IO流
概述
如何选择
如果数据通过Window自带的记事本软件打开,我们还可以读懂里面的内容,就使用字符流,否则使用字节流。 如果你不知道该使用哪种类型的流,就使用字节流。
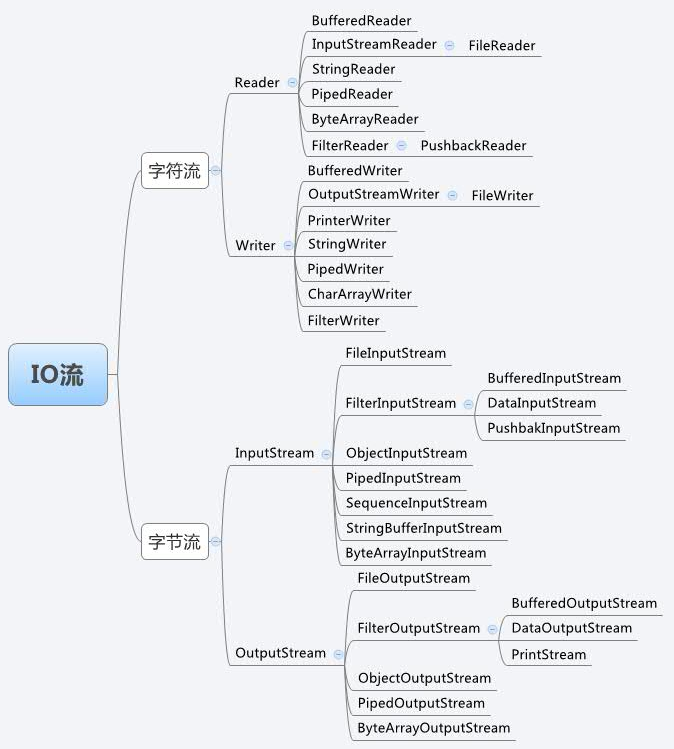
字节流
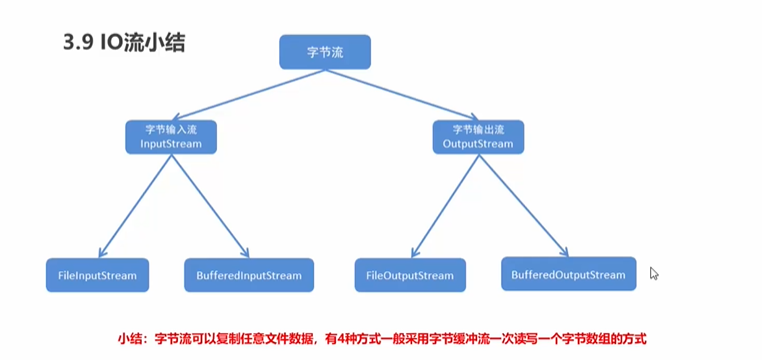
字符流
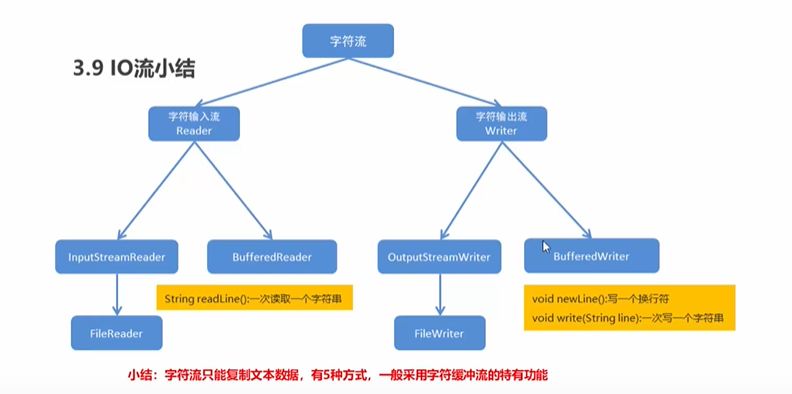
字节流
InputStream
| 方法名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| abstract int read() | 从输入流中读取数据的下一个字节 |
| int read(byte[] b) | 从输入流读取一些字节数,并将它们存储到缓冲区 b |
| int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 从输入流读取最多 len字节的数据到一个字节数组。 |
| void close() | 关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源 |
OutputStream
| 方法名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| void write(byte[] b) | 将 b.length 个字节从指定的 byte 数组写入此输出流 |
| void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) | 将指定 byte 数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len 个字节写入此输出流 |
| abstract void write(int b) | 将指定的字节写入此输出流 |
| void close() | 关闭此输出流并释放与此流有关的所有系统资源 |
| void flush() | 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节 |
FileInputStream
字节文件输入流,从文件系统中的某个文件中获得输入字节,用于读取诸如图像数据之类的原始字节流。
public class FileInputStream_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt");
int by;
//一次读取一个字节
while ((by=fis.read())!=-1)
{
//因为字符在底层存储的时候就是存储的数值。即字符对应的ASCII码。
//所以需要强制转换一下类型
System.out.print((char)by);
}
//关闭IO流
fis.close();
}
}
// 一次读取一个字节数组,提高了操作效率,IO流使用完毕一定要关闭
public class FileInputStream_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt");
byte[] s1= new byte[1024];
int len;
// 一次读取一个字节数组
while ((len=fileInputStream.read(s1))!=-1)
{
System.out.println(new String(s1,0,len));
}
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
FileOutputStream
字节文件输出流是用于将数据写入到File,从程序中写入到其他位置
//65 66 67数字变成了字符ABC,因为字符在底层存储的时候就是存储的数值。即字符对应的ASCII码。
public class FileOutputStream_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\text.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
int a=scanner.nextInt();
fos.write(a);
}
scanner.close();
fos.close();
}
}
//write写入的数组为byte类型
//输入:65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74
//输出的目的地文件不存在,则会自动创建,不指定盘符的话,默认创建在项目目录下;
//写入是重新写的,想追加的话需要多传一个参数。new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt",true);
public class FileOutputStream_02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
byte[] s1=new byte[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
s1[i]=scanner.nextByte();
}
fos.write(s1[0]);//A
fos.write('\n');//换行
fos.write(s1);//ABCDEFGHIJ
fos.write('\n');//换行
fos.write(s1,1,2);//BC
fos.write('\n');
//getBeytes()返回字符串对应的字节流数组
byte[] bytes = "asdfghjkl".getBytes();
fos.write(bytes);//asdfghjkl
scanner.close();
}
}
BufferedInputStream
字节缓冲输入流,提高了读取效率
public class BufferedInputStream_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt"));
byte[] s1=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(s1))!=-1)
{
System.out.print(new String(s1,0,len));
}
bis.close();
}
}
BufferedOutputStream
class test04{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Desktop\\test.txt"));
bos.write("你好".getBytes());
bos.close();
}
}
字符流
Reader
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读取单个字符 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 将字符读入数组 |
