[clickhouse] Clickhouse之开窗函数篇
1 概述
1.0 序
- clickhouse :
21.3.4.25
1.1 开窗函数
开窗函数的定义
- 窗口函数可让用户对与当前行相关的一组行执行计算。用户可以执行的一些计算与使用聚合函数执行的计算类似,但窗口函数不会导致行被分组为单个输出 - 仍会返回各个行。
clickhouse开窗函数
- clickhouse 开窗函数的启用与版本支持情况
- clickhouse开窗函数的功能,不过当前为试验阶段,不建议在生产环境中使用,可以先学习一下准备着,等官网去掉了实验标记就可以愉快的使用啦~
- 详见官网:https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/sql-reference/window-functions
- 在部分clickhouse版本中尚未默认开启窗函数功能,可以通过参数设置开启:
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- clickhouse 对【标准开窗函数】支持情况
ClickHouse 支持定义窗口和窗口函数的标准语法。下表指示某个功能当前是否受支持。
| 标准窗口的特性 | clickhouse 支持情况 |
|---|---|
临时窗口规范 ( count(*) over (partition by id order by time desc)) |
支持 |
窗口函数的表达式,例如(count(*) over ()) / 2) |
支持 |
WINDOW子句(select ... from table window w as (partition by id)) |
支持 |
ROWS框架 |
支持 |
RANGE框架 |
支持(默认) |
INTERVAL DateTime RANGE OFFSET框架语法 |
不支持(指定秒数(RANGE适用于任何数字类型) |
GROUPS框架 |
不支持 |
计算框架内的聚合函数 ( sum(value) over (order by time)) |
支持(支持所有聚合函数) |
窗口排序函数:rank()/dense_rank()/row_number() |
支持 |
lag/lead(value, offset) |
不支持 但您可使用以下解决方法之一: 1) any(value) over (.... rows between <offset> preceding and <offset> preceding),或following for lead2) lagInFrame/leadInFrame,它们是类似的,但遵循窗口框架。要获得与 相同的行为lag/lead,请使用rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following |
| ntile(桶) | 支持 指定类似窗口,(按 x 顺序分区,按 y 行在无界前导和无舍入后导之间进行分区)。 |
信息来源: https://clickhouse.com/docs/en/sql-reference/window-functions
clickhouse开窗语法
over(partition by {分组字段} order by {排序字段} asc|desc rows between {起始行} and {结束行})
rows between {起始行} and {结束行}可以指定操作行的范围, 包左包右, 涉及到的关键字如下:
- unbounded preceding # 第1行开始 := 前面所有行
UNBOUNDED:不受控的,无限的;PRECEDING: 在 ... 之前;FOLLOWING: 在 ... 之后;
- {n} preceding # 向上的n行开始 := 前面n行
- current row # 当前行
- {n} following # 向下的n行结束 := 后面n行
- unbounded following # 最后1行结束 := 后面所有行
- 示例:当前行与后面所有行的累加(分区内)
// 从当前行到最后的数据
sum(sales_volume) over(partition by id rows between current row and unbounded following) sum_sales
- 示例:前面所有行与当前行的累加(分区内)
起始行( unbounded preceding) 到 当前行(current row)
sum(sales_volume) over(partition by id rows between unbounded preceding and current row) sum_sales
补充示例:
select
*
, sum(pv) over(partition by cookieid order by createtime rows between unbounded preceding and current row ) as n1 # 起始行 到 当前行
from website_pv_info; # 写order by, 局部统计(统计组内第一行 至 当前行的内容)
- 示例:当前行与后两行的累加(分区内)
sum(sales_volume) over(partition by id rows between current row and 2 following) sum_sales
- 示例:前一行与当前行的累加(分区内)
sum(sales_volume) over(partition by id rows between 1 preceding and current row) sum_sales
- 示例:前一行的值+当前行的值+后一行的值
sum(id) over(partition by category rows between 1 preceding and 1 following) rank from t
- 示例:取当前行的前两条及后两条来参与计算,一般用于移动平均值
rows between 2 preceding and 2 following
- 示例:按DEPTNO分区,ENAME顺序排列,统计从开始到结束的所有数据
这里相当于没有写ORDER BY
SUM(SAL) OVER(PARTITION BY DEPTNO ORDER BY ENAME ROWS BETWEEN UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING)
- 示例:按DEPTNO分区,ENAME顺序排列,统计从当前行到下一行数据
SUM(SAL) OVER(PARTITION BY DEPTNO ORDER BY ENAME ROWS BETWEEN CURRENT ROW AND 1 FOLLOWING)
1.2 数据准备
表结构定义
- 职工薪水发放记录表 | 业务1
CREATE TABLE default.employee_salary_l (
month Date,
name String ,
department String,
salary UInt32
) ENGINE = MergeTree()
partition by month
ORDER BY month;
- 网站点击量表 | 业务2
create table default.website_pv_info (
cookieid varchar(20), # 用户id
createtime varchar(20), # 访问时间
pv int # 页面浏览量
);
- 网站访问记录表 | 业务2
create table default.website_url_info (
