spring-boot 速成(9) druid+mybatis 多数据源及读写分离的处理
按上节继续学习,稍微复杂的业务系统,一般会将数据库按业务拆开,比如产品系统的数据库放在product db中,订单系统的数据库放在order db中...,然后,如果量大了,可能每个库还要考虑做读、写分离,以进一步提高系统性能,下面就来看看如何处理:
核心思路:配置多个数据源,然后利用RoutingDataSource结合AOP来动态切不同的库。
要解决的问题:
1、配置文件中,多数据源的配置节点如何设计?

1 druid: 2 type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource 3 study: 4 master: #study库的主库 5 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true 6 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 7 username: root 8 password: A1b2c3@def.com 9 initial-size: 5 10 min-idle: 1 11 max-active: 20 12 test-on-borrow: true 13 slave: #study库的从库 14 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study_slave?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true 15 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 16 username: root 17 password: A1b2c3@def.com 18 initial-size: 5 19 min-idle: 1 20 max-active: 20 21 test-on-borrow: true 22 product: 23 master: #product库的主库 24 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/product?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true 25 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 26 username: root 27 password: A1b2c3@def.com 28 initial-size: 5 29 min-idle: 1 30 max-active: 20 31 test-on-borrow: true 32 slave: #product库的从库 33 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/product_slave?useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8&autoReconnect=true&zeroDateTimeBehavior=convertToNull&useUnicode=true 34 driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver 35 username: root 36 password: A1b2c3@def.com 37 initial-size: 5 38 min-idle: 1 39 max-active: 20 40 test-on-borrow: true
上面的配置写法供参数,如果slave节点数要扩展,按这个格式,改造成slave1,slave2... 自行扩展。
2、配置类如何设计?

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.config; 2 3 /** 4 * Created by jimmy on 6/18/17. 5 */ 6 7 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.datasource.DbContextHolder; 8 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.datasource.MasterSlaveRoutingDataSource; 9 import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value; 10 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBuilder; 11 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; 12 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; 13 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; 14 import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; 15 import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource; 16 import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; 17 18 import javax.sql.DataSource; 19 import java.util.HashMap; 20 import java.util.Map; 21 22 23 @Configuration 24 @EnableTransactionManagement 25 public class DataSourceConfiguration { 26 27 @Value("${druid.type}") 28 private Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceType; 29 30 @Bean(name = "studyMasterDataSource") 31 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "druid.study.master") 32 public DataSource studyMasterDataSource() { 33 return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); 34 } 35 36 @Bean(name = "studySlaveDataSource") 37 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "druid.study.slave") 38 public DataSource studySlaveDataSource1() { 39 return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); 40 } 41 42 @Bean(name = "productMasterDataSource") 43 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "druid.product.master") 44 public DataSource productMasterDataSource() { 45 return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); 46 } 47 48 @Bean(name = "productSlaveDataSource") 49 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "druid.product.slave") 50 public DataSource productSlaveDataSource1() { 51 return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); 52 } 53 54 @Bean(name = "dataSource") 55 @Primary 56 public AbstractRoutingDataSource dataSource() { 57 MasterSlaveRoutingDataSource proxy = new MasterSlaveRoutingDataSource(); 58 Map<Object, Object> targetDataResources = new HashMap<>(); 59 targetDataResources.put(DbContextHolder.DbType.PRODUCT_MASTER, productMasterDataSource()); 60 targetDataResources.put(DbContextHolder.DbType.PRODUCT_SLAVE, productSlaveDataSource1()); 61 targetDataResources.put(DbContextHolder.DbType.STUDY_MASTER, studyMasterDataSource()); 62 targetDataResources.put(DbContextHolder.DbType.STUDY_SLAVE, studySlaveDataSource1()); 63 proxy.setDefaultTargetDataSource(productMasterDataSource()); 64 proxy.setTargetDataSources(targetDataResources); 65 proxy.afterPropertiesSet(); 66 return proxy; 67 } 68 69 }
参考这个,一看就明,不说多(注:@Primary一定要在动态数据源上,否则事务回滚无效!)
3、根据什么来切换db?
