堆与堆排序 红黑树
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6709644
数组的堆化
把一个无序数组,原地变成堆的结构。
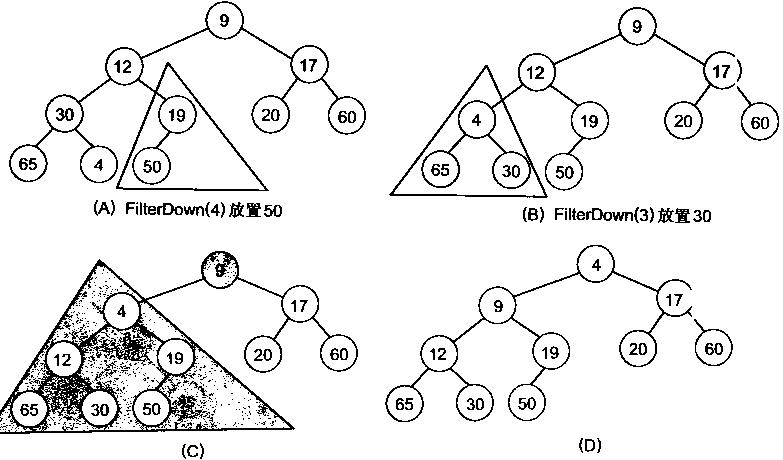
上图是堆化成最小堆的结构。
可以看到,它是按照由小树 -> 到大树的逐步堆化。这样做是为了避免使用第二个数组。
假如是大树 到 小树 的堆化,在大树的堆化时,它并不能保证父节点的一次堆化能取到最小(大)的元素。而小树到大树的结构,可以保证小树的根节点肯定是小树的最小元素,从而保证大树只需判断左儿子和右儿子就能取到最小值。
1 package algorithm; 2 //堆排序 3 public class HeapSort { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 int[] arr = {6,4,2,8,1,9}; 7 heapSort(arr); 8 } 9 public static void heapSort(int[] arr){ 10 for (int i = (arr.length>>>1)-1; i >= 0; i--) { //从小树到大树的逐步堆调整 11 heapAdjust(arr,i,arr.length); 12 } 13 for (int i = arr.length-1; i > 0; i--) { //逐步找到最大的元素,放在最后,减少堆的长度(i) 14 int temp = arr[0]; //交换最大和最后个 15 arr[0]=arr[i]; 16 arr[i] = temp; 17 heapAdjust(arr,0,i); //调整堆结构 18 } 19 for (int i : arr) { 20 System.out.println(i); 21 } 22 } 23 24 public static void heapAdjust(int[] arr, int i,int n){ 25 int child = 0; //儿子为 2*i+1 和 2*i+2 26 for (; (child=(i<<1)+1) < n; i=child) { //堆调整,父亲到儿子的逐步迭代 27 if (child<n-1 && arr[child+1]>arr[child]) //右儿子较大,注意检查右儿子是否越界 28 child++; 29 if (arr[child]>arr[i]) { //交换儿子和父亲 30 int temp = arr[i]; 31 arr[i] = arr[child]; 32 arr[child] = temp; 33 }else //不用交换 迭代结束 34 break; 35 } 36 } 37 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号