【Spring】每个程序员都使用Spring(四)——Aop+自定义注解做日志拦截
一、前言
上一篇博客向大家介绍了Aop的概念,对切面=切点+通知 、连接点、织入、目标对象、代理(jdk动态代理和CGLIB代理)有所了解了。理论很强,实用就在这篇博客介绍。
这篇博客中,小编向大家介绍springAop很常见的使用方式——日志拦截
二、实战
2.1 全局观说明
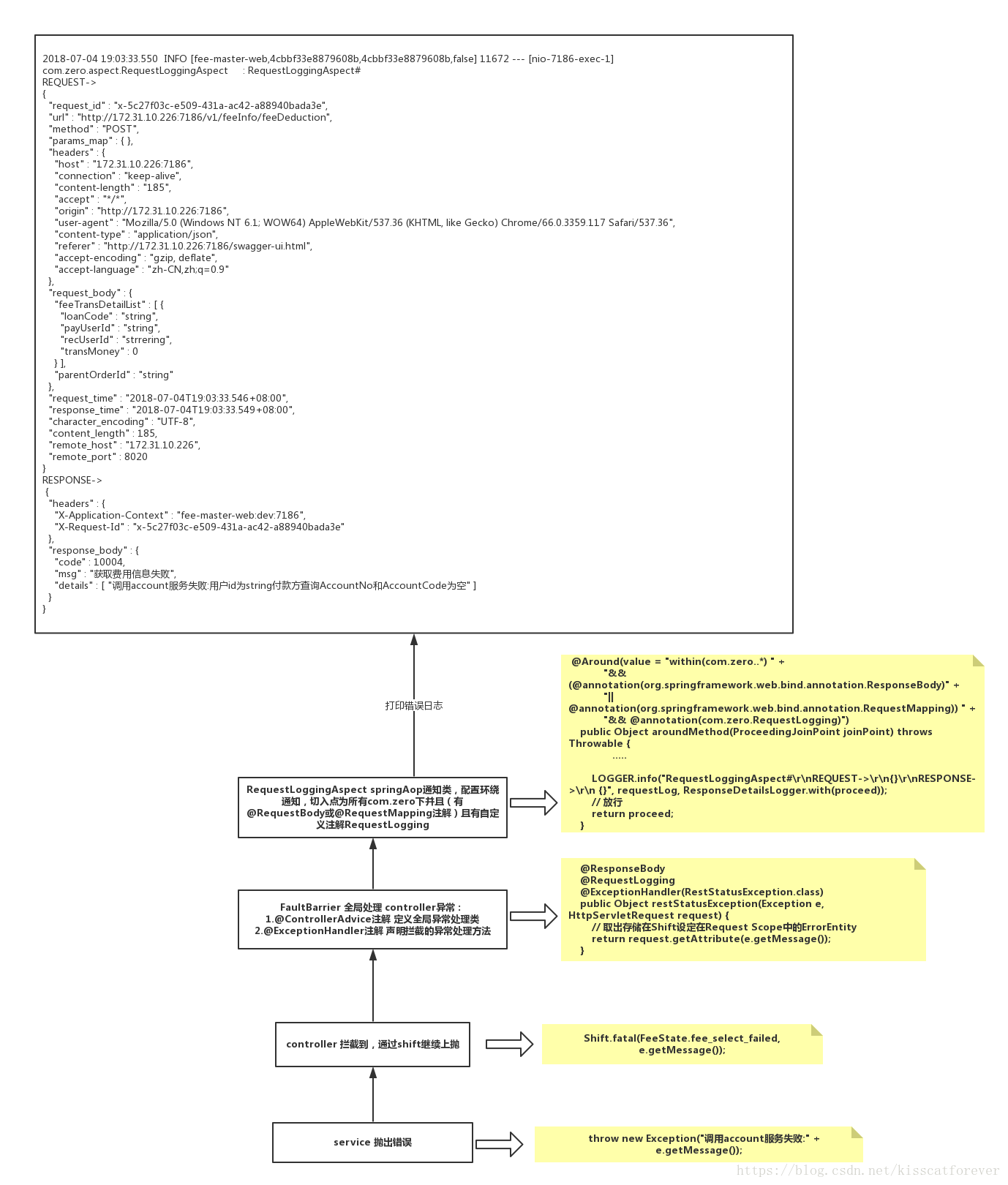
说明:
假如service出错了,这样错误会抛出到controller,controller捕捉到后,抛出自定义异常。然后@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler 全局处理 Controller 层异常,捕获controller抛出的异常。在这个方法中为AOP的连接点,会触发AOP的通知方法。通知方法捕获request和response,打印出详细的错误日志信息。
2.2 建立springboot项目 引入相关依赖
主要添加springmvc和springaop的依赖。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.wl</groupId>
<artifactId>sbDemo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>sbDemo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.10.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--aop-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--springmvc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>21.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--swagger2-->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.0.7.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2.3 建立 切面类
使用@Aspect 和 @Component两个注解,表示是切面类,并且可以被spring管理。
在切面中,添加环绕通知,切点是 com.wl.sbDemo包路径下的 且带有ResponseBody或RequestMapping注解的 且带有RequestLogging自定义注解的。
当有同上满足这三个条件的连接点触发的时候,就会触发环绕通知的方法。这个环绕通知的方法主要就是拦截request和response的信息,打印日志。
package com.wl.sbDemo.aspect;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.config.RequestAttributeConst;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.web.RequestDetailsLogger;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.web.ResponseDetailsLogger;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.web.ServletContextHolder;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.time.OffsetDateTime;
/**
* 本类设计为当有被@RequestBodyLogs修饰的@ControllerAdvice或者@Controller抛出异常时记录输入输出,
* 其他情况仅记录被标记的@RequestMapping或@ResponseBody方法
*
* @author soul
* @see //RequestLogging
* @see org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class RequestLoggingAspect {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RequestLoggingAspect.class);
@Around(value = "within(com.wl.sbDemo..*) " +
"&& (@annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody)" +
"|| @annotation(org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping)) " +
"&& @annotation(com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.RequestLogging)")
public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 生成请求日志
RequestDetailsLogger requestLog = generateJsonRequestDetails();
// 获取Swagger上的API描述
injectApiOperationDescription(joinPoint, requestLog);
// 执行真实请求
final Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
// 当响应完成时, 打印完整的'request & response'信息
requestLog.setResponseTime(OffsetDateTime.now());