有很多选择,
a、用约定的方法前缀,比如:get/query/list开头的约定为读从库,其它为主库,但是这样还要考虑不同业务库的切换(即:何时切换到product库,何时切换到order库,可以再用不同的Scanner来处理,略复杂)
b、用自定义注解来处理,比如 @ProductMaster注解,表示切换到product的master库,这样同时把业务库,以及主还是从,一次性解决了,推荐这种。
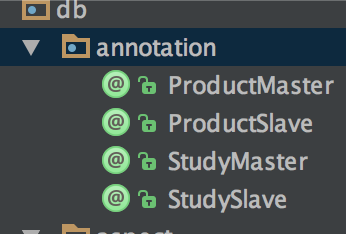
这里,我定义了4个注解,代表product,study二个库的主及从。
4、aop在哪里拦截,如何拦截?
service层和mapper层都可以拦截,推荐在服务层拦截,否则如果一个业务方法里,即有读又有写,还得考虑如果遇到事务,要考虑的东西更多。
当然,如果拦截特定的注解,就不用过多考虑在哪个层,只认注解就行(当然,注解还是建议打在服务层上)。
dubbo-starter的一个小坑:spring boot中,只有managed bean才能用aop拦截,而dubbo-starter中的@service注解不是spring中的注解(是阿里package下的自定义注解),生成的service provider实例,aop拦截不到,解决办法,再加一个注解让spring认识它,参考:
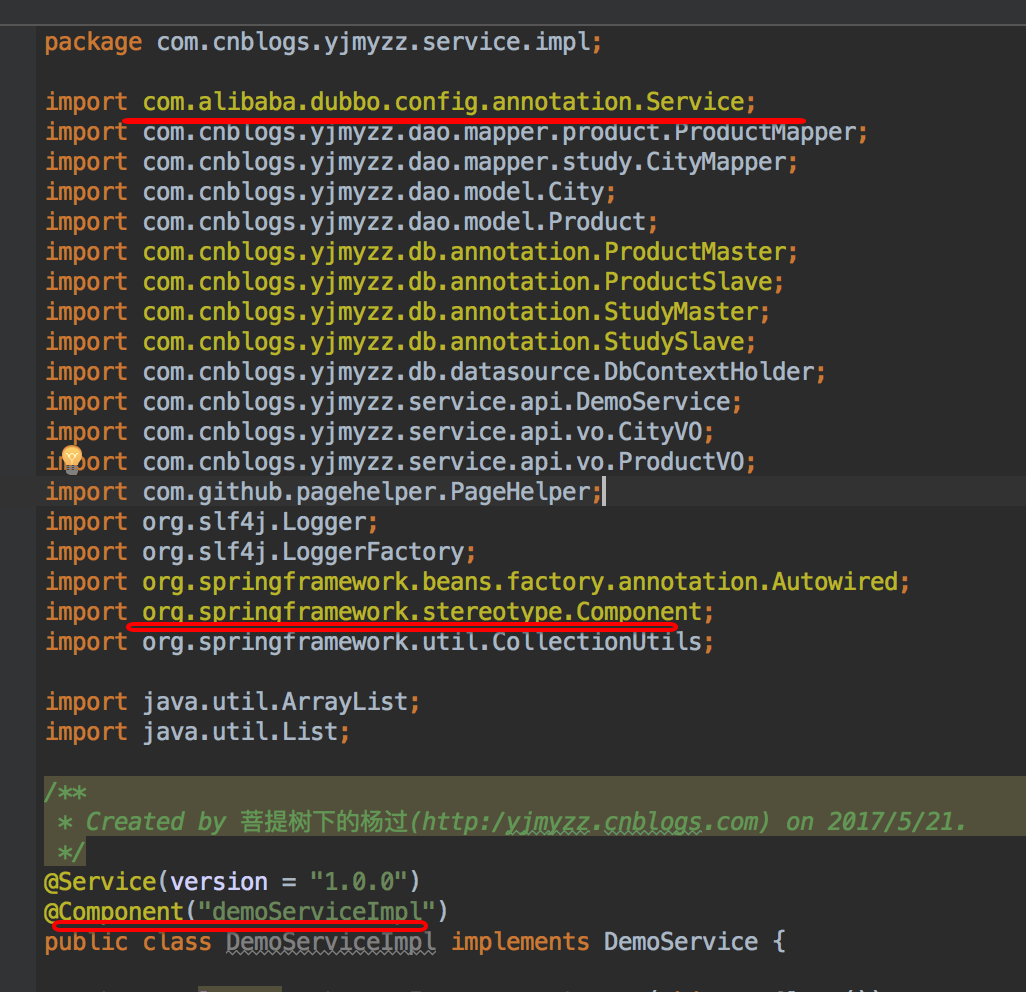
Aop拦截类的参考代码如下:

1 package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.aspect; 2 3 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.annotation.ProductMaster; 4 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.annotation.ProductSlave; 5 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.annotation.StudyMaster; 6 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.annotation.StudySlave; 7 import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.datasource.DbContextHolder; 8 import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; 9 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; 10 import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; 11 import org.slf4j.Logger; 12 import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; 13 import org.springframework.core.Ordered; 14 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 15 16 17 @Aspect 18 @Component 19 public class MasterSlaveAspect implements Ordered { 20 21 public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MasterSlaveAspect.class); 22 23 24 /** 25 * 切换到product主库 26 * 27 * @param proceedingJoinPoint 28 * @param productMaster 29 * @return 30 * @throws Throwable 31 */ 32 @Around("@annotation(productMaster)") 33 public Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, ProductMaster productMaster) throws Throwable { 34 try { 35 logger.info("set database connection to product-master only"); 36 DbContextHolder.setDbType(DbContextHolder.DbType.PRODUCT_MASTER); 37 Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); 38 return result; 39 } finally { 40 DbContextHolder.clearDbType(); 41 logger.info("restore database connection"); 42 } 43 } 44 45 46 /** 47 * 切换到product从库 48 * 49 * @param proceedingJoinPoint 50 * @param productSlave 