java-2.容器之List
1.java容器有哪些?
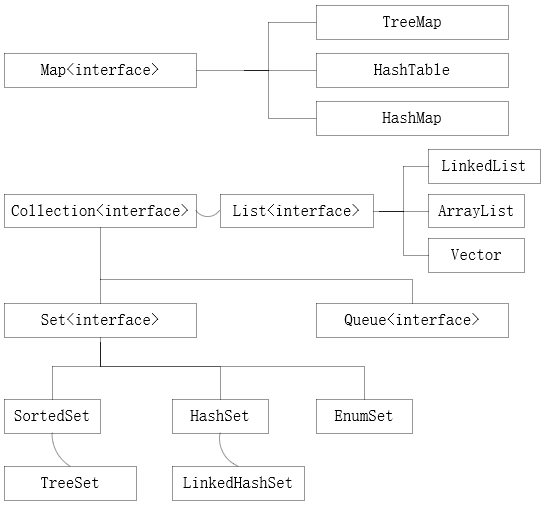
2.Collection和Collections有什么区别?
java.util.Collection是一个集合接口(集合类的一个顶级接口)。
Collections是集合类的一个工具类/帮助类,其中提供了一系列静态方法。
3.List,Set,Map之间的区别是什么?
| 比较 | List | Set | Map |
|---|---|---|---|
| 继承接口 | Collection | Collection | |
| 常见实现类 | AbstractList(其常用子类有ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector) | Abstract(其常用子类有HashSet,LinkedHashSet,TreeSet) | HashMap,HashTable |
| 常见方法 | add(),remove(),clear(),get(),contains(),size() | add(),remove(),clear(),contains(),size() | put(),get(),remove(),clear(),containsKey(),containsValue(),keySet(),values(),size() |
| 元素 | 可重复 | 不可重复(用equals()判断) | 不可重复 |
| 顺序 | 有序 | 无序(实际上由HashCode决定) | |
| 线程安全 | Vector线程安全 | Hashtable线程安全 |
4.ArrayList源码分析?
底层:数组
源码:
// 定义的变量 transient Object[] elementData; private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 构造方法 // 无参构造方法 public ArrayList() { this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } // 一个参数的构造方法 public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity > 0) { this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; } else if (initialCapacity == 0) { this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } else { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); } } // 一个参数的构造方法 public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); if ((size = a.length) != 0) { if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) { elementData = a; } else { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class); } } else { // replace with empty array. elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA; } } // get方法 public E get(int index) { rangeCheck(index); return elementData(index); } private void rangeCheck(int index) { if (index >= size) throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index)); } E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; } // add方法 public boolean add(E e) { ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); elementData[size++] = e; return true; } private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) { ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity)); } private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) { if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) { return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity); } return minCapacity; } private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) { modCount++; if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } // 从size+1和当前长度的1.5倍中取一个大的值 private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } public static <T> T[] copyOf(T[] original, int newLength) { return (T[]) copyOf(original, newLength, original.getClass()); } public static <T,U> T[] copyOf(U[] original, int newLength, Class<? extends T[]> newType) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T[] copy = ((Object)newType == (Object)Object[].class) ? (T[]) new Object[newLength] : (T[]) Array.newInstance(newType.getComponentType(), newLength); // 拷贝后的数组的内容:将原数组的长度拷贝到copy新数组中 System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; } // set方法 public E set(int index, E element) { rangeCheck(index); E oldValue = elementData(index); elementData[index] = element; return oldValue; } E elementData(int index) { return (E) elementData[index]; }
// remove方法

// clear方法 public void clear() { modCount++; for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) elementData[i] = null; size = 0; } // contains方法 public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; } // contains public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) >= 0; } public int indexOf(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (elementData[i]==null) return i; } else { for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) if (o.equals(elementData[i])) return i; } return -1; }
5.LinkedList源码分析?