LOGGER.info("RequestLoggingAspect#\r\nREQUEST->\r\n{}\r\nRESPONSE->\r\n {}", requestLog, ResponseDetailsLogger.with(proceed));
// 放行
return proceed;
}
/**
* 创建通用的日志输出模式并绑定线程
*
* @return 日志模型
*/
private RequestDetailsLogger generateJsonRequestDetails() {
RequestDetailsLogger logDetails = (RequestDetailsLogger) ServletContextHolder.getRequest().getAttribute(RequestAttributeConst.DETAILS_KEY);
if (logDetails == null) {
logDetails = new RequestDetailsLogger();
ServletContextHolder.getRequest().setAttribute(RequestAttributeConst.DETAILS_KEY, logDetails);
}
return logDetails;
}
private void injectApiOperationDescription(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RequestDetailsLogger logDetails) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
final ApiOperation operate = method.getAnnotation(ApiOperation.class);
if (operate != null) {
logDetails.setApiDesc(operate.value());
}
}
}
自定义注解:
定义了自定义注解,用于标记连接点。标记出是切点。
@Retention– 定义该注解的生命周期,RUNTIME : 始终不会丢弃,运行期也保留该注解,因此可以使用反射机制读取该注解的信息。
@Target – 表示该注解用于什么地方,METHOD:用于描述方法。
package com.wl.sbDemo.aspect;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author soul
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface RequestLogging {
}
2.4 Controller
就是一个普遍的controller类,这里小编用于抛出异常,抛出指定的自定义异常。
package com.wl.sbDemo.controller;
import com.wl.sbDemo.common.StatusCode;
import com.wl.sbDemo.exception.Shift;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by Ares on 2018/7/5.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/findById")
public int findById(@RequestParam("id") int id ){
try {
if (id>10){
id = id /0;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Shift.fatal(StatusCode.INVALID_MODEL_FIELDS,e.getMessage());
}
return id;
}
}
Shift抛出异常类:
package com.wl.sbDemo.exception;
import com.wl.sbDemo.common.RestStatus;
import com.wl.sbDemo.model.ErrorEntity;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestAttributes;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import java.util.Optional;
import static com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkNotNull;
/**
* @author soul
*/
public final class Shift {
private Shift() {
}
/**
* 抛出具体的{@code RestStatus}异常
*
* @param status 自定义异常实体
* @param details 额外添加至details字段中的任意实体, 最终会被解析成JSON
*/
public static void fatal(RestStatus status, Object... details) {
checkNotNull(status);
final ErrorEntity entity = new ErrorEntity(status);
// inject details
if (details.length > 0) {
Optional.of(details).ifPresent(entity::setDetails);
}
// put it into request, details entity by Rest Status's name
String errorCode = String.valueOf(status.code());
bindStatusCodesInRequestScope(errorCode, entity);
throw new RestStatusException(errorCode);
}
private static void bindStatusCodesInRequestScope(String key, ErrorEntity entity) {
