算法学习记录-图(DFS BFS)
图:
目录:
1.概念
2.邻接矩阵(结构,深度/广度优先遍历)
3.邻接表(结构,深度/广度优先遍历)
图的基本概念:
数据元素:顶点
1.有穷非空(必须有顶点)
2.顶点之间为边(可空)
无向图:边没有方向,用(vi,vj)表示,(vj,vi)也可。
有向图:边有方向,称为弧,用<vi,vj>表示。vi尾,vj头
简单图:不存在顶点到其自身的边,且同一条边不重复出现。
无向完全图:无向图中,所有的顶点都有边连接。 边的条数:n*(n-1)/2
有向完全图:在有向图中,如果任意两个顶点之间都存在方向互为相反的两条弧。
有很少条边或者弧的图称 稀疏图,反之称为稠密图。
边的相关数称为权。
图的存储
有向图:
入度:就是指向该顶点的边的个数
出度:就是该顶点指向其他顶点的边的个数
存放图的方式:
1.邻接矩阵
2.邻接表
3.十字链表
4.邻接多重表
5.边集数组
遍历:
1.深度优先遍历(DFS)
2.广度优先遍历(BFS)
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
================================================

以此无向图作例子:
##################################################################
(1).邻接矩阵(9个顶点)
##################################################################
我们需要一个顶点数组,一个边数组:
顶点数组 {A,B,C,D,E,F,G,H,I}
边数组:
 (其中 $代表无临边,在数组总存放为65535)
(其中 $代表无临边,在数组总存放为65535)
a.结构:
#define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; //静态图-邻接矩阵 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; EdgeType Mat[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; int numVexs,numEdges; }MGraph;
存储形式:
一个数组存放顶点;一个二维数组存放邻接矩阵。
b.初始化图:
bool checkMat(EdgeType *p,VertexType numvex) { int i,j; for (i=0;i<numvex;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<numvex;j++) { //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\t",i,j,*(p + MAXVEX*i + j)); //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\n",j,i,*(p + MAXVEX*j + i)); if (*(p + MAXVEX*i + j) != *(p + MAXVEX*j +i) ) { printf("ERROR:Mat[%d][%d] or Mat[%d][%d] not equal!\n",i,j,j,i); return false; } } } return true; } void init_Grp(MGraph *g,VertexType *v,EdgeType *p) { int i,j; // init vex num (*g).numVexs = getVexNum(v); //init vexter for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { (*g).vexs[i]=*v; v++; } //init Mat for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { for (j=0;j<(*g).numVexs;j++) { (*g).Mat[i][j] = *(p + MAXVEX*i + j); } } if(checkMat(&((*g).Mat[0][0]),(*g).numVexs) == false) { printf("init error!\n"); exit(0); } }
c1:深度优先遍历:
//DFS void DFS(MGraph G,int num) { int j; g_visited[num]=true; printf(" %c ",G.vexs[num]); for (j = 0;j<G.numVexs;j++) { if (!g_visited[j] && G.Mat[num][j] == 1) { //printf("g_vis[%d] = %d",j,g_visited[j]); //printf("Mat[%d][%d] = %d\n",num,j,G.Mat[num][j]); DFS(G,j); } } } void grp_DFS(MGraph G) { int i; for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) // (1)
{ g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) // (2) { if (!g_visited[i]) { DFS(G,i); } } }
解释:
在grp_DFS()函数中,(1)对每个顶点初始化,记录顶点是否被访问过。
(2)对每个没有被访问过的顶点访问。
在DFS()函数中:
for (j = 0;j<G.numVexs;j++)
if (!g_visited[j] && G.Mat[num][j] == 1)
判断该点是否被访问过而且有边,对每个顶点进行递归调用。
下图:

红色:grp_DFS()中,第一次调用时,访问A。从A开始递归调用。
从A开始,首先设置 g_visited[0] = true;判断edge[0][0](A自己)--> [0][1](B顶点),递归调用DFS()。(注意这里还没完成,在最后递归调用完成后还会继续判断[0][2]...[0][8])。
进入B,首先设置g_visited[1] = true;判断edge[1][0](A访问过了) --> [1][1](B自己)-->[1][2](C顶点),递归调用
。。。
绿色:进入G,首先设置g_visited[1] = true;判断edge[6][0] ...[6][8] (DFS函数中for全部循环完成),退出 --->退回到F,继续完成F的DFS的for循环 --->
退回到E,继续完成DFS的for,进入到H。如此。。。
---> E ---> D ---> C ---> B ---> I
