ORACLE 日常
新增重做日志组文件(记录事务操作,位于内存中)
alter database add logfile group 5('d:\ORACLE\LogFiles\REDO4_A.LOG','d:\ORACLE\LogFiles\REDO4_B.LOG') size 20M;
add database add logfile member 'xxx' to group 5
归档操作
archivelog - no archivelog
重做日志文件-记录用户日志信息,临时存档
重做归档文件-记录用户操作,在重做日志文件之前进行记录,相当于备份
重做控制文件- 加载数据库控制初始化进程
表空间
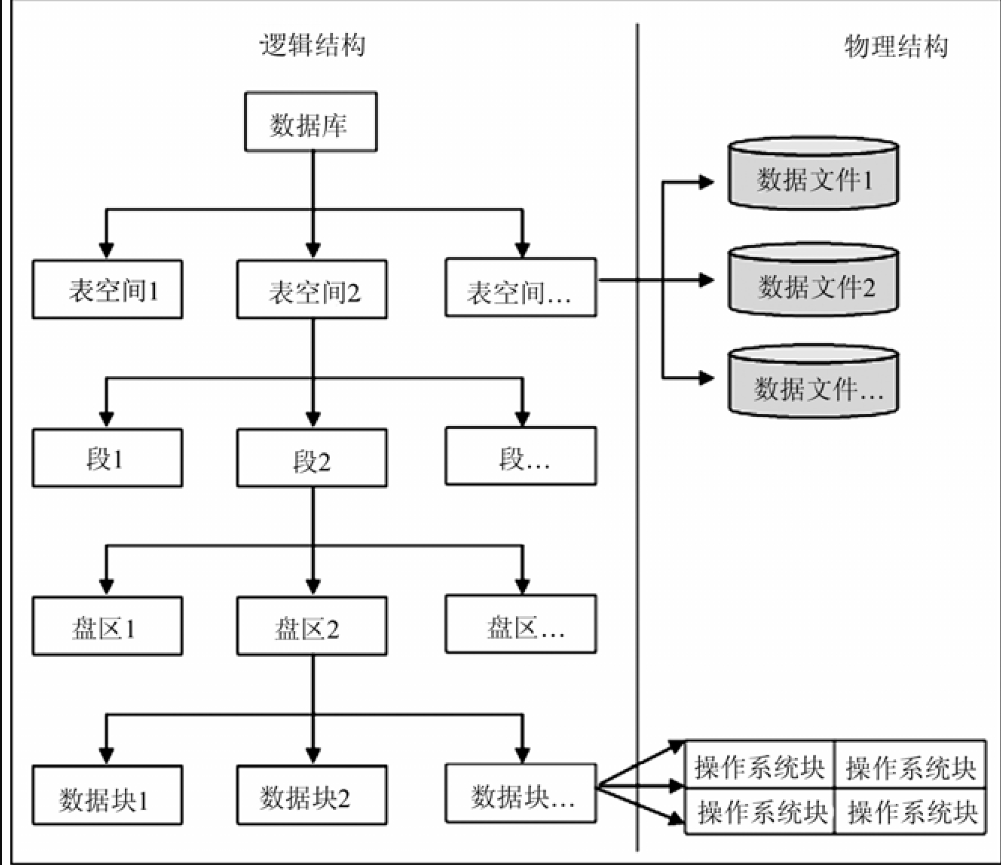
永久表空间- 存储数据的逻辑结构
创建表空间
create tablespace space_name datafile 'xxxxxxx\xxxx.dbf' size 10m autoextend on next 10m
maxsize 1g ;

