Clang AST到IR的转换
前
边介绍了几节Clang AST,包括AST的读取,Rewriter,AST的插入等,这里想从AST到IR的转换,介绍一点Clang源码的内容。
前边已经提到了想打印AST树内容的话,需要使用clang -fsyntax-only -Xclang -ast-dump 命令来进行。对于llvm各种文件格式的转换,有一个图说的比较清楚,内容来源见水印。
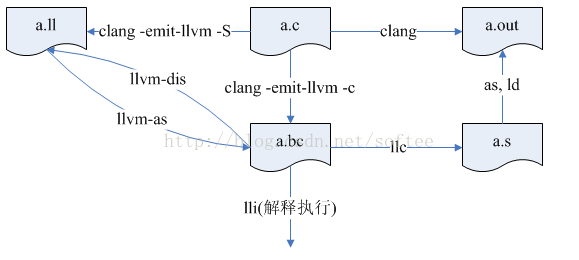
我们使用的源码还是以上次使用的view.cpp

1 int foo(int a, int b, int *c) { 2 int ret = 0; 3 if (a > b) { 4 ret = a; 5 } else { 6 ret = b; 7 } 8 for (int temp = 0; temp < 100; ++temp) { 9 *c = (*c + temp); 10 } 11 return ret; 12 } 13 14 15 int main() { 16 int a = 1, b = 2; 17 int c = 0; 18 int d = foo(a, b, &c); 19 return 0; 20 }
打印出来的view.ll文件如下:
; ModuleID = 'view.cpp'
source_filename = "view.cpp"
target datalayout = "e-m:e-p270:32:32-p271:32:32-p272:64:64-i64:64-f80:128-n8:16:32:64-S128"
target triple = "x86_64-unknown-linux-gnu"
; Function Attrs: noinline nounwind optnone uwtable mustprogress
define dso_local i32 @_Z3fooiiPi(i32 %0, i32 %1, i32* %2) #0 {
%4 = alloca i32, align 4
%5 = alloca i32, align 4
%6 = alloca i32*, align 8
%7 = alloca i32, align 4
%8 = alloca i32, align 4
store i32 %0, i32* %4, align 4
store i32 %1, i32* %5, align 4
store i32* %2, i32** %6, align 8
store i32 0, i32* %7, align 4
%9 = load i32, i32* %4, align 4
%10 = load i32, i32* %5, align 4
%11 = icmp sgt i32 %9, %10
br i1 %11, label %12, label %14
12: ; preds = %3
%13 = load i32, i32* %4, align 4
store i32 %13, i32* %7, align 4
br label %16
14: ; preds = %3
%15 = load i32, i32* %5, align 4
store i32 %15, i32* %7, align 4
br label %16
16: ; preds = %14, %12
store i32 0, i32* %8, align 4
br label %17
17: ; preds = %26, %16
%18 = load i32, i32* %8, align 4
%19 = icmp slt i32 %18, 100
br i1 %19, label %20, label %29
20: ; preds = %17
%21 = load i32*, i32** %6, align 8
%22 = load i32, i32* %21, align 4
%23 = load i32, i32* %8, align 4
%24 = add nsw i32 %22, %23
%25 = load i32*, i32** %6, align 8
store i32 %24, i32* %25, align 4
br label %26
26: ; preds = %20
%27 = load i32, i32* %8, align 4
%28 = add nsw i32 %27, 1
store i32 %28, i32* %8, align 4
br label %17, !llvm.loop !2
29: ; preds = %17
%30 = load i32, i32* %7, align 4
ret i32 %30
}
; Function Attrs: noinline norecurse nounwind optnone uwtable mustprogress
define dso_local i32 @main() #1 {
%1 = alloca i32, align 4
%2 = alloca i32, align 4
%3 = alloca i32, align 4
%4 = alloca i32, align 4
%5 = alloca i32, align 4
store i32 0, i32* %1, align 4
store i32 1, i32* %2, align 4
store i32 2, i32* %3, align 4
store i32 0, i32* %4, align 4
%6 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4
%7 = load i32, i32* %3, align 4
%8 = call i32 @_Z3fooiiPi(i32 %6, i32 %7, i32* %4)
store i32 %8, i32* %5, align 4
ret i32 0
}
; Function Attrs: noinline norecurse nounwind optnone uwtable mustprogress
define dso_local i32 @main() #1 {
%1 = alloca i32, align 4
%2 = alloca i32, align 4
%3 = alloca i32, align 4
%4 = alloca i32, align 4
%5 = alloca i32, align 4
store i32 0, i32* %1, align 4
store i32 1, i32* %2, align 4
store i32 2, i32* %3, align 4
store i32 0, i32* %4, align 4
%6 = load i32, i32* %2, align 4
%7 = load i32, i32* %3, align 4
%8 = call i32 @_Z3fooiiPi(i32 %6, i32 %7, i32* %4)