最后退回到A,完成DFS的for循环。
我们可以发现,连通图只需要调用了grp_DFS() 即可完成全部循环。
深度优先遍历完整代码:
#include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; //静态图-邻接矩阵 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; EdgeType Mat[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; int numVexs,numEdges; }MGraph; VertexType g_init_vexs[MAXVEX] = { 'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I'}; EdgeType g_init_edges1[MAXVEX][MAXVEX] = { {0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,IFY,IFY,1}, //'A' {1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1}, //'B' {IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY},//'C' {IFY,IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY},//'D' {IFY,IFY,IFY,1,0,1,1,1,IFY}, //'E' {1,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY}, //'F' {IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,1,0,IFY,IFY}, //'G' {IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,IFY,IFY,0,IFY}, //'H' {1,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,0}, //'I' }; bool g_visited[MAXVEX]; //打印数组 void prt_maxtix(EdgeType *p,int vexs) { int i,j; for (i=0;i<vexs;i++) { printf("\t"); for (j=0;j<vexs;j++) { if( (*(p + MAXVEX*i + j)) == IFY) { printf(" $ "); } else { printf(" %d ", *(p + MAXVEX*i + j)); } } printf("\n"); } } //check the number of vextex int getVexNum(VertexType *vexs) { VertexType *pos = vexs; int cnt=0; while(*pos <= 'Z' && *pos >= 'A') { cnt++; pos++; } return cnt; } //DFS void DFS(MGraph G,int num) { int j; g_visited[num]=true; printf(" %c ",G.vexs[num]); for (j = 0;j<G.numVexs;j++) { if (!g_visited[j] && G.Mat[num][j] == 1) { //printf("g_vis[%d] = %d",j,g_visited[j]); //printf("Mat[%d][%d] = %d\n",num,j,G.Mat[num][j]); DFS(G,j); } } } void grp_DFS(MGraph G) { int i; for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { if (!g_visited[i]) { //printf("xxx[%d]\n",i); DFS(G,i); } } } bool checkMat(EdgeType *p,VertexType numvex) { int i,j; for (i=0;i<numvex;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<numvex;j++) { //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\t",i,j,*(p + MAXVEX*i + j)); //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\n",j,i,*(p + MAXVEX*j + i)); if (*(p + MAXVEX*i + j) != *(p + MAXVEX*j +i) ) { printf("ERROR:Mat[%d][%d] or Mat[%d][%d] not equal!\n",i,j,j,i); return false; } } } return true; } void init_Grp(MGraph *g,VertexType *v,EdgeType *p) { int i,j; // init vex num (*g).numVexs = getVexNum(v); //init vexter for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { (*g).vexs[i]=*v; v++; } //init Mat for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { for (j=0;j<(*g).numVexs;j++) { (*g).Mat[i][j] = *(p + MAXVEX*i + j); } } if(checkMat(&((*g).Mat[0][0]),(*g).numVexs) == false) { printf("init error!\n"); exit(0); } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { MGraph grp; init_Grp(&grp,g_init_vexs,&g_init_edges1[0][0]); //print the number of Vexters printf("vex num = %d\n",grp.numVexs); //print the maxtix prt_maxtix(&grp.Mat[0][0],grp.numVexs); grp_DFS(grp); getchar(); return 0; }
