[CVPR 2020]StarGAN v2: Diverse Image Synthesis for Multiple Domains 合成效果堪称惊人

导言
文章提出了StarGAN v2,这是一种可以同时解决生成图像多样性和多域扩展性的单一框架。相比于了baselines,它取得了明显的提升。文章对StarGAN 取得的视觉质量、多样性以及可扩展性都进行了验证。
paper: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=9157662
code: https://github.com/clovaai/stargan-v2
cite:
@inproceedings{DBLP:conf/cvpr/ChoiUYH20,
author = {Yunjey Choi and
Youngjung Uh and
Jaejun Yoo and
Jung{-}Woo Ha},
title = {StarGAN v2: Diverse Image Synthesis for Multiple Domains},
booktitle = {{CVPR}},
pages = {8185--8194},
publisher = {{IEEE}},
year = {2020}
}
下方↓公众号后台回复“starGAN2”,即可获得论文电子资源。

@
1. Introduction
- domain :a set of images that can be grouped as a visually distinctive category
- style: each image has a unique appearance, which we call style
例如,我们可以用性别作为不同的域,则风格就是妆容、胡子和发型等(图1的上部分)。
- An ideal image-to-image translation method : should be able to synthesize images considering the diverse styles in each domain.
现有的方法: 只考虑的两个域之间的映射,当域数量增加的时候,他们不具备扩展性。
- StarGAN [6]:one of the earliest models, which learns the mappings between all available domains using a single generator。
生成器将域标签作为附加的输入,学习图像到对应域的转换。
然而,StarGAN仍然学习每个域的确定性映射,该映射没有捕获数据分布的多模式本质。
- StarGAN v2: a scalable approach that can generate diverse images across multiple domains.
基于StarGAN,并用我们提出的域特定风格代码取代掉了StarGAN的域标签,这个域特定风格代码可以表示特定域的不同风格。
为此,我们引入了两个模块,一个映射网络(mapping network),一个风格编码器(style encoder)。
- mapping network : learns to transform random Gaussian noise into a style code
学习如何将随机高斯噪声转换为风格编码
- style encoder: the encoder learns to extract the style code from a given reference image.
而编码器则学习从给定的参考图像中提取风格编码。
在多个域的情况下,这两个模块都拥有多个输出分支,每一个都为特定域提供了风格编码。最终,使用这些风格编码,生成器就可以成功地学习在多个域下合成风格图像。
2. StarGAN v2
2.1. Proposed framework
我们用X 和Y来分别表示图像和域的集合,给定x属于X 和任意域y属于Y,我们的目标是训练一个单一的生成器G ,使它能够根据x针对每一个域y生成多样化的图像。 我们在每个域学习到的风格空间中生成域特定的风格向量,并且训练G来表达这个风格向量。图2 阐释了我们框架的概述, 其中包含了如下的四个模块。

Generator (Figure 2a)
生成器G(x,s)需要输入图像x和特定风格编码s,s由映射网络F或者风格编码器E提供。
我们使用adaptive instance normalization(AdaIN)来注入s到G中。
s被设计为表示特定域y的风格,从而消除了向G提供y的必要性,并允许G合成所有域的图像。
Mapping network (Figure 2b)
给定一个潜在编码z和一个域y,映射网络F生成风格编码\(s = F_y(z)\),其中\(F_y(\cdot)\) 表示F对应于域y的输出。
F由带有多个输出分支的MLP组成,用来为所有可用域提供风格编码。
F 通过随机采样潜在向量z和域y来提供多样化风格编码。
我们的多任务架构允许F高效地学习所有域的风格表达。
Style encoder(Figure 2c)
给定图像x和它对应的域y,编码器E提取风格编码\(s = E_y(x)\). 其中\(E_y(\cdot)\)表示编码器特定域域y的输出。 和F类似,风格编码器E也受益于多任务学习设置。
E可以使用不同参考图片生成多样化风格编码。
这允许G合成反映参考图像x的风格s的输出图像。
Discriminator (Figure 2d)
判别器D是一个多任务判别器,由多个输出分支组成。
每个分支\(D_y\) 学习一个二进制分类决定输入图像x是否是它对应域y的真实图像,或者是由G产生的假图像G(x,s)
2.2. Training objectives
给定一张图像x和它对应的原始域y。
Adversarial objective
对抗目标:
我们随机采样潜在编码z和目标域y,并且生成目标风格编码 \(\tilde{s} = F_{\tilde{y}}(z)\).
编码器G 将图像x和\(\tilde{s}\) 作为输入,并通过对抗损失学习生成输出图像\(G(x,\tilde{s})\)
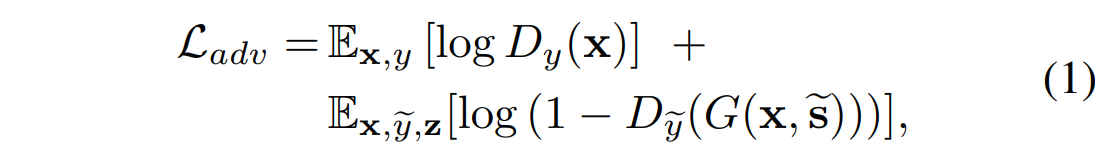
Style reconstruction.
风格重建:
为了增强生成器 来在生成图像\(G(x,\tilde{s})\)的时候,使用风格编码\(\tilde{s}\), 我们采用风格重建损失:
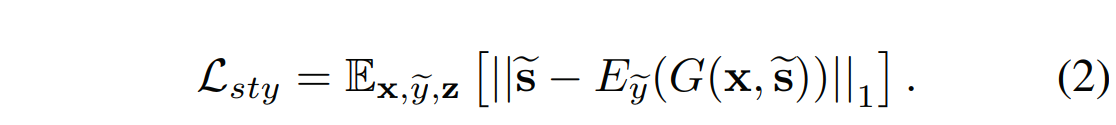
在测试时,我们学习的编码器E允许G变换输入图像,以反映参考图像的风格。
Style diversification.
风格多样化:
为了进一步增强生成器G来产生多样化图像,我们用多样性敏感损失来调整G。
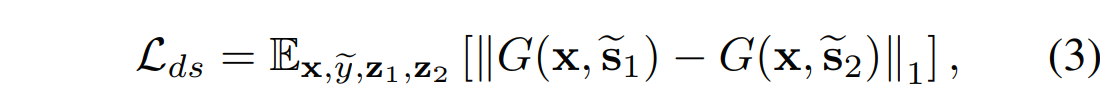
其中目标风格编码\(\tilde{s}_1\) 和\(\tilde{s}_2\)由F根据两个随机潜在编码\(z_1\)和\(z_2\)产生。
最大化正则项会迫使G探索图像空间并发现有意义的风格特征,以生成各种图像。
我们删除了分母部分,并设计了一个新的方程来进行稳定的训练,但要保持直觉。
Preserving source characteristics.
保留原始特征:
为了保证生成的图像适当地保留输入图像x域无关特征(例如,姿势),我们采用了循环一致性损失:
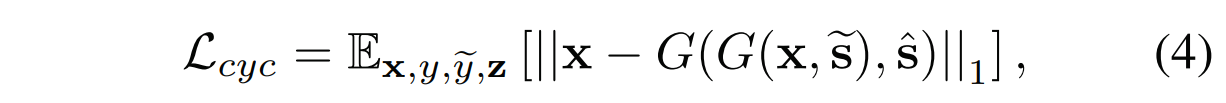
其中,\(\hat{s} = E_y(x)\) 是输入图像x的估计风格编码,y是x的原始域。
通过鼓励生成器G 重新构造带有估计风格编码\(\hat{s}\)的输入图像x, G学习在改变风格的同时保留x的原始特征。
Full objective.

