13.排序链表
算法描述
给你链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
原题链接
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/
样例
示例一:
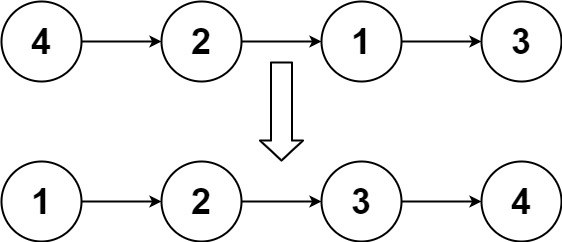
输入:head = [4,2,1,3] 输出:[1,2,3,4]
示例二:
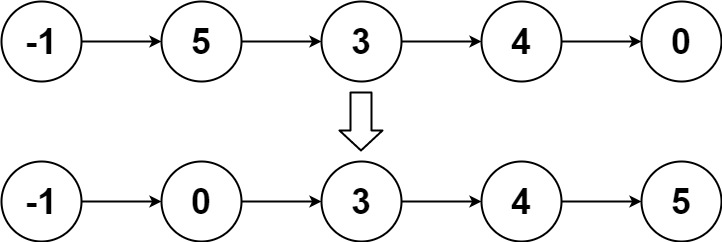
输入:head = [-1,5,3,4,0] 输出:[-1,0,3,4,5]
示例三:
输入:head = [] 输出:[]
解法一
思路
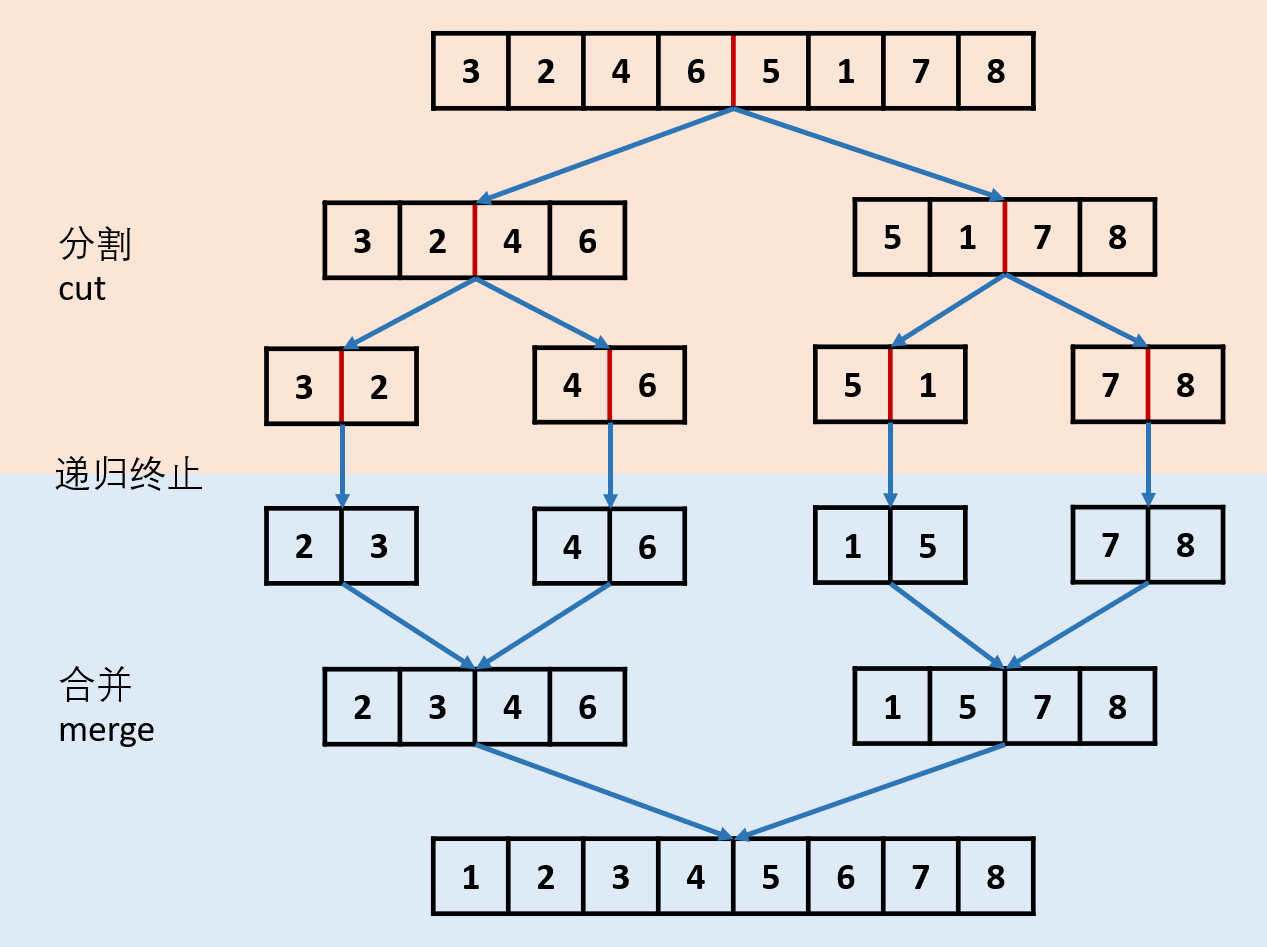
复杂度分析,n为链表长度
时间复杂度分析:
根据二分法可知,时间复杂度为O(nlogn)
空间复杂度分析:O(logn)
对数组做归并排序的空间复杂度为O(n),分别由新开辟数组O(n)和递归函数调用O(logn)组成,而根据链表特性:
数组额外空间:链表可以通过修改引用来更改节点顺序,无需像数组一样开辟额外空间;
递归额外空间:递归调用函数将带来O(logn)的空间复杂度,因此若希望达到O(1)空间复杂度,则不能使用递归。
代码
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * struct ListNode { * int val; * ListNode *next; * ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {} * ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head) { return sortList(head, nullptr); } ListNode* sortList(ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) { if (head == nullptr) { return head; } if (head->next == tail) { head->next = nullptr; return head; } ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast->next; } } ListNode* mid = slow; return merge(sortList(head, mid), sortList(mid, tail)); } ListNode* merge(ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode* temp = dummyHead; ListNode* temp1 = head1; ListNode* temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != nullptr && temp2 != nullptr) { if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) { temp->next = temp1; temp1 = temp1->next; } else { temp->next = temp2; temp2 = temp2->next; } temp = temp->next; } if (temp1 != nullptr) { temp->next = temp1; } if (temp2 != nullptr) { temp->next = temp2; } return dummyHead->next; } };