底层:双向链表
源码:
transient int size = 0; transient Node<E> first; transient Node<E> last; // 无参构造函数 public LinkedList() { } // 有参构造函数 public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c); } // 在双向链表的头部插入一个节点 private static class Node<E> { E item; Node<E> next; Node<E> prev; Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) { this.item = element; this.next = next; this.prev = prev; } } private void linkFirst(E e) { final Node<E> f = first; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f); first = newNode; if (f == null) last = newNode; else f.prev = newNode; size++; modCount++; } // 在双向链表的尾部插入一个节点 void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); last = newNode; if (l == null) first = newNode; else l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } // 在某一个指定节点succ 前插入元素 void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++; } // 添加一个元素 // 添加到双向链表的尾部 public boolean add(E e) { linkLast(e); return true; } // 在指定节点前面添加一个节点 public void add(int index, E element) { checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) linkLast(element); else linkBefore(element, node(index)); } Node<E> node(int index) { if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } // 移除第一个元素 remove() public E remove() { return removeFirst(); } public E removeFirst() { final Node<E> f = first; if (f == null) throw new NoSuchElementException(); return unlinkFirst(f); } // 删除双向链表中的第一个元素 private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) { final E element = f.item; final Node<E> next = f.next; f.item = null; f.next = null; first = next; if (next == null) last = null; else next.prev = null; size--; modCount++; return element; // 返回要删除的节点的值E } // 删除某个下标的元素 remove(int index) public E remove(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return unlink(node(index)); } E unlink(Node<E> x) { final E element = x.item; final Node<E> next = x.next; final Node<E> prev = x.prev; if (prev == null) { first = next; } else { prev.next = next; x.prev = null; } if (next == null) { last = prev; } else { next.prev = prev; x.next = null; } x.item = null; size--; modCount++; return element; } // 如果双向链表中包含指定的元素,就在链表中删除掉该元素第一次出现的位置 public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) { return remove(o); } public boolean remove(Object o) { if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) { unlink(x); return true; } } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) { unlink(x); return true; } } } return false; } // 清空元素 clear() public void clear() { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; ) { Node<E> next = x.next; x.item = null; x.next = null; x.prev = null; x = next; } first = last = null; size = 0; modCount++; } // 获得元素 get() public E get(int index) { checkElementIndex(index); return node(index).item; } Node<E> node(int index) { if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; } } // 包含什么元素 contains() public boolean contains(Object o) { return indexOf(o) != -1; } public int indexOf(Object o) { int index = 0; if (o == null) { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (x.item == null) return index; index++; } } else { for (Node<E> x = first; x != null; x = x.next) { if (o.equals(x.item)) return index; index++; } } return -1; } // 链表的长度 size() public int size() { return size; }
6.LinkedList和ArrayList比较
总结:LinkedList的 get(index)方法效率比较低,因为需要遍历链表,虽然可通过头节点和尾节点选择从头遍历还是从尾遍历,但总归还是要遍历。
但是add()方法要比ArrayList效率高,默认直接插入链表尾部,不用考虑扩容问题。
remove(index)和add(index,e)这两个方法虽然需要先遍历到index的位置,但是效率还是比ArrayList高的,不需要数组拷贝。
7.Vector源码分析?
底层:是用数组实现的List,相关的方法都加了同步检查,因此"线程安全,效率低"。
源码:
protected Object[] elementData; protected int elementCount; protected int capacityIncrement; // 构造函数 public Vector(int initialCapacity, int capacityIncrement) { super(); if (initialCapacity < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+ initialCapacity); this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; this.capacityIncrement = capacityIncrement; } // 构造函数 public Vector(int initialCapacity) { this(initialCapacity, 0); } // 构造函数 public Vector() { this(10); } // 构造函数 public Vector(Collection<? extends E> c) { Object[] a = c.toArray(); elementCount = a.length; if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) { elementData = a; } else { elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, elementCount, Object[].class); } } // 添加元素 add方法 public synchronized boolean add(E e) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = e; return true; } // 在某一个下标index插入元素 public void add(int index, E element) { insertElementAt(element, index); } public synchronized void insertElementAt(E obj, int index) { modCount++; if (index > elementCount) { throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " > " + elementCount); } ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, elementCount - index); elementData[index] = obj; elementCount++; } // 添加一个集合 addAll(Collection<> c) public synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { modCount++; Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew); System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, elementCount, numNew); elementCount += numNew; return numNew != 0; } // 将集合c拷贝到从下标为index开始的位置 public synchronized boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { modCount++; if (index < 0 || index > elementCount) throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + numNew); int numMoved = elementCount - index; // 先将elementData数组从下标index开始往后移动numMoved个单位 if (numMoved > 0) System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew, numMoved); // 将集合c拷贝到下标从index开始的位置 System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew); elementCount += numNew; return numNew != 0; } // 添加指定元素 public synchronized void addElement(E obj) { modCount++; ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1); elementData[elementCount++] = obj; } private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) grow(minCapacity); } private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ? capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; }
本文来自博客园,作者:jsqup,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jsqup/p/15852268.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?