结果:
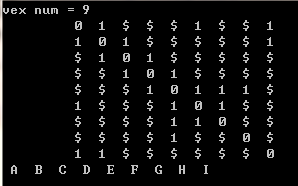
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
c2:广度优先遍历
void BFS(MGraph G) { int i,j; spQueue que; init_Queue(&que); for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { g_visited[i]=false; } for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { if (!g_visited[i]) { g_visited[i]=true; unshiftQueue(&que,i); printf(" %c ",G.vexs[i]); while(!isEmptyQueue(que)) { QueueType crnt = shiftQueue(&que); for (j=0;j<G.numVexs;j++) { if (!g_visited[j] && G.Mat[crnt][j] == 1) { g_visited[j]=true; unshiftQueue(&que,j); printf(" %c ",G.vexs[j]); } } i=crnt; } } } }
解释:
从一个顶点开始,查看所有和他相连的顶点;从这些相连的顶点中逐次查找与它们相连且没有访问过的点。
这里要借助一个辅助的数据结构---队列。
如下,先将图转化为右边形式。
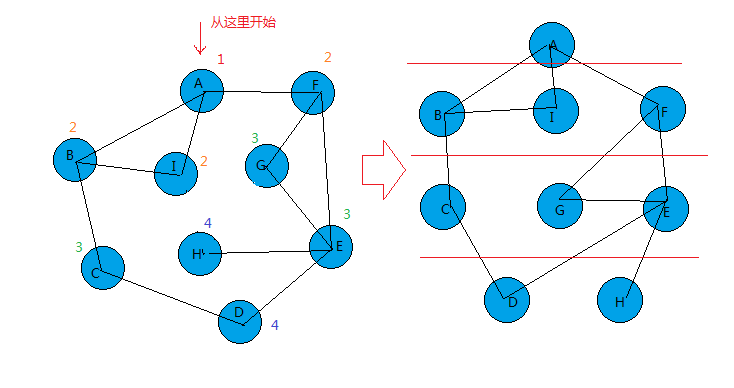
第一层为A,第二层为B I F,第三层为C G E,第四层为 D H。
过程:
a.A开始,A进队。
队列 | A |
b.队列出队一个元素(此时为A),查找与它相连且没有被访问过的元素(B、I、F),使其进队。
队列 A | | --> | B I F | 第一层完成
---
c.重复b过程,直到队列中没有元素为止。 (如果是连通图,则此时全部访问,否则继续查其他顶点,直到所有顶点都遍历。)
队列出列一个元素(此时为B),查找与它相连且没有被访问过的元素(C),使其进队。
队列 B | I F|--> | I F C|
队列出列一个元素(此时为I),。。。 (无)
队列 I | F C | --> | F C |
队列出列一个元素(此时为F),。。。 (G、E),使其进队。
队列 F | C | ---> | C G E | 第二层完成
---
队列 C | G E | ---> | G E D|
队列 G | E D | ---> |E D|
队列 E | D | ---> | D H|
队列 D | H | ---> | H |
队列 H || 完成。。。
完整程序如下:
// grp-mat-bfs-self.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; typedef int QueueType; bool g_visited[MAXVEX]; VertexType g_init_vexs[MAXVEX] = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I'}; EdgeType g_init_edges[MAXVEX][MAXVEX] = { {0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,IFY,IFY,1}, //'A' {1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1}, //'B' {IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY},//'C' {IFY,IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY},//'D' {IFY,IFY,IFY,1,0,1,1,1,IFY}, //'E' {1,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,0,1,IFY,IFY}, //'F' {IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,1,0,IFY,IFY}, //'G' {IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,1,IFY,IFY,0,IFY}, //'H' {1,1,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,IFY,0}, //'I' }; //========================================================================== //静态图-邻接矩阵 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; EdgeType Mat[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; int numVexs,numEdges; }MGraph; //========================================================================== //队列 //队列节点 typedef struct Node { QueueType data; struct Node *next; }QNode,*qQNode; //队列指示 typedef struct { int length; qQNode frnt,rear; }spQueue; void init_Queue(spQueue *Q) { (*Q).frnt = NULL; (*Q).rear = NULL; (*Q).length = 0; } bool isEmptyQueue(spQueue Q) { if (Q.length == 0) { return true; } return false; } //进队 void unshiftQueue(spQueue *Q,QueueType elem) { //队列空 if (isEmptyQueue(*Q)) { qQNode n = (qQNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); n->data = elem; n->next = NULL; (*Q).frnt = n; (*Q).rear = n; (*Q).length = 1; } else { qQNode n = (qQNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); n->data = elem; n->next = NULL; (*Q).rear->next = n; (*Q).rear = n; (*Q).length++; } } //出队 QueueType shiftQueue(spQueue *Q) { if (isEmptyQueue(*Q)) { printf("Warning:Queue is empty!!!