store i32 %8, i32* %5, align 4
ret i32 0
}
attributes #0 = { noinline nounwind optnone uwtable mustprogress "frame-pointer"="all" "no-trapping-math"="true" "stack-protector-buffer-size"="8" "target-cpu"="x86-64" "target-features"="+cx8,+fxsr,+mmx,+sse,+sse2,+x87" "tune-cpu"="generic" }
attributes #1 = { noinline norecurse nounwind optnone uwtable mustprogress "frame-pointer"="all" "no-trapping-math"="true" "stack-protector-buffer-size"="8" "target-cpu"="x86-64" "target-features"="+cx8,+fxsr,+mmx,+sse,+sse2,+x87" "tune-cpu"="generic" }
!llvm.module.flags = !{!0}
!llvm.ident = !{!1}
!0 = !{i32 1, !"wchar_size", i32 4}
!1 = !{!"clang version 13.0.0"}
!2 = distinct !{!2, !3}
!3 = !{!"llvm.loop.mustprogress"}
对于如何生成llvm的IR(其实是以bc文件格式存在,这里为了human read),主要通过namespace clang::CodeGen来记性,在llvm/lib/CodeGen目录下有很多以CG开头的文件,负责各种类型的AST节点的CodeGen工作,这里我仅以ForStmt这个节点来进行介绍。
从Clang 的Doxgen图上来看,ForStmt继承至Stmt(https://clang.llvm.org/doxygen/classclang_1_1ForStmt.html)
很多AST节点类型都继承至Stmt,因此,不看代码,从设计的调度来看,应该是一个switch case的结构,通过判断节点的类型来分别进入到每个AST节点进行CodeGen。
定位到clang/lib/CodeGen/CGStmt.cpp中,第二个函数就看到了

1 void CodeGenFunction::EmitStmt(const Stmt *S, ArrayRef<const Attr *> Attrs) { 2 assert(S && "Null statement?"); 3 llvm::errs()<<"EmitStmt\n"; 4 PGO.setCurrentStmt(S); 5 6 // These statements have their own debug info handling. 7 if (EmitSimpleStmt(S, Attrs)) 8 return; 9 10 // Check if we are generating unreachable code. 11 if (!HaveInsertPoint()) { 12 // If so, and the statement doesn't contain a label, then we do not need to 13 // generate actual code. This is safe because (1) the current point is 14 // unreachable, so we don't need to execute the code, and (2) we've already 15 // handled the statements which update internal data structures (like the 16 // local variable map) which could be used by subsequent statements. 17 if (!ContainsLabel(S)) { 18 // Verify that any decl statements were handled as simple, they may be in 19 // scope of subsequent reachable statements. 20 assert(!isa<DeclStmt>(*S) && "Unexpected DeclStmt!"); 21 return; 22 } 23 24 // Otherwise, make a new block to hold the code. 25 EnsureInsertPoint(); 26 } 27 llvm::errs()<<"EmitStmt Emit\n"; 28 // Generate a stoppoint if we are emitting debug info. 29 EmitStopPoint(S); 30 31 // Ignore all OpenMP directives except for simd if OpenMP with Simd is 32 // enabled. 33 if (getLangOpts().OpenMP && getLangOpts().OpenMPSimd) { 34 if (const auto *D = dyn_cast<OMPExecutableDirective>(S)) { 35 EmitSimpleOMPExecutableDirective(*D); 36 return; 37 } 38 } 39 40 switch (S->getStmtClass()) { 41 case Stmt::NoStmtClass: 42 case Stmt::CXXCatchStmtClass: 43 case Stmt::SEHExceptStmtClass: 44 case Stmt::SEHFinallyStmtClass: 45 case Stmt::MSDependentExistsStmtClass: 46 llvm_unreachable("invalid statement class to emit generically"); 47 case Stmt::NullStmtClass: 48 case Stmt::CompoundStmtClass: 49 case Stmt::DeclStmtClass: 50 case Stmt::LabelStmtClass: 51 case Stmt::AttributedStmtClass: 52 case Stmt::GotoStmtClass: 53 case Stmt::BreakStmtClass: 54 case Stmt::ContinueStmtClass: 55 case Stmt::DefaultStmtClass: 