51 * @return 52 * @throws Throwable 53 */ 54 @Around("@annotation(productSlave)") 55 public Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, ProductSlave productSlave) throws Throwable { 56 try { 57 logger.info("set database connection to product-slave only"); 58 DbContextHolder.setDbType(DbContextHolder.DbType.PRODUCT_SLAVE); 59 Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); 60 return result; 61 } finally { 62 DbContextHolder.clearDbType(); 63 logger.info("restore database connection"); 64 } 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * 切换到study主库 69 * 70 * @param proceedingJoinPoint 71 * @param studyMaster 72 * @return 73 * @throws Throwable 74 */ 75 @Around("@annotation(studyMaster)") 76 public Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, StudyMaster studyMaster) throws Throwable { 77 try { 78 logger.info("set database connection to study-master only"); 79 DbContextHolder.setDbType(DbContextHolder.DbType.STUDY_MASTER); 80 Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); 81 return result; 82 } finally { 83 DbContextHolder.clearDbType(); 84 logger.info("restore database connection"); 85 } 86 } 87 88 /** 89 * 切换到study从库 90 * 91 * @param proceedingJoinPoint 92 * @param studySlave 93 * @return 94 * @throws Throwable 95 */ 96 @Around("@annotation(studySlave)") 97 public Object proceed(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint, StudySlave studySlave) throws Throwable { 98 try { 99 logger.info("set database connection to study-slave only"); 100 DbContextHolder.setDbType(DbContextHolder.DbType.STUDY_SLAVE); 101 Object result = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed(); 102 return result; 103 } finally { 104 DbContextHolder.clearDbType(); 105 logger.info("restore database connection"); 106 } 107 } 108 109 @Override 110 public int getOrder() { 111 return 0; 112 } 113 }
5、其它事项
启用类上,一定要排除spring-boot自带的datasource配置,即:

1 @SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}) 2 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy 3 @ComponentScan("com.cnblogs.yjmyzz") 4 @MapperScan(basePackages = "com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.dao.mapper") 5 public class ServiceProvider { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 SpringApplication.run(ServiceProvider.class, args); 8 } 9 }
第1行:@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
6、日志中如何输出格式化且带参数值的sql?