对应的物理结构- 物理数据文件
数据段
数据分区
数据块
临时表空间
针对排序等临时性操作,系统创建临时信息
undo表空间
记录未提交的记录信息,update 一条数据后,旧的记录保存在undo,再commit 后提交刷新。
数据对象
LOB 大数据类型-
- blob 二进制文件最大128m
- clob 大字符串最大128m,转为unicode 存储
- bfile 保存二进制文件的指针- 只读
rowid - 伪列
保存数据指向的实际物理地址,使用rowid 访问数据是最快的一种访问方式
PCT-FREE 与PCT-USEED
数据块中如果到达了PCT-FREE 的上限,则不再进行insert 此数据块,剩余的空闲空间用来作为update 与delete 操作
PCT-USERED - 相对限制参数
参数值相加必须低于等于100。
针对update操作多,且update会增量的表,pctfree 设置较大,pctused设置较小,避免在update 后数据溢出的情况,20:40
针对insert 与 delete 较多,设置pctfree 较小,pctused 较大,保证数据块中保存的空间重用性,10:60
和值与100 相差越大,存储效率越高。
-- 设置表空间大小,free/used
create table tb_name(
)
tablespace tb_space_name -- 所属表空间
storage (initial 256K) -- 盘区
pctfree 20
pctused 60;
initrans -- 事物数据条目
nologging -- 重做日志记录,对表进行的操作不会记录到重做日志记录,但是insert、update、delete 还是会进行记录。
nocache -- 不使用缓存策略
LRU - 查询操作,优化策略后的查询计划会并入库告诉缓存,并会记录查询结果,当LRU 列表满或一定时间后会清空使用次数少的缓存。
-- 复制表
create table tb_name as select * from table_from;
-- 增加删除字段
alter table tb_name add (xxx varchar2(2))
alter table tb_name drop [column col_name]/(c1,c2)
alter table tb_name modify c_name varchar(20); -- 存在字段 兼容,从低到高 ,无值(高-低、低-高)
表名更改
alter table tb_name rename to new_name;
移动表空间
alter table tb_name move tablespace tb_space_name;
删除表
drop table tb_name [cascade constraints]; -- 如果存在级联关系则需要使用参数
delete table - 删除表数据,保留结构,且可恢复(重做日志文件或归档)
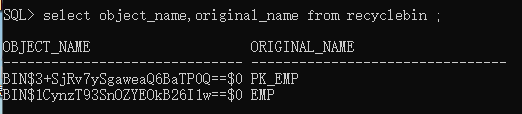
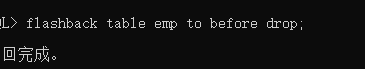
drop table - 删除(可恢复)利用闪回记录 flashback table
-- select object_name,original_name from recyclebin ; 查询回收站
-- flashback table emp to before drop; 回到删除之前
-- drop table tb_name purge; -- 立即释放空间,不可恢复
truncate table -- 截断,不可恢复(文件不保留历史)
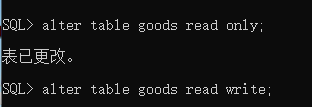
更改表的状态(只读,可写)(或模式、空间只读)
约束
- 主键、非空、唯一、其他、外键
主键: primary key
非空:not null
唯一:unique
alter table tb_name add constraint XX_NAME unique(column_name)
外键:被引用键为唯一键,删除外键表(主表数据)后方可删除引用表中的引用数据
alter table tb_name add constraint XX_F_K foreign key(column_name)
references tb2_name(column_name) [on delete action];
外键级联选项:
no action - 默认行为,报错
set null - 删除引用,外键表设置为null
cascade - 级联删除,删除引用数据导致外键数据同时被删除
其他
alter table tt add constraint id_chk check(id>1 and id <20) [disable/];
禁用
alter table tt disable constraint id_chk ;
启动
alter table tt enable [novalidate] constraint con_name;
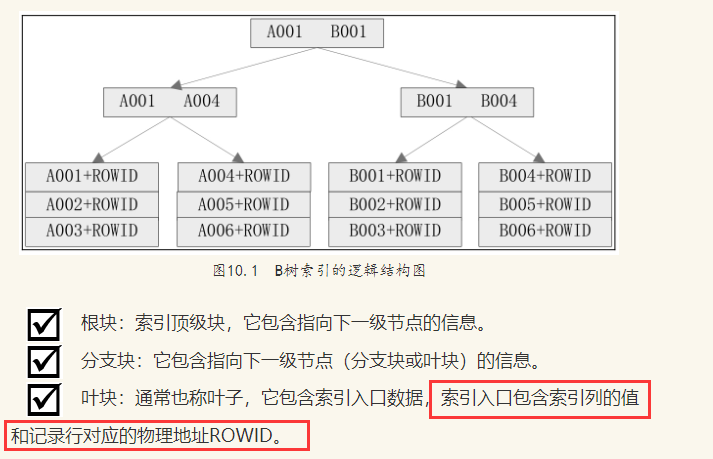
索引(目录的存在,rowid- 页码的存在)
- 将索引和对应的表放在不同的表空间里,可以提高查询速度(并行io进程)
存储方式:b树、位图、反向、函数
唯一性:唯一索引、非唯一
列数:单列所有、复合索引(多列)
索引的目的:提高查询速度,针对condition 查询条件或排序字段使用较为频繁的列建立索引,查询数据低于15% 应建立索引,相反使用较低的情况,建立的索引性能会不升反降。
索引会降低DML 操作的速度,因为每条数据需要建立索引,势必在进行dml操作时设计到额外的索引操作。
简化管理:索引与表在同一表空间
提高性能:索引与表分布在不同的表空间
使用nologging 建表,减少日志操作,提高建立索引的速度
在连接列上建立索引并且不要再小表上建立索引。
B树索引:(标准的一棵树)
无论查询某条数据,查询的层次都是一样的,相同的i/o操作,B- balance 平衡
create index xxx_index on tb_name(col_name)
pctfree 15
tablespace tp_name;
此处的pctfree 是针对索引的,跟原表的pctfree 无关。
B树索引的建立(normal) 基于“基数低”,oracle 建议低于1% 的情况建立normal index
比如10000行数据中有100中不同,则计算为 1%
位图索引
低于上述的基数,可以建立位图索引,oracle 通过图表的方式进行存储
位图索引的大小建立通过 create_bitmap_area_size 确定,默认8m 值越大查询速度越快
create bitmap index index_name on(tb_name)
tablespace ts_name;
更改位图索引的大小(必须重启数据库)
alter system set create_bitmap_area_size = 00000000 scope = spfile ;
反向索引
针对自增有序的列值使用反向索引,避免b树索引中叶子指向过大的情况,反向索引(随机索引)
create index index_name on (tb_name) reverse
tablespace ts_name;
- 重建索引
rebuild
-- 重建为反向索引
alter index index_name
rebuild reverse;
函数索引
某些情况下,索引没有起到一定的作用,如
select * from tb_name where col_name = upper('xxxx');
针对这个col_name 建立了普通索引,但是upper 函数导致索引无效,最终查询需要检索全表,因为upper 需要先更改为大写。
这种情况下建立函数索引。
create index index_name on tb_name(upper(col_name))
tablespace ts_name;
合并索引- 重新组合索引(针对表的dml 操作产生的索引碎片进行合并)不会释放索引空间
alter index index_name
coalesce deallocate unused;
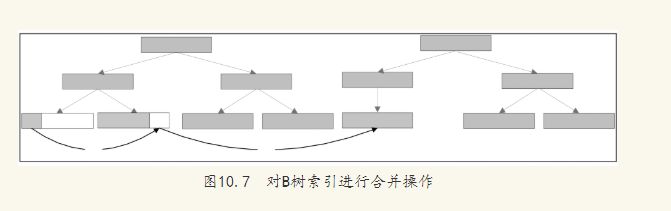
重建索引- 释放索引空间在建索引
alter index index_name rebuild;
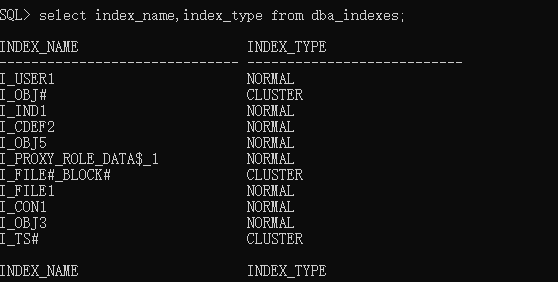
查询所有索引dba_indexes、all_indexes 当前用户所有可访问的索引、user_indexes 当前用户索引
同义词
建立表的别名,在源表修改后可以进行修改,通过同义词解耦与数据表引用表
共有
所有用户可访问