56 case Stmt::CaseStmtClass: 57 case Stmt::SEHLeaveStmtClass: 58 llvm_unreachable("should have emitted these statements as simple"); 59 60 #define STMT(Type, Base) 61 #define ABSTRACT_STMT(Op) 62 #define EXPR(Type, Base) \ 63 case Stmt::Type##Class: 64 #include "clang/AST/StmtNodes.inc" 65 { 66 // Remember the block we came in on. 67 llvm::BasicBlock *incoming = Builder.GetInsertBlock(); 68 assert(incoming && "expression emission must have an insertion point"); 69 70 EmitIgnoredExpr(cast<Expr>(S)); 71 72 llvm::BasicBlock *outgoing = Builder.GetInsertBlock(); 73 assert(outgoing && "expression emission cleared block!"); 74 75 // The expression emitters assume (reasonably!) that the insertion 76 // point is always set. To maintain that, the call-emission code 77 // for noreturn functions has to enter a new block with no 78 // predecessors. We want to kill that block and mark the current 79 // insertion point unreachable in the common case of a call like 80 // "exit();". Since expression emission doesn't otherwise create 81 // blocks with no predecessors, we can just test for that. 82 // However, we must be careful not to do this to our incoming 83 // block, because *statement* emission does sometimes create 84 // reachable blocks which will have no predecessors until later in 85 // the function. This occurs with, e.g., labels that are not 86 // reachable by fallthrough. 87 if (incoming != outgoing && outgoing->use_empty()) { 88 outgoing->eraseFromParent(); 89 Builder.ClearInsertionPoint(); 90 } 91 break; 92 } 93 94 case Stmt::IndirectGotoStmtClass: 95 EmitIndirectGotoStmt(cast<IndirectGotoStmt>(*S)); break; 96 97 case Stmt::IfStmtClass: EmitIfStmt(cast<IfStmt>(*S)); break; 98 case Stmt::WhileStmtClass: EmitWhileStmt(cast<WhileStmt>(*S), Attrs); break; 99 case Stmt::DoStmtClass: EmitDoStmt(cast<DoStmt>(*S), Attrs); break; 100 case Stmt::ForStmtClass: llvm::errs()<<"EmitForStmt\n"; EmitForStmt(cast<ForStmt>(*S), Attrs); break; 101 102 case Stmt::ReturnStmtClass: EmitReturnStmt(cast<ReturnStmt>(*S)); break; 103 104 case Stmt::SwitchStmtClass: EmitSwitchStmt(cast<SwitchStmt>(*S)); break; 105 case Stmt::GCCAsmStmtClass: // Intentional fall-through. 106 case Stmt::MSAsmStmtClass: EmitAsmStmt(cast<AsmStmt>(*S)); break; 107 case Stmt::CoroutineBodyStmtClass: 108 EmitCoroutineBody(cast<CoroutineBodyStmt>(*S)); 109 break; 110 case Stmt::CoreturnStmtClass: 111 EmitCoreturnStmt(cast<CoreturnStmt>(*S)); 112 break; 113 case Stmt::CapturedStmtClass: { 114 const CapturedStmt *CS = cast<CapturedStmt>(S); 115 EmitCapturedStmt(*CS, CS->getCapturedRegionKind()); 116 } 117 break; 118 case Stmt::ObjCAtTryStmtClass: 119 EmitObjCAtTryStmt(cast<ObjCAtTryStmt>(*S)); 120 break; 121 case Stmt::ObjCAtCatchStmtClass: 122 llvm_unreachable( 123 "@catch statements should be handled by EmitObjCAtTryStmt"); 124 case Stmt::ObjCAtFinallyStmtClass: 125 llvm_unreachable( 126 "@finally statements should be handled by EmitObjCAtTryStmt"); 127 case Stmt::ObjCAtThrowStmtClass: 128 EmitObjCAtThrowStmt(cast<ObjCAtThrowStmt>(*S)); 129 break; 130 case