C# 自定义特性
特性是一种允许我们向程序集增加元数据的语言结构,它是用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类。
根据惯例,特性名使用Pascal命名法并且以Attribute后缀结尾。当为目标应用特性时,我们可以不使用后缀。例如对于SerializableAttribute和MyAttributeAttribute这两个特性,我们在把他们应用到结构时可以使用Serializable和MyAttribute短名称。
所有特性类都派生自System.Attribute,用户自定义的特殊类叫做自定义特性。
声明自定义特性
- 派生自
System.Attribute - 起一个以后缀为
Attribute结尾的名字
为安全起见,建议声明一个sealed的特性类
- 由于特性持有目标的信息,所以特性类的公共成员只能是:字段,属性,构造函数。
使用特性的构造函数
和其他类一样,都有构造函数,每一个特性至少必须有一个公共构造函数,如果不声明构造函数,编译器会为我们产生一个隐式,公共且无参的构造函数,也可以被重载,声明构造函数时,必须使用类全名(即包括后缀)。在应用时,才可以使用短名称(不包括后缀)。
[MyAttribute("Holds a value")] //使用了一个字符串的构造函数,它只是声明语句,只有特性的消费者访问特性时候才能调用构造函数,它不会决定什么时候构造特性类的对象。
public int MyField;
构造函数中的位置参数和命名参数
[MyAttribute("An excellent class",Review="Amy",ver="0.7.1")]
第一个参数是位置参数,后两个是命名参数。
public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute:System.Attribute
{
public string Description;
public string Ver;
public string Reviewer;
public MyAttributeAttribute(string desc){
Description=desc;
}
}
[MyAttribute("Excellent class",Reviewer="CJ266",Ver="0.7.1")] //虽然构造函数只有一个形参,但我们可以通过命名参数给构造函数3个实参,这与普通的类是不一样的。
class MyClass{
}
上述代码表示,构造函数的声明只列出一个形参,但我们可以通过命名参数给构造函数3个,但需要注意的是,构造函数需要的任何位置参数都必须放在命名参数之前。
限制特性
特性本身就是类,有一个很重要的预定义特性可以应用到自定义特性上,那就是AttributeUsage特性,可以用它来限制特性使用在某个目标类型上。
例如,如果我们希望自定义特性MyAttribute只应用到方法上,那么可以以如下方式使用AttributeUsage:
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTarget.Method)]
public sealed class MyAttributeAttribute:System.Attribute{...}
AttributeUsage有三个重要的公共属性:
| 名字 | 意义 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|
ValidOn |
限制特性能应用的目标类型的列表,构造函数的第一个参数必须是AttributeTarget类型的枚举值 |
|
Inherited |
一个布尔值,指示特性是否会被装饰类型的派生类所继承 | true |
AllowMultiple |
一个指示目标是否被应用多个特性的实例的布尔值 | false |
AttributeTarget的枚举值成员:
All |
Assembly |
Class |
Constructor |
|---|---|---|---|
Delegate |
Enum |
Event |
Field |
GenericParameter |
Interface |
Method |
Module |
Parameter |
Property |
ReturnValue |
Struct |
在使用AttributeUsage时,构造函数至少需要一个参数,参数包含的目标类型会保存在ValidOn中,还可以通过命名参数有选择地设置Inherited和AllowMultiple属性。
访问特性
我们可以通过Type对象获取了解有关类型的几乎所有信息:
| 成员 | 成员类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
Name |
属性 | 返回类型的名字 |
Namespace |
属性 | 返回包含类型声明的命名空间 |
Assembly |
属性 | 返回声明类型的程序集,如果类型是泛型的,返回定义这个类型的程序集 |
GetFields |
方法 | 返回类型的字段列表 |
GetProperties |
方法 | 返回类型的属性列表 |
GetMethods |
方法 | 返回类型的方法列表 |
对于访问自定义特性来说,我们也可以用Type的两个方法(IsDefined和GetCustomAttributes)
IsDefined方法
使用IsDefined方法来判断特性是否应用到了,第一个参数是接受需要检查特性的Type对象,第二个参数是bool类型,指示是否搜索继承树来查找这个特性。
GetCustomAttributes方法
该方法返回的对象是object的数组,因此我们必须强制转换为相应的特性类型,布尔参数指定是否搜索继承树来查找特性。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class)]
public sealed class ReviewCommentAttribute : System.Attribute
{
public string Description { get; set; }
public string VersionNumber { get; set; }
public string ReviewerID { get; set; }
public ReviewCommentAttribute(string desc,string ver)
{
Description = desc;
VersionNumber = ver;
}
}
class BaseClass
{
public int BaseField = 0;
}
[ReviewComment("This is Derived","0.8.1")]
class DerivedClass : BaseClass
{
public int DerivedField = 0;
}
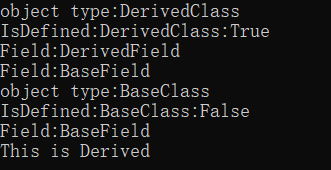
class Program1
{
static void Main()
{
var bc = new BaseClass();
var dc = new DerivedClass();
BaseClass[] bca = new BaseClass[] { dc, bc };
foreach (var v in bca)
{
Console.WriteLine("object type:{0}", v.GetType().Name);
var fi = v.GetType().GetFields();
Console.WriteLine($"IsDefined:{v.GetType().Name}:{v.GetType().IsDefined(typeof(ReviewCommentAttribute), false)}");
foreach (var f in fi)
{
Console.WriteLine("Field:{0}", f.Name);
}
}
var t = dc.GetType();
var Attrs = t.GetCustomAttributes(true);
foreach (var attr in Attrs)
{
var attr1 = attr as ReviewCommentAttribute;
Console.WriteLine($"{attr1.Description}");
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号