私有
创建用户可访问

当源表名更改后必须重新编译
视图(没有实际的存储地址,数据基于实际的表)

create or replace view v_name (col_1,col_2)
as select col_11,col_22 from table_name
with read only;
简单视图
针对单一的表,且没有执行表达式,聚集函数等。(可以执行dml 操作)
只读视图
with read only
复杂视图
使用表达式建立的视图(group 、 函数等)
连接视图(常用)
多个视图连接后的视图,使用连接,否则会出现笛卡尔积的情况。
create or replace view v_name as
select col_1,col_2 from a,b where a.id = b.subid;
序列(自增、自减序号)


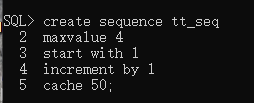
nextval 下一个值,currentval 当前值
修改序列
alter sequence tt_seq
maxvalue xxxx;
分区(表分区-索引分区)
范围分区(range )如日期
create table tb_name(
id varchar2(20) primary key,
col_tt int
)
partition by range(col_name)
(
partition par_n_1 values less than (to_date('1999-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') ) tabspace ts_name,
partition par_n_2 values less than (to_date('1999-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd') ) tabspace ts_name
);
通过分区查询
select * from tb_name partition(par_n_1);
散列分区 hash (高速,均匀,但无法或者数据具体存放在哪个分区)
create table tb_name(
xxx varchar2(20)
)
partition by hash(xxx)
(
partition p_1 tablespace ts_1
)
列表分区(枚举分区)如省份
create table tt_t(
id varchar2(20),
province varchar2(50)
)
partition by list(province)
(
partition p1 values('山东省'),
partition p1 values('江苏省')
)
组合分区(主分区与子分区)
sub partition...
interval 分区(范围分区增强版)
随着数据表的增加会自动增加分区
create table ...
(
...
d date
)
partition by range(d)
interval(numtoyinterval(1,'year')) -- 设置自动分区间隔
(
partition p_first values less then(to_date('xxxx-xx-xx','yyyy-mm-dd'))
);
添加表分区(已分区的表)
alter table tb_name
add partition p_new values('XX') -- 添加一个列表分区
storage(initial 10K next 20K) tablespace tt_1
nologging;
合并分区
hash
alter table tb_name coalesce partition;
复合分区(指定分区名)
删除分区
范围分区和复合分区中删除分区,散列分区只能通过合并进行删除。
alter table tb_name drop partition p_x;
删除分区后如有索引的存在需要进行重建索引(rebuild) 否则会为不可用状态。
针对有约束的分区需要先禁用约束在执行删除分区操作,最后在激活约束。
索引分区(全局索引分区、局部分区)
局部分区(与表分区采用同样分区结构)
create table t(
...
)
partition by range(xxx)
(
partition t_1 values less than (xxx)
)
-- 根据表分区进行索引分区
local(
partition i_1 tablespace ts_name
)
全局索引分区(不一定与表分区一致(不能进行位图索引分区))
create table index on tb_name(col_name)
global partition by range(col_name)
(
partition p_1 values less than (xxx)
);