Stmt::ObjCAtSynchronizedStmtClass: 131 EmitObjCAtSynchronizedStmt(cast<ObjCAtSynchronizedStmt>(*S)); 132 break; 133 case Stmt::ObjCForCollectionStmtClass: 134 EmitObjCForCollectionStmt(cast<ObjCForCollectionStmt>(*S)); 135 break; 136 case Stmt::ObjCAutoreleasePoolStmtClass: 137 EmitObjCAutoreleasePoolStmt(cast<ObjCAutoreleasePoolStmt>(*S)); 138 break; 139 140 case Stmt::CXXTryStmtClass: 141 EmitCXXTryStmt(cast<CXXTryStmt>(*S)); 142 break; 143 case Stmt::CXXForRangeStmtClass: 144 EmitCXXForRangeStmt(cast<CXXForRangeStmt>(*S), Attrs); 145 break; 146 case Stmt::SEHTryStmtClass: 147 EmitSEHTryStmt(cast<SEHTryStmt>(*S)); 148 break; 149 case Stmt::OMPCanonicalLoopClass: 150 EmitOMPCanonicalLoop(cast<OMPCanonicalLoop>(S)); 151 break; 152 case Stmt::OMPParallelDirectiveClass: 153 EmitOMPParallelDirective(cast<OMPParallelDirective>(*S)); 154 break; 155 case Stmt::OMPSimdDirectiveClass: 156 EmitOMPSimdDirective(cast<OMPSimdDirective>(*S)); 157 break; 158 case Stmt::OMPTileDirectiveClass: 159 EmitOMPTileDirective(cast<OMPTileDirective>(*S)); 160 break; 161 case Stmt::OMPForDirectiveClass: 162 EmitOMPForDirective(cast<OMPForDirective>(*S)); 163 break; 164 case Stmt::OMPForSimdDirectiveClass: 165 EmitOMPForSimdDirective(cast<OMPForSimdDirective>(*S)); 166 break; 167 case Stmt::OMPSectionsDirectiveClass: 168 EmitOMPSectionsDirective(cast<OMPSectionsDirective>(*S)); 169 break; 170 case Stmt::OMPSectionDirectiveClass: 171 EmitOMPSectionDirective(cast<OMPSectionDirective>(*S)); 172 break; 173 case Stmt::OMPSingleDirectiveClass: 174 EmitOMPSingleDirective(cast<OMPSingleDirective>(*S)); 175 break; 176 case Stmt::OMPMasterDirectiveClass: 177 EmitOMPMasterDirective(cast<OMPMasterDirective>(*S)); 178 break; 179 case Stmt::OMPCriticalDirectiveClass: 180 EmitOMPCriticalDirective(cast<OMPCriticalDirective>(*S)); 181 break; 182 case Stmt::OMPParallelForDirectiveClass: 183 EmitOMPParallelForDirective(cast<OMPParallelForDirective>(*S)); 184 break; 185 case Stmt::OMPParallelForSimdDirectiveClass: 186 EmitOMPParallelForSimdDirective(cast<OMPParallelForSimdDirective>(*S)); 187 break; 188 case Stmt::OMPParallelMasterDirectiveClass: 189 EmitOMPParallelMasterDirective(cast<OMPParallelMasterDirective>(*S)); 190 break; 191 case Stmt::OMPParallelSectionsDirectiveClass: 192 EmitOMPParallelSectionsDirective(cast<OMPParallelSectionsDirective>(*S)); 193 break; 194 case Stmt::OMPTaskDirectiveClass: 195 EmitOMPTaskDirective(cast<OMPTaskDirective>(*S)); 196 break; 197 case Stmt::OMPTaskyieldDirectiveClass: 198 EmitOMPTaskyieldDirective(cast<OMPTaskyieldDirective>(*S)); 199 break; 200 case Stmt::OMPBarrierDirectiveClass: 201 EmitOMPBarrierDirective(cast<OMPBarrierDirective>(*S)); 202 break; 203 case Stmt::OMPTaskwaitDirectiveClass: 204 EmitOMPTaskwaitDirective(cast<OMPTaskwaitDirective>(*S)); 205 break; 206 case Stmt::OMPTaskgroupDirectiveClass: 207 EmitOMPTaskgroupDirective(cast<OMPTaskgroupDirective>(*S)); 208 break; 209 case Stmt::OMPFlushDirectiveClass: 210 EmitOMPFlushDirective(cast<OMPFlushDirective>(*S)); 211 break; 212 case Stmt::OMPDepobjDirectiveClass: 213 