checkNotNull(entity);
checkNotNull(key);
final RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (requestAttributes != null) {
((ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttributes).getRequest().setAttribute(key, entity);
}
}
}自定义异常RestStatusException:
package com.wl.sbDemo.exception;
/**
* @author soul
*/
public class RestStatusException extends RuntimeException {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8541311111016065562L;
public RestStatusException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public RestStatusException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
public RestStatusException(Throwable cause) {
super(cause);
}
protected RestStatusException(String message, Throwable cause, boolean enableSuppression, boolean writableStackTrace) {
super(message, cause, enableSuppression, writableStackTrace);
}
}
2.5 Controller的全局异常拦截类
使用了@ControllerAdvice + @ExceptionHandler 全局处理 Controller 层异常。
@ControllerAdvice : 定义全局异常处理类
@ExceptionHandler : 声明拦截指定异常的方法
以本例中的restStatusException方法来说,开头添加了@ResponseBody和@RequestLogging注解,并且这个方法也在com.wl.sbDemo包下,符合Springaop的连接点的条件。所以当这个方法触发的时候就会触发切面类中的通知方法。
package com.wl.sbDemo.controller.advice;
import com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.RequestLogging;
import com.wl.sbDemo.aspect.config.RequestAttributeConst;
import com.wl.sbDemo.common.RestStatus;
import com.wl.sbDemo.common.StatusCode;
import com.wl.sbDemo.exception.IllegalValidateException;
import com.wl.sbDemo.exception.ReservationExpireException;
import com.wl.sbDemo.exception.RestStatusException;
import com.wl.sbDemo.model.ErrorEntity;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.dao.DuplicateKeyException;
import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageNotReadableException;
import org.springframework.web.HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.method.annotation.MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* @author soul
*/
@ControllerAdvice
public class FaultBarrier {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(FaultBarrier.class);
private static final ImmutableMap<Class<? extends Throwable>, RestStatus> EXCEPTION_MAPPINGS;
static {
final ImmutableMap.Builder<Class<? extends Throwable>, RestStatus> builder = ImmutableMap.builder();
// HTTP Request Method不存在
// 账户更新错误
builder.put(ReservationExpireException.class, StatusCode.RESERVATION_EXPIRE);
// 其他未被发现的异常
// SpringMVC中参数类型转换异常,常见于String找不到对应的ENUM而抛出的异常
builder.put(MethodArgumentTypeMismatchException.class, StatusCode.INVALID_PARAMS_CONVERSION);
builder.put(UnsatisfiedServletRequestParameterException.class, StatusCode.INVALID_PARAMS_CONVERSION);
builder.put(IllegalValidateException.class, StatusCode.INVALID_PARAMS_CONVERSION);
