Java线程池快速学习教程
1. Java线程池
线程池:顾名思义,用一个池子装载多个线程,使用池子去管理多个线程。
问题来源:应用大量通过new Thread()方法创建执行时间短的线程,较大的消耗系统资源并且系统的响应速度变慢。【在一个什么程度上能够判断启用线程池对系统的资源消耗比启动定量的new Thread()资源消耗低?这个怎么测试?】【用户体验卡顿?慢?观察CPU百分比?】
解决办法:使用线程池管理短时间执行完毕的大量线程,通过重用已存在的线程,降低线程创建和销毁造成的消耗,提高系统响应速度。
2. Java线程池快速学习教程
2.1 创建线程池
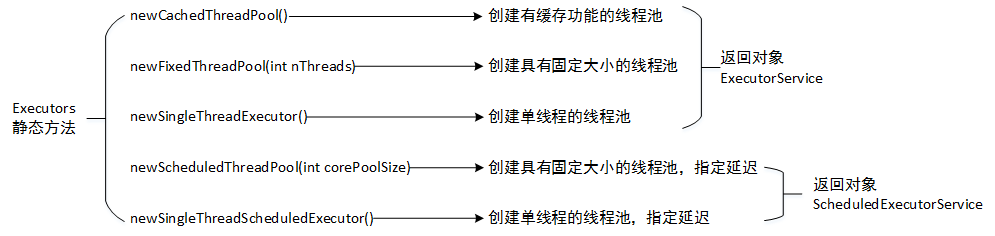
图1 Executors静态方法图
2.2 线程池使用方法

图2 ExecutorService方法图
2.3 线程池快速使用举例
问题:线程池同时接受两个线程,两个线程分别执行打印0~100;

1 import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
2 import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
3
4 public class Test {
5 public static void main(String[] args) {
6 ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
7 pool.submit(new TestThread());
8 pool.submit(new TestThread());
9 pool.shutdown();
10 }
11
12 }
13
14
15 class TestThread implements Runnable{
16 @Override
17 public void run(){
18 for(int i = 0; i <= 100; ++i){
19 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + i);
20 try {
21 Thread.sleep( (long) (1000L * Math.random()));
22 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
23 e.printStackTrace();
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 }
3. 线程池原理:
3.1 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor
Executors类提供静态工厂方法,如图1所示,这些方法最终都是通过ThreadPoolExecutor类来实现。
构造函数如下所示:

1 public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
2 int maximumPoolSize,
3 long keepAliveTime,
4 TimeUnit unit,
5 BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
6 this(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue,
7 Executors.defaultThreadFactory(), defaultHandler);
8 }
备注:
1、corePoolSize(线程池基本大小) >= 0;【当前最大并行运行线程数】
2、maximumPoolSize(线程池最大大小) >= 1;【当前最大创建线程数】
3、keepAliveTime(线程存活保持时间) >= 0;【线程在线程池空闲时间超过这个时间,会被终止掉】
4、workQueue(任务队列)不能为空;【用于传输和保存等待执行任务的阻塞队列】
5、handler(线程饱和策略)不能为空。【当线程池和队列已满的处理策略】
3.2 Executors类提供静态工厂方法默认参数
|
工厂方法 |
corePoolSize |
maximumPoolSize |
KeepAliveTime |
workQueue |
|
nreCachedThreadPool() |
0 |
Integer.MAX_VALUE |
60L |
SyschronousQueue |
|
newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) |
nThreads |
nThreads |
0 |
LindedBlockingQueue |
|
newSingleThreadExecutor() |
1 |
1 |
0 |
LindedBlockingQueue |
|
newScheduledThreadPool(int corePoolSize) |
corePoolSize |
Integer.MAX_VALUE |
0 |
DelayedWorkQueue |
|
newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor() |
1 |
Integer.MAX_VALUE |
0 |
DelayedWorkQueue |
3.3 线程池添加任务过程
添加线程即提交任务,线程添加到线程池的过程:
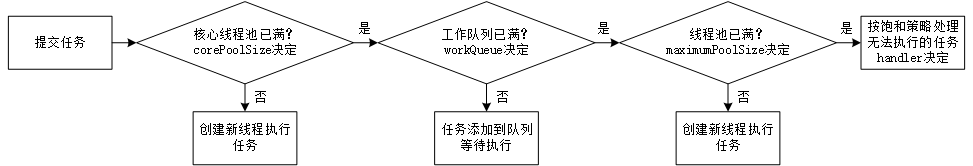
图3 线程添加到线程池过程图
4. 总结:
1、根据需要生成线程池;
2、类实现Runnable中的run方法;
3、使用execute或submit方法提交任务;
4、线程池全部线程执行完毕并且不再需要线程池时,应用shutdown()关闭资源。
2016.09.17
5. 正式工作三个月后感想:
1、假设你只是想要一个线程执行完一些操作并且没有任何与其他线程进行通信与阻塞问题,你大概可以用匿名生成new Thread().start()方法来执行。
2、corePoolSize这个参数很重要,当前最大并行运行线程数,就是可以使用newSingleThreadExecutor创建单线程的线程池,将execute执行的任务,一个一个线程顺序执行摆脱锁的问题。
3、shutdown关闭线程池,但是会执行完已提交的任务,shutdownNow关闭线程池并关闭所有任务,切记。
2017.08.06




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号