| abstract int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 将字符读入数组的某一部分 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过字符 |
| abstract void close() | 关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源 |
Writer
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| void write(char[] cbuf) | 写入字符数组 |
| abstract void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 写入字符数组的某一部分 |
| void write(int c) | 写入单个字符 |
| void write(String str) | 写入字符串 |
| void write(String str, int off, int len) | 写入字符串的某一部分 |
| abstract void close() | 关闭此流,但要先刷新它 |
| abstract void flush() | 刷新该流的缓冲 |
InputStreamReader
字节流转字符流,所以不管字节流还是字符流本质都是字节流,它使用的字符集可以由名称指定或显式给定,否则将接受平台默认的字符集。
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in) | 创建一个使用默认字符集的 InputStreamReader |
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in, Charset cs) | 创建一个使用给定字符集的InputStreamReader。 |
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in, CharsetDecoder dec) | 创建一个使用给定字符集解码器的InputStreamReader。 |
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in, String charsetName) | 创建一个使用命名字符集的InputStreamReader。 |
| String getEncoding() | 返回此流使用的字符编码的名称 |
OutputStreamWriter
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) | 创建一个使用默认字符编码的OutputStreamWriter。 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, Charset cs) | 创建一个使用给定字符集的OutputStreamWriter。 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, CharsetEncoder enc) | 创建一个使用给定字符集编码器的OutputStreamWriter。 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName) | 创建一个使用命名字符集的OutputStreamWriter。 |
class test05 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("D:\\tools\\study\\循环\\src\\com\\jpy\\123.txt"));
osw.write("我是中国人");
osw.close();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("D:\\tools\\study\\循环\\src\\com\\jpy\\123.txt"));
char[] bytes = new char[1024];
int len;
while ((len = isr.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
isr.close();
}
}
BufferedReader
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| BufferedReader(Reader in) | 创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流 |
| BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) | 创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流 |
| String readLine() | 读取一个文本行 |
class test06 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("D:\\tools\\study\\循环\\src\\com\\jpy\\123.txt"));
String s;
while ((s=br.readLine())!=null)
{
System.out.println(s);
}
br.close();
}
}
BufferWriter
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| BufferedWriter(Writer out) | 创建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流 |
| BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) | 创建一个使用给定大小输出缓冲区的新缓冲字符输出流 |
| void newLine() | 写入一个行分隔符 |
public class BufferedWriter_01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("D:\\Desktop\\test2.txt",true));
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
bufferedWriter.write("我真的很爱学BufferedReader");
bufferedWriter.newLine();
}
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号