\n"); return NULL; } if ((*Q).length == 1) { QueueType sh = (*Q).frnt->data; (*Q).frnt = NULL; (*Q).rear = NULL; (*Q).length = 0; return sh; } QueueType sh = (*Q).frnt->data; (*Q).frnt = (*Q).frnt->next; (*Q).length--; return sh; } //打印队列 void prt_que(spQueue que) { if (isEmptyQueue(que)) { return ; } qQNode pos = que.frnt; while(que.rear->next != pos && pos != NULL) { printf(" %d ",pos->data); pos = pos->next; } printf("\n"); } //==================================================================== //打印矩阵 void prt_maxtix(EdgeType *p,int vexs) { int i,j; for (i=0;i<vexs;i++) { printf("\t"); for (j=0;j<vexs;j++) { if( (*(p + MAXVEX*i + j)) == IFY) { printf(" $ "); } else { printf(" %d ", *(p + MAXVEX*i + j)); } } printf("\n"); } } //check the number of vextex int getVexNum(VertexType *vexs) { VertexType *pos = vexs; int cnt=0; while(*pos <= 'Z' && *pos >= 'A') { cnt++; pos++; } return cnt; } bool checkMat(EdgeType *p,VertexType numvex) { int i,j; for (i=0;i<numvex;i++) { for(j=i+1;j<numvex;j++) { //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\t",i,j,*(p + MAXVEX*i + j)); //printf("[%d][%d] = %d\n",j,i,*(p + MAXVEX*j + i)); if (*(p + MAXVEX*i + j) != *(p + MAXVEX*j +i) ) { printf("ERROR:Mat[%d][%d] or Mat[%d][%d] not equal!\n",i,j,j,i); return false; } } } return true; } void init_Grp(MGraph *g,VertexType *v,EdgeType *p) { int i,j; // init vex num (*g).numVexs = getVexNum(v); //init vexter for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { (*g).vexs[i]=*v; v++; } //init Mat for (i=0;i<(*g).numVexs;i++) { for (j=0;j<(*g).numVexs;j++) { (*g).Mat[i][j] = *(p + MAXVEX*i + j); } } if(checkMat(&((*g).Mat[0][0]),(*g).numVexs) == false) { printf("init error!\n"); exit(0); } } void BFS(MGraph G) { int i,j; spQueue que; init_Queue(&que); for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { g_visited[i]=false; } for (i=0;i<G.numVexs;i++) { if (!g_visited[i]) { g_visited[i]=true; unshiftQueue(&que,i); printf(" %c ",G.vexs[i]); while(!isEmptyQueue(que)) { QueueType crnt = shiftQueue(&que); for (j=0;j<G.numVexs;j++) { if (!g_visited[j] && G.Mat[crnt][j] == 1) { g_visited[j]=true; unshiftQueue(&que,j); printf(" %c ",G.vexs[j]); } } i=crnt; } } } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { MGraph grp; init_Grp(&grp,g_init_vexs,&g_init_edges[0][0]); BFS(grp); getchar(); return 0; }
结果:

=================================================================

##################################################################
(2).邻接表
##################################################################
如上图:
邻接表如下:
顶点 边
A -> B -> F -> I
B -> A -> C -> I
C -> B -> D
D -> C -> E
E -> D -> F -> G -> H
F -> A -> E -> G
G -> E -> F
H -> E
I -> A -> B
结构:
