.reflect; public class Book { private final static String TAG = "BookTag"; private String name; private String author; @Override public String toString() { return "Book{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", author='" + author + '\'' + '}'; } public Book() { } private Book(String name, String author) { this.name = name; this.author = author; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } private String declaredMethod(int index) { String string = null; switch (index) { case 0: string = "I am declaredMethod 1 !"; break; case 1: string = "I am declaredMethod 2 !"; break; default: string = "I am declaredMethod 1 !"; } return string; } }
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.Field; import java.lang.reflect.Method; public class Reflect { public static void main(String[] args) { reflectNewInstance(); reflectPrivateConstructor(); reflectPrivateField(); reflectPrivateMethod(); } /** * 通过反射获取对象 */ public static void reflectNewInstance() { try { Class<?> classBook = Class.forName("demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Book"); Object objectBook = classBook.newInstance(); Book book = (Book) objectBook; book.setName("Java进阶之光"); book.setAuthor("蕾蕾"); System.out.println("reflectNewInstance book = " + book.toString()); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } // 反射私有的构造方法 public static void reflectPrivateConstructor() { try { Class<?> classBook = Class.forName("demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Book"); Constructor<?> declaredConstructorBook = classBook.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,String.class); declaredConstructorBook.setAccessible(true); Object objectBook = declaredConstructorBook.newInstance("Java开发艺术探索","磊磊"); Book book = (Book) objectBook; System.out.println("reflectPrivateConstructor book = " + book.toString()); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } // 反射私有属性 public static void reflectPrivateField() { try { Class<?> classBook = Class.forName("demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Book"); Object objectBook = classBook.newInstance(); Field fieldTag = classBook.getDeclaredField("TAG"); fieldTag.setAccessible(true); String tag = (String) fieldTag.get(objectBook); System.out.println("reflectPrivateField tag = " + tag); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } // 反射私有方法 public static void reflectPrivateMethod() { try { Class<?> classBook = Class.forName("demo.knowledgepoints.reflect.Book"); Method methodBook = classBook.getDeclaredMethod("declaredMethod",int.class); methodBook.setAccessible(true); Object objectBook = classBook.newInstance(); String string = (String) methodBook.invoke(objectBook,1); System.out.println("reflectPrivateMethod string = " + string); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
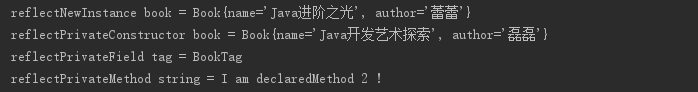
This moment will nap, you will have a dream; But this moment study,you will interpret a dream.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号