EmitOMPDepobjDirective(cast<OMPDepobjDirective>(*S)); 214 break; 215 case Stmt::OMPScanDirectiveClass: 216 EmitOMPScanDirective(cast<OMPScanDirective>(*S)); 217 break; 218 case Stmt::OMPOrderedDirectiveClass: 219 EmitOMPOrderedDirective(cast<OMPOrderedDirective>(*S)); 220 break; 221 case Stmt::OMPAtomicDirectiveClass: 222 EmitOMPAtomicDirective(cast<OMPAtomicDirective>(*S)); 223 break; 224 case Stmt::OMPTargetDirectiveClass: 225 EmitOMPTargetDirective(cast<OMPTargetDirective>(*S)); 226 break; 227 case Stmt::OMPTeamsDirectiveClass: 228 EmitOMPTeamsDirective(cast<OMPTeamsDirective>(*S)); 229 break; 230 case Stmt::OMPCancellationPointDirectiveClass: 231 EmitOMPCancellationPointDirective(cast<OMPCancellationPointDirective>(*S)); 232 break; 233 case Stmt::OMPCancelDirectiveClass: 234 EmitOMPCancelDirective(cast<OMPCancelDirective>(*S)); 235 break; 236 case Stmt::OMPTargetDataDirectiveClass: 237 EmitOMPTargetDataDirective(cast<OMPTargetDataDirective>(*S)); 238 break; 239 case Stmt::OMPTargetEnterDataDirectiveClass: 240 EmitOMPTargetEnterDataDirective(cast<OMPTargetEnterDataDirective>(*S)); 241 break; 242 case Stmt::OMPTargetExitDataDirectiveClass: 243 EmitOMPTargetExitDataDirective(cast<OMPTargetExitDataDirective>(*S)); 244 break; 245 case Stmt::OMPTargetParallelDirectiveClass: 246 EmitOMPTargetParallelDirective(cast<OMPTargetParallelDirective>(*S)); 247 break; 248 case Stmt::OMPTargetParallelForDirectiveClass: 249 EmitOMPTargetParallelForDirective(cast<OMPTargetParallelForDirective>(*S)); 250 break; 251 case Stmt::OMPTaskLoopDirectiveClass: 252 EmitOMPTaskLoopDirective(cast<OMPTaskLoopDirective>(*S)); 253 break; 254 case Stmt::OMPTaskLoopSimdDirectiveClass: 255 EmitOMPTaskLoopSimdDirective(cast<OMPTaskLoopSimdDirective>(*S)); 256 break; 257 case Stmt::OMPMasterTaskLoopDirectiveClass: 258 EmitOMPMasterTaskLoopDirective(cast<OMPMasterTaskLoopDirective>(*S)); 259 break; 260 case Stmt::OMPMasterTaskLoopSimdDirectiveClass: 261 EmitOMPMasterTaskLoopSimdDirective( 262 cast<OMPMasterTaskLoopSimdDirective>(*S)); 263 break; 264 case Stmt::OMPParallelMasterTaskLoopDirectiveClass: 265 EmitOMPParallelMasterTaskLoopDirective( 266 cast<OMPParallelMasterTaskLoopDirective>(*S)); 267 break; 268 case Stmt::OMPParallelMasterTaskLoopSimdDirectiveClass: 269 EmitOMPParallelMasterTaskLoopSimdDirective( 270 cast<OMPParallelMasterTaskLoopSimdDirective>(*S)); 271 break; 272 case Stmt::OMPDistributeDirectiveClass: 273 EmitOMPDistributeDirective(cast<OMPDistributeDirective>(*S)); 274 break; 275 case Stmt::OMPTargetUpdateDirectiveClass: 276 EmitOMPTargetUpdateDirective(cast<OMPTargetUpdateDirective>(*S)); 277 break; 278 case Stmt::OMPDistributeParallelForDirectiveClass: 279 EmitOMPDistributeParallelForDirective( 280 cast<OMPDistributeParallelForDirective>(*S)); 281 break; 282 case Stmt::OMPDistributeParallelForSimdDirectiveClass: 283 EmitOMPDistributeParallelForSimdDirective( 284 cast<OMPDistributeParallelForSimdDirective>(*S)); 285 break; 286 case Stmt::OMPDistributeSimdDirectiveClass: 287 EmitOMPDistributeSimdDirective(cast<OMPDistributeSimdDirective>(*S)); 