解法二
思路
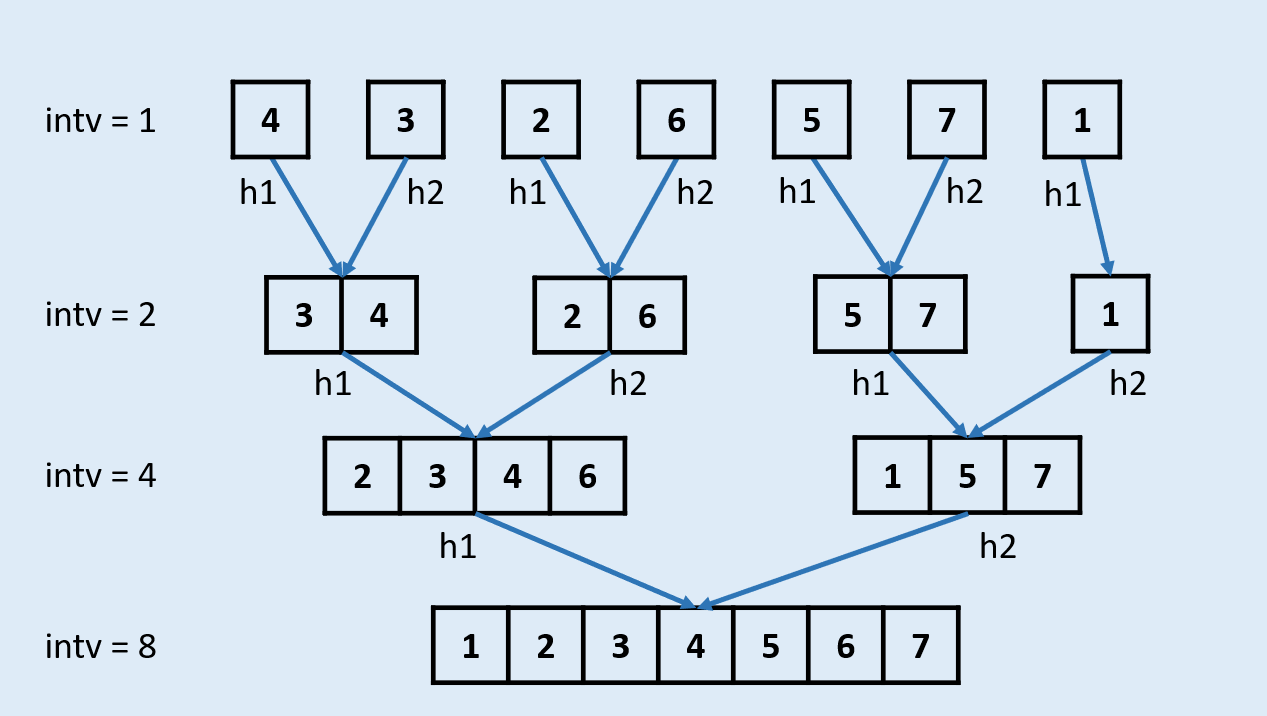
复杂度分析
时间复杂度分析:
O(nlogn)
空间复杂度分析:
O(1)
代码
class Solution { public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { if (head == null) { return head; } int length = 0; ListNode node = head; while (node != null) { length++; node = node.next; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0, head); for (int subLength = 1; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1) { ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next; while (curr != null) { ListNode head1 = curr; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr.next != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode head2 = curr.next; curr.next = null; curr = head2; for (int i = 1; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode next = null; if (curr != null) { next = curr.next; curr.next = null; } ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2); prev.next = merged; while (prev.next != null) { prev = prev.next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead.next; } public ListNode merge(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
本文来自博客园,作者:jsqup,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/jsqup/p/15805613.html




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?