builder.put(IllegalArgumentException.class, StatusCode.INVALID_PARAMS_CONVERSION);
// HTTP Request Method不存在
builder.put(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException.class, StatusCode.REQUEST_METHOD_NOT_SUPPORTED);
// 要求有RequestBody的地方却传入了NULL
builder.put(HttpMessageNotReadableException.class, StatusCode.HTTP_MESSAGE_NOT_READABLE);
// 通常是操作过快导致DuplicateKey
builder.put(DuplicateKeyException.class, StatusCode.DUPLICATE_KEY);
// 其他未被发现的异常
builder.put(Exception.class, StatusCode.SERVER_UNKNOWN_ERROR);
EXCEPTION_MAPPINGS = builder.build();
}
/**
* <strong>Request域取出对应错误信息</strong>, 封装成实体ErrorEntity后转换成JSON输出
*
* @param e {@code StatusCode}异常
* @param request HttpServletRequest
* @return ErrorEntity
* @see ErrorEntity
* @see StatusCode
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestLogging
@ExceptionHandler(RestStatusException.class)
public Object restStatusException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {
// 取出存储在Shift设定在Request Scope中的ErrorEntity
return request.getAttribute(e.getMessage());
}
/**
* <strong>Request域取出对应错误信息</strong>, 封装成实体ErrorEntity后转换成JSON输出
*
* @param e {@code IllegalValidateException}异常
* @param request HttpServletRequest
* @return ErrorEntity
* @see ErrorEntity
*/
@ResponseBody
@RequestLogging
@ExceptionHandler(IllegalValidateException.class)
public Object illegalValidateException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {
LOGGER.error("request id: {}\r\nexception: {}", request.getAttribute(RequestAttributeConst.REQUEST_ID), e.getMessage());
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 取出存储在Request域中的Map
return request.getAttribute(e.getMessage());
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestLogging
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ErrorEntity exception(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request) {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
LOGGER.error("request id: {}\r\nexception: {}", request.getAttribute(RequestAttributeConst.REQUEST_ID), e.getMessage());
final RestStatus status = EXCEPTION_MAPPINGS.get(e.getClass());
final ErrorEntity error;
if (status != null) {
error = new ErrorEntity(status);
}
else {
error = new ErrorEntity(StatusCode.SERVER_UNKNOWN_ERROR);
}
return error;
}
}
2.6 运行
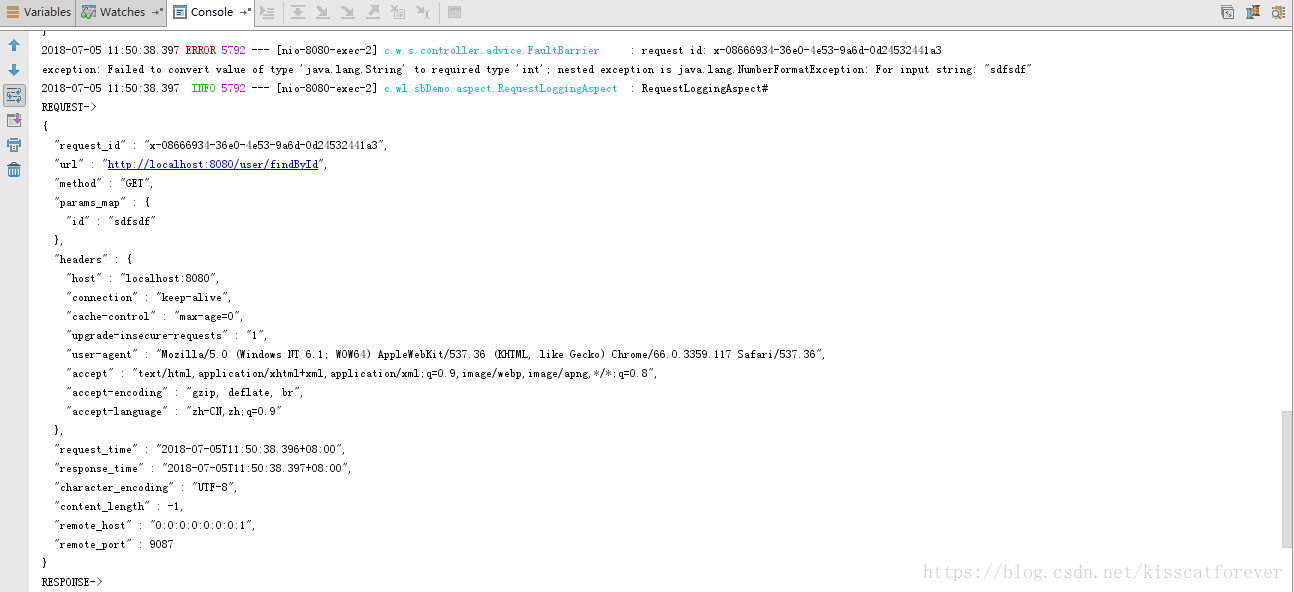
运行代码后,输入http://localhost:8080/user/findById?id=sdfsdf,因为id接收的是int,所以传入字符串是肯定报错的。在看我们的打印的日志:
将详细信息完美的打印出来,如果有ES日志收集,更加方便我们查看。
三、小结
这个实战,主要用到了springaop,把日志很好的拦截下来,使用也很方便。同上也用到了自定义注解,指明了在方法使用。还用到了springmvc的全局异常处理类注解@ControllerAdvice 和@ExceptionHandler 更加准确的捕捉问题。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/kisscatforever/article/details/80921561


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号