288 break; 289 case Stmt::OMPTargetParallelForSimdDirectiveClass: 290 EmitOMPTargetParallelForSimdDirective( 291 cast<OMPTargetParallelForSimdDirective>(*S)); 292 break; 293 case Stmt::OMPTargetSimdDirectiveClass: 294 EmitOMPTargetSimdDirective(cast<OMPTargetSimdDirective>(*S)); 295 break; 296 case Stmt::OMPTeamsDistributeDirectiveClass: 297 EmitOMPTeamsDistributeDirective(cast<OMPTeamsDistributeDirective>(*S)); 298 break; 299 case Stmt::OMPTeamsDistributeSimdDirectiveClass: 300 EmitOMPTeamsDistributeSimdDirective( 301 cast<OMPTeamsDistributeSimdDirective>(*S)); 302 break; 303 case Stmt::OMPTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirectiveClass: 304 EmitOMPTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirective( 305 cast<OMPTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirective>(*S)); 306 break; 307 case Stmt::OMPTeamsDistributeParallelForDirectiveClass: 308 EmitOMPTeamsDistributeParallelForDirective( 309 cast<OMPTeamsDistributeParallelForDirective>(*S)); 310 break; 311 case Stmt::OMPTargetTeamsDirectiveClass: 312 EmitOMPTargetTeamsDirective(cast<OMPTargetTeamsDirective>(*S)); 313 break; 314 case Stmt::OMPTargetTeamsDistributeDirectiveClass: 315 EmitOMPTargetTeamsDistributeDirective( 316 cast<OMPTargetTeamsDistributeDirective>(*S)); 317 break; 318 case Stmt::OMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForDirectiveClass: 319 EmitOMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForDirective( 320 cast<OMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForDirective>(*S)); 321 break; 322 case Stmt::OMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirectiveClass: 323 EmitOMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirective( 324 cast<OMPTargetTeamsDistributeParallelForSimdDirective>(*S)); 325 break; 326 case Stmt::OMPTargetTeamsDistributeSimdDirectiveClass: 327 EmitOMPTargetTeamsDistributeSimdDirective( 328 cast<OMPTargetTeamsDistributeSimdDirective>(*S)); 329 break; 330 } 331 }
前边是一些判断,主要的结构和我们猜想的一样是一个大的switch case判断,根据S->getStmtClass()来进行,中间还搞进来一个大的宏include,
#define STMT(Type, Base) #define ABSTRACT_STMT(Op) #define EXPR(Type, Base) \ case Stmt::Type##Class: #include "clang/AST/StmtNodes.inc"
这里是把所有的StmtNodes.inc都包进来。后边紧跟着就是case Stmt::ForStmtClass类型的判断。
我们进入EmitForStmt(cast<ForStmt>(*S), Attrs);里边看一下
1 void CodeGenFunction::EmitForStmt(const ForStmt &S, 2 ArrayRef<const Attr *> ForAttrs) { 3 JumpDest LoopExit = getJumpDestInCurrentScope("for.end"); 4 5 LexicalScope ForScope(*this, S.getSourceRange()); 6 7 // Evaluate the first part before the loop. 8 if (S.getInit()) 9 EmitStmt(S.getInit()); 10 11 // Start the loop with a block that tests the condition. 12 // If there's an increment, the continue scope will be overwritten 13 // later. 