#define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; typedef int ArrayIdx; //边节点 typedef struct EdgeNode{ ArrayIdx idx; struct EdgeNode* next; }edgeNode; //顶点节点 typedef struct VexNode{ ArrayIdx idx; edgeNode *fitstedge; }vexNode; //图的集合:包含了一个顶点数组 typedef struct { vexNode adjList[MAXVEX]; int numVextexs,numEdges; }GraphAdjList;

我通过一个二维字符数组来初始化该图结构:
VertexType g_init_vexs[MAXVEX] = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I'};
//====================================
char *g_input[] = {
"A->B->F->I",
"B->A->C->I",
"C->B->D",
"D->C->E",
"E->D->F->G->H",
"F->A->E->G",
"G->E->F",
"H->E",
"I->A->B"
};
初始化函数:
void init_GrapAdjList(GraphAdjList *g,char **str) { char **pos = str; int cnt=0; while (*pos != NULL) //g_input的每行的首指针 { int i=0; while(**pos != NULL) //g_input的每行字母 { if(isVexter(**pos)) //判断是否为顶点(我规定‘A’-‘Z’之间为顶点标志) { if (i == 0) //建立顶点的节点 { (*g).adjList[cnt].idx = strFindIdx(**pos); (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = NULL; i=1; } else if(i == 1) //建立第一个边的节点 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = n; i=2; } else //边节点连接到前一个边节点上 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; //first splist edgeNode *r = (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge; while (r->next != NULL) { r = r->next; } r->next = n; } } (*pos)++; } pos++; cnt++; } (*g).numVextexs = cnt; }
这样之后,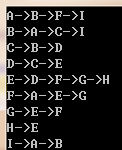
内存中,以其中A为例子:
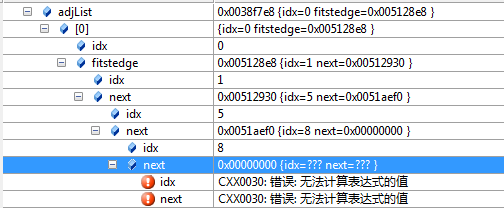
idx 为 索引值 0 ---> 'A'
0(A)---> 1(B) ---> 5(F) ---> 8(I)。
深度优先遍历(邻接矩阵类似)
遍历顺序为:

代码:
void DFS(GraphAdjList GL,int i) { edgeNode *p; g_visited[i]=true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[GL.adjList[i].idx]); p = GL.adjList[i].fitstedge; while(p) { if (!g_visited[p->idx]) { DFS(GL,p->idx); } p=p->next; } } void DFS_Trvs(GraphAdjList GL) { int i; for (i = 0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { if (!g_visited[i]) { DFS(GL,i); } } }
结果:
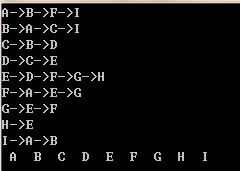
完整代码:
// grp-tab-dfs.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; typedef int ArrayIdx; //边节点 typedef struct EdgeNode{ ArrayIdx idx; struct EdgeNode* next; }edgeNode; //顶点节点 typedef struct VexNode{ ArrayIdx idx; edgeNode *fitstedge; }vexNode; //图的集合:包含了一个顶点数组 typedef struct { vexNode adjList[MAXVEX]; int numVextexs,numEdges; }GraphAdjList; bool g_visited[MAXVEX]; VertexType g_init_vexs[MAXVEX] = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I'}; //==================================== char *g_input[] = { "A->B->F->I", "B->A->C->I", "C->B->D", "D->C->E", "E->D->F->G->H", "F->A->E->G", "G->E->F", "H->E", "I->A->B" }; ArrayIdx strFindIdx(char ch) { int i=0; VertexType *p = g_init_vexs; while(p != NULL) { if(*p == ch) { return i; } p++; i++; } } VertexType idxFindStr(ArrayIdx i) { return g_init_vexs[i]; } void prt_strings(char *p) { char *pos = p; while (NULL != *pos) { printf("%c",*pos); pos++; } printf("\n"); } void prt_strArrays(char *p[]) { char **pos = p; while( *pos != NULL) { prt_strings(*pos); pos++; } } bool isVexter(char p) { if (p>='A' && p<='Z') { return true; } return false; } void