一般的sql输出是这样的:

我们可以把它变成下面这样:
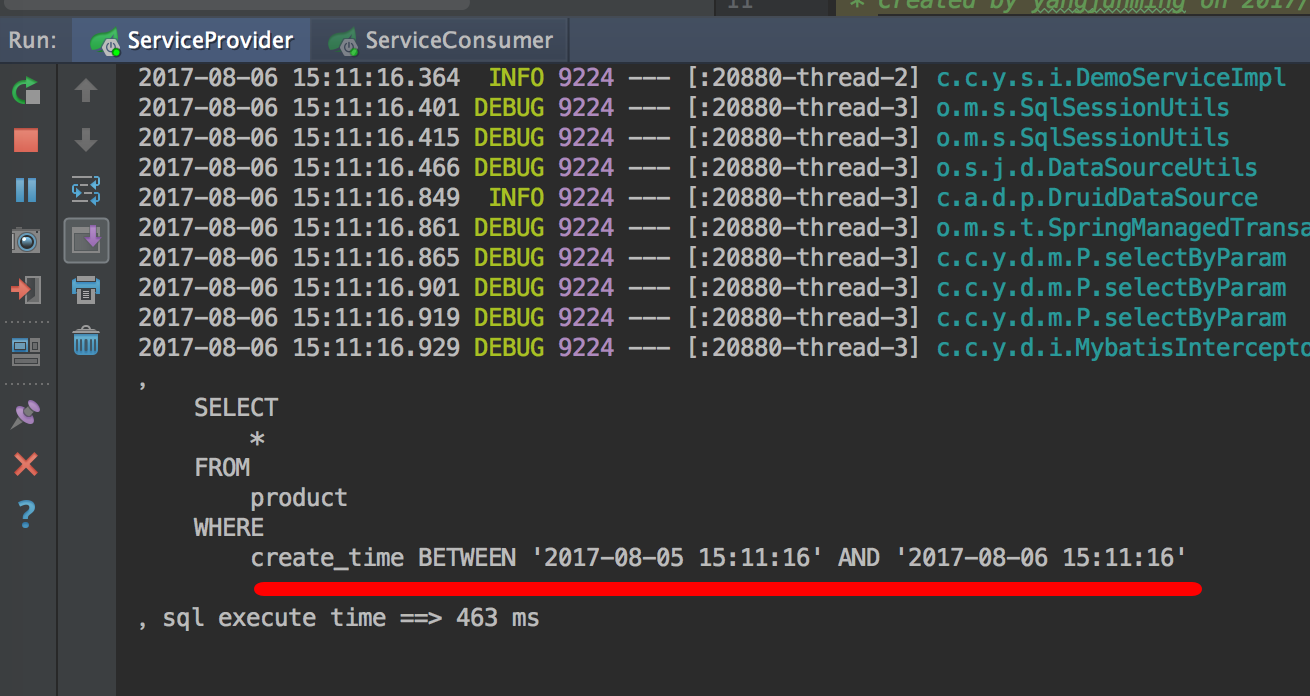
是不是更友好!