14 JumpDest Continue = getJumpDestInCurrentScope("for.cond"); 15 llvm::BasicBlock *CondBlock = Continue.getBlock(); 16 EmitBlock(CondBlock); 17 18 bool LoopMustProgress = false; 19 Expr::EvalResult Result; 20 if (LanguageRequiresProgress()) { 21 if (!S.getCond()) { 22 FnIsMustProgress = false; 23 } else if (!S.getCond()->EvaluateAsInt(Result, getContext())) { 24 LoopMustProgress = true; 25 } 26 } 27 28 const SourceRange &R = S.getSourceRange(); 29 LoopStack.push(CondBlock, CGM.getContext(), CGM.getCodeGenOpts(), ForAttrs, 30 SourceLocToDebugLoc(R.getBegin()), 31 SourceLocToDebugLoc(R.getEnd()), LoopMustProgress); 32 33 // If the for loop doesn't have an increment we can just use the 34 // condition as the continue block. Otherwise we'll need to create 35 // a block for it (in the current scope, i.e. in the scope of the 36 // condition), and that we will become our continue block. 37 if (S.getInc()) 38 Continue = getJumpDestInCurrentScope("for.inc"); 39 40 // Store the blocks to use for break and continue. 41 BreakContinueStack.push_back(BreakContinue(LoopExit, Continue)); 42 43 // Create a cleanup scope for the condition variable cleanups. 44 LexicalScope ConditionScope(*this, S.getSourceRange()); 45 46 if (S.getCond()) { 47 // If the for statement has a condition scope, emit the local variable 48 // declaration. 49 if (S.getConditionVariable()) { 50 EmitDecl(*S.getConditionVariable()); 51 } 52 53 llvm::BasicBlock *ExitBlock = LoopExit.getBlock(); 54 // If there are any cleanups between here and the loop-exit scope, 55 // create a block to stage a loop exit along. 56 if (ForScope.requiresCleanups()) 57 ExitBlock = createBasicBlock("for.cond.cleanup"); 58 59 // As long as the condition is true, iterate the loop. 60 llvm::BasicBlock *ForBody = createBasicBlock("for.body"); 61 62 // C99 6.8.5p2/p4: The first substatement is executed if the expression 63 // compares unequal to 0. The condition must be a scalar type. 64 llvm::Value *BoolCondVal = EvaluateExprAsBool(S.getCond()); 65 llvm::MDNode *Weights = createProfileOrBranchWeightsForLoop( 66 S.getCond(), getProfileCount(S.getBody()), S.getBody()); 67 68 if (llvm::ConstantInt *C = dyn_cast<llvm::ConstantInt>(BoolCondVal)) 69 if (C->isOne()) 70 FnIsMustProgress = false; 71 72 Builder.CreateCondBr(BoolCondVal, ForBody, ExitBlock, Weights); 73 74 if (ExitBlock != LoopExit.getBlock()) { 75 EmitBlock(ExitBlock); 76 EmitBranchThroughCleanup(LoopExit); 77 } 78 79 EmitBlock(ForBody); 80 } else { 81 // Treat it as a non-zero constant. Don't even create a new block for the 82 // body, just fall into it. 83 } 84 incrementProfileCounter(&S); 85 86 { 87 // Create a separate cleanup scope for the body, in case it is not 88 // a compound statement. 89 RunCleanupsScope BodyScope(*this); 90 EmitStmt(S.getBody()); 91 } 92 93 // If there is an increment, emit it next. 94 if (S.getInc()) { 95 EmitBlock(Continue.getBlock()); 96 EmitStmt(S.getInc()); 97 } 98 99 BreakContinueStack.pop_back(); 100 101 ConditionScope.ForceCleanup(); 102 103 EmitStopPoint(&S); 104 EmitBranch(CondBlock); 105 106 ForScope.ForceCleanup(); 107 108 LoopStack.pop(); 109 110 // Emit the fall-through block. 111 EmitBlock(LoopExit.getBlock(), true); 112 }
大概流程和我之前处理ForStmt的读取的方式是一样的,getInit()/getCond()/getInc()/getBody()分别进行处理,每个生成对应Block,这里处理的时候,因为最后都需要处理成跳转的形式,需要预先记录下for结束的出口,然后按照Init() / Cond() /Body() / Inc() / Cond() 的顺序进行处理。