init_GrapAdjList(GraphAdjList *g,char **str) { char **pos = str; int cnt=0; while (*pos != NULL) //g_input的每行的首指针 { int i=0; while(**pos != NULL) //g_input的每行字母 { if(isVexter(**pos)) //判断是否为顶点(我规定‘A’-‘Z’之间为顶点标志) { if (i == 0) //建立顶点的节点 { (*g).adjList[cnt].idx = strFindIdx(**pos); (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = NULL; i=1; } else if(i == 1) //建立第一个边的节点 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = n; i=2; } else //边节点连接到前一个边节点上 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; //first splist edgeNode *r = (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge; while (r->next != NULL) { r = r->next; } r->next = n; } } (*pos)++; } pos++; cnt++; } (*g).numVextexs = cnt; } void DFS(GraphAdjList GL,int i) { edgeNode *p; g_visited[i]=true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[GL.adjList[i].idx]); p = GL.adjList[i].fitstedge; while(p) { if (!g_visited[p->idx]) { DFS(GL,p->idx); } p=p->next; } } void DFS_Trvs(GraphAdjList GL) { int i; for (i = 0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { if (!g_visited[i]) { DFS(GL,i); } } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { GraphAdjList grp; prt_strArrays(g_input); init_GrapAdjList(&grp,g_input); DFS_Trvs(grp); getchar(); return 0; }
广度优先遍历:
与邻接矩阵类似。
void BFS(GraphAdjList GL) { int i,j; spQueue Q; init_Queue(&Q); for (i = 0 ;i < GL.numVextexs;i++) { g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { if(!g_visited[i]) { g_visited[i] = true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[i]); unshiftQueue(&Q,i); while(!isEmptyQueue(Q)) { i = shiftQueue(&Q); edgeNode *p = GL.adjList[i].fitstedge; while(p != NULL) { if (!g_visited[p->idx]) { g_visited[p->idx]=true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[p->idx]); unshiftQueue(&Q,p->idx); } p=p->next; } } } } }
结构,初始化与广度一样。
多了一个辅助结构-队列。与邻接矩阵中队列一样。
结果:
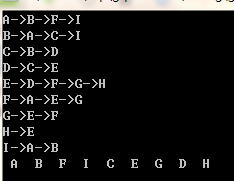
完整函数:
// grp-tab-bfs.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #define MAXVEX 100 #define IFY 65535 typedef char VertexType; typedef int EdgeType; typedef int ArrayIdx; //边节点 typedef struct EdgeNode{ ArrayIdx idx; struct EdgeNode* next; }edgeNode; //顶点节点 typedef struct VexNode{ ArrayIdx idx; edgeNode *fitstedge; }vexNode; //图的集合:包含了一个顶点数组 typedef struct { vexNode adjList[MAXVEX]; int numVextexs,numEdges; }GraphAdjList; typedef int QueueType; bool g_visited[MAXVEX]; VertexType g_init_vexs[MAXVEX] = {'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I'}; char *g_input[] = { "A->B->F->I", "B->A->C->I", "C->B->D", "D->C->E", "E->D->F->G->H", "F->A->E->G", "G->E->F", "H->E", "I->A->B" }; //========================================================================== //队列 //队列节点 typedef struct Node { QueueType data; struct Node *next; }QNode,*qQNode; //队列指示 typedef struct { int length; qQNode frnt,rear; }spQueue; void init_Queue(spQueue *Q) { (*Q).frnt = NULL; (*Q).rear = NULL; (*Q).length = 0; } bool isEmptyQueue(spQueue Q) { if (Q.length == 0) { return true; } return false; } //进队 void unshiftQueue(spQueue *Q,QueueType elem) { //队列空 if (isEmptyQueue(*Q)) { qQNode n = (qQNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); n->data = elem; n->next = NULL; (*Q).frnt = n; (*Q).rear = n; (*Q).length = 1; } else { qQNode n = (qQNode)malloc(sizeof(QNode)); n->data = elem; n->next = NULL; (*Q).rear->next = n; (*Q).rear = n; (*Q).length++; } } //出队 QueueType shiftQueue(spQueue *Q) { if (isEmptyQueue(*Q)) { printf("Warning:Queue is empty!!!