我们还以与上述目标相同的方式训练模型,在生成风格编码时使用参考图像而不是潜在向量。 我们在附录中提供了训练详细信息。
3. Experiments
在训练阶段,所有实验均使用看不见的图像进行
baselines:
- MUNIT [13]
- DRIT [22]
- MSGAN[27]
- StarGAN [6]
All the baselines are trained using the implementations provided by the authors.
datasets:
- CelebA-HQ [17]
分为两个域,男性和女性 - our new AFHQ dataset (Appendix)
分为三个域,猫,狗,野生动物
评估策略:
- Frechét inception distance (FID) [11]
- learned perceptual image patch similarity (LPIPS) [38].
3.1. Analysis of individual components
We evaluate individual components that are added to our baseline StarGAN using CelebA-HQ.

FID 表示真实和生成图像的分布之间的距离,越小越好,LPIPS表示生成图像的多样性,越大越好
一个输入图像在不同配置情况下的相应生成图像如图3所示。

baseline 配置(A)就相当于是StarGAN。
如图3a所示,StarGAN程序只通过在输入图像上进行了妆容的局部改变。
配置(F)对应着我们提出的方法 StarGAN v2
图4展示了StarGAN v2 可以合成参照包括发型、妆容和胡须在内的反应多样化风格的图像,同时,还没有破坏原有的特征。

学习了妆容、发现、胡须等风格,保留了姿势和身份。
3.2. Comparison on diverse image synthesis
In this section, we evaluate StarGAN v2 on diverse image synthesis from two perspectives: latent-guided synthesis and reference-guided synthesis.
Latent-guided synthesis.
潜在引导合成

图5提供了质量的比较。

For both CelebA-HQ and AFHQ, our method achieves FIDs of 13.8 and 16.3, respectively, which are more than two times improvement over the previous leading method.
Reference-guided synthesis.
参考引导合成


Here, MUNIT and DRIT suffer from mode-collapse in AFHQ, which results in lower LPIPS and higher FID than other methods.
Human evaluation.
For each comparison, we randomly generate 100 questions, and each question is answered by 10 workers. We also ask each worker a few simple questions to detect unworthy workers. The number of total valid workers is 76.

These results show that StarGAN v2 better extracts and renders the styles onto the input image than the other baselines.
4. Discussion
We discuss several reasons why StarGAN v2 can successfully synthesize images of diverse styles over multiple domains.
- our style code is separately generated per domain by the multi-head mapping network and style encoder.
- our style space is produced by learned transformations
- our modules benefit from fully exploiting training data from multiple domains
To show that our model generalizes over the unseen images, we test a few samples from FFHQ [18] with our model trained on CelebA-HQ (Figure 7). Here, StarGAN v2 successfully captures styles of references and renders these styles correctly to the source images.

6. Conclusion
我们提出来 StarGAN v2,解决了两个image-to-image转化的主要挑战,转换一个域的单张图像到目标域的多张不同风格的图像,以及支持多目标域。 实验结果表明,我们的模型可以跨多个域中生成丰富的风格图像,并且超过了此前的领先方法 [13, 22, 27]。 我们还发布了一个新的动物脸集(AFHQ)数据集,用来在大规模域内域间变化设置中评估各种方法。