方法:加一个mybtais的拦截器即可
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 | package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.interceptor;import com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.util.PrettySQLFormatter;import org.apache.ibatis.cache.CacheKey;import org.apache.ibatis.executor.Executor;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.BoundSql;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.MappedStatement;import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.ParameterMapping;import org.apache.ibatis.plugin.*;import org.apache.ibatis.reflection.MetaObject;import org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration;import org.apache.ibatis.session.ResultHandler;import org.apache.ibatis.session.RowBounds;import org.apache.ibatis.type.TypeHandlerRegistry;import org.slf4j.Logger;import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;import java.util.Date;import java.util.List;import java.util.Properties;/** * Created by 菩提树下的杨过(http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com/) on 28/07/2017. */@Intercepts({ @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "update", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class}), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class}), @Signature(type = Executor.class, method = "query", args = {MappedStatement.class, Object.class, RowBounds.class, ResultHandler.class, CacheKey.class, BoundSql.class})})public class MybatisInterceptor implements Interceptor { private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MybatisInterceptor.class); private Properties properties; private final static SimpleDateFormat sdt = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss"); @Override public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable { MappedStatement mappedStatement = (MappedStatement) invocation.getArgs()[0]; Object parameter = null; if (invocation.getArgs().length > 1) { parameter = invocation.getArgs()[1]; } String sqlId = mappedStatement.getId(); BoundSql boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameter); Configuration configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration(); Object returnValue; long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); returnValue = invocation.proceed(); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); long time = (end - start); if (time > 1) { String sql = getSql(configuration, boundSql, sqlId, time); logger.debug("mapper method ==> " + sql.split("\\^")[0] + "\n," + PrettySQLFormatter.getPrettySql(sql.split("\\^")[1]) + "\n\n," + "sql execute time ==> " + time + " ms\n\n"); } return returnValue; } @Override public Object plugin(Object target) { return Plugin.wrap(target, this); } @Override public void setProperties(Properties properties) { this.properties = properties; } public static String getSql(Configuration configuration, BoundSql boundSql, String sqlId, long time) { String sql = showSql(configuration, boundSql); StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder(100); str.append(sqlId); str.append("^"); str.append(sql); str.append("^"); str.append(time); str.append("ms"); return str.toString(); } private static String getParameterValue(Object obj) { String value; if (obj instanceof String) { value = "'" + obj.toString() + "'"; } else if (obj instanceof Date) { value = "'" + sdt.format(obj) + "'"; } else { if (obj != null) { value = obj.toString(); } else { value = ""; } } return value; } public static String showSql(Configuration configuration, BoundSql boundSql) { Object parameterObject = boundSql.getParameterObject(); List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings(); String sql = boundSql.getSql().replaceAll("[\\s]+", " "); if (parameterMappings.size() > 0 && parameterObject != null) { TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry(); if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) { sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(parameterObject)); } else { MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject); for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) { String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty(); if (metaObject.hasGetter(propertyName)) { Object obj = metaObject.getValue(propertyName); sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj)); } else if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) { Object obj = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName); sql = sql.replaceFirst("\\?", getParameterValue(obj)); } } } } return sql; }} |
这里面还用了hibernate的一个小工具,用于格式化sql
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | package com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.util;import org.hibernate.engine.jdbc.internal.FormatStyle;public class PrettySQLFormatter { public static void print(String sql) { System.out.println(FormatStyle.BASIC.getFormatter().format(sql)); } public static void print(String remark, String sql) { System.out.println(remark + FormatStyle.BASIC.getFormatter().format(sql)); } public static String getPrettySql(String sql) { return FormatStyle.BASIC.getFormatter().format(sql); } public static String getPrettySql(String remark, String sql) { return remark + FormatStyle.BASIC.getFormatter().format(sql); } public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(getPrettySql("select * from MyUser as A join MyFriend as B on A.id = B.pid where B.name like ? ")); }} |
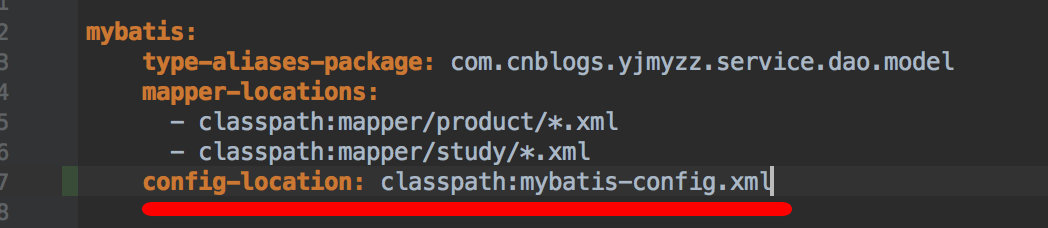
接下来,把这个拦截器配置在mybatis-config.xml里

1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" 3 "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> 4 <configuration> 5 <settings> 6 <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> 7 </settings> 8 9 <plugins> 10 <plugin interceptor="com.cnblogs.yjmyzz.db.interceptor.MybatisInterceptor"> 11 </plugin> 12 </plugins> 13 14 </configuration>
最后在application.yml里指定mybatis-config.xml所在的路径:
示例源码见:https://github.com/yjmyzz/spring-boot-dubbo-demo (dubbox2.8.5-multi-ds分支)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号