\n"); return NULL; } if ((*Q).length == 1) { QueueType sh = (*Q).frnt->data; (*Q).frnt = NULL; (*Q).rear = NULL; (*Q).length = 0; return sh; } QueueType sh = (*Q).frnt->data; (*Q).frnt = (*Q).frnt->next; (*Q).length--; return sh; } //打印队列 void prt_que(spQueue que) { if (isEmptyQueue(que)) { return ; } qQNode pos = que.frnt; while(que.rear->next != pos && pos != NULL) { printf(" %d ",pos->data); pos = pos->next; } printf("\n"); } //=============================================================== ArrayIdx strFindIdx(char ch) { int i=0; VertexType *p = g_init_vexs; while(p != NULL) { if(*p == ch) { return i; } p++; i++; } } VertexType idxFindStr(ArrayIdx i) { return g_init_vexs[i]; } void prt_strings(char *p) { char *pos = p; while (NULL != *pos) { printf("%c",*pos); pos++; } printf("\n"); } void prt_strArrays(char *p[]) { char **pos = p; while( *pos != NULL) { prt_strings(*pos); pos++; } } bool isVexter(char p) { if (p>='A' && p<='Z') { return true; } return false; } void init_GrapAdjList(GraphAdjList *g,char **str) { char **pos = str; int cnt=0; while (*pos != NULL) //g_input的每行的首指针 { int i=0; while(**pos != NULL) //g_input的每行字母 { if(isVexter(**pos)) //判断是否为顶点(我规定‘A’-‘Z’之间为顶点标志) { if (i == 0) //建立顶点的节点 { (*g).adjList[cnt].idx = strFindIdx(**pos); (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = NULL; i=1; } else if(i == 1) //建立第一个边的节点 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge = n; i=2; } else //边节点连接到前一个边节点上 { edgeNode* n = (edgeNode*)malloc(sizeof(edgeNode)); n->idx = strFindIdx(**pos); n->next = NULL; //first splist edgeNode *r = (*g).adjList[cnt].fitstedge; while (r->next != NULL) { r = r->next; } r->next = n; } } (*pos)++; } pos++; cnt++; } (*g).numVextexs = cnt; } void BFS(GraphAdjList GL) { int i,j; spQueue Q; init_Queue(&Q); for (i = 0 ;i < GL.numVextexs;i++) { g_visited[i] = false; } for (i=0;i<GL.numVextexs;i++) { if(!g_visited[i]) { g_visited[i] = true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[i]); unshiftQueue(&Q,i); while(!isEmptyQueue(Q)) { i = shiftQueue(&Q); edgeNode *p = GL.adjList[i].fitstedge; while(p != NULL) { if (!g_visited[p->idx]) { g_visited[p->idx]=true; printf(" %c ",g_init_vexs[p->idx]); unshiftQueue(&Q,p->idx); } p=p->next; } } } } } int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { GraphAdjList grp; prt_strArrays(g_input); init_GrapAdjList(&grp,g_input); BFS(grp); getchar(); return 0; }
这两种是常用的图的遍历算法。时间复杂度在 邻接矩阵结构时候为 O(n2),邻接表结构时候为O(n)。
对于图的存储结构还有:十字链表、多重邻接表等等。
==================================================================

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号