cookieid varchar(20), # 用户id
createtime varchar(20), # 访问时间
url varchar(20) # 访问的url页面
);
- 商品销售明细表 | 业务3
CREATE TABLE default.commodity_sales (
month Date,
goods String,
sales UInt32
) ENGINE = MergeTree()
partition by month
ORDER BY month
样例数据
- 职工薪水发放记录表 | 业务1
INSERT INTO default.employee_salary_l VALUES
('2020-01-01', 'Ali', 'Sales', 6000),
('2020-01-01', 'Bob', 'Sales', 6000),
('2020-01-01', 'Cindy', 'Sales', 5000),
('2020-01-01', 'Davd', 'Finance', 8000),
('2020-01-01', 'Elena', 'Sales', 9000),
('2020-01-01', 'Fancy', 'Finance', 10000),
('2020-01-01', 'George', 'Finance', 10000),
('2020-01-01', 'Haffman', 'Marketing', 6000),
('2020-01-01', 'Ilaja', 'Marketing', 7000),
('2020-01-01', 'Joey', 'Sales', 8000);
- 网站点击量表 | 业务2
use default;
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10', 1);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-11', 5);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-12', 7);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-13', 3);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-14', 2);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-15', 4);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-16', 4);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10', 2);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-11', 3);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-12', 5);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-13', 6);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-14', 3);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-15', 9);
insert into website_pv_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-16', 7);
- 网站访问记录表 | 业务2
use default;
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:00:02', 'url2');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:00:00', 'url1');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:03:04', '1url3');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:50:05', 'url6');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 11:00:00', 'url7');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:10:00', 'url4');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie1', '2018-04-10 10:50:01', 'url5');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:00:02', 'url22');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:00:00', 'url11');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:03:04', '1url33');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:50:05', 'url66');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 11:00:00', 'url77');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:10:00', 'url44');
insert into website_url_info value ('cookie2', '2018-04-10 10:50:01', 'url55');
- 商品销售明细表 | 业务3
INSERT INTO default.commodity_sales VALUES
('2020-01-01', 'apple', 8000),('2020-01-01', 'orange', 7000),
('2020-01-01', 'banana', 6500),('2020-02-01', 'apple', 5000),
('2020-02-01', 'orange', 5000),('2020-02-01', 'banana', 5000),
('2020-03-01', 'apple', 6000),('2020-03-01', 'orange', 5000),
('2020-03-01', 'banana', 5500),('2020-04-01', 'apple', 7000),
('2020-04-01', 'orange', 6000),('2020-04-01', 'banana', 6500),
('2020-05-01', 'apple', 7000),('2020-05-01', 'orange', 6000),
('2020-05-01', 'banana', 7000),('2020-06-01', 'apple', 6700),
('2020-06-01', 'orange', 6700),('2020-06-01', 'banana', 7700),
('2020-07-01', 'apple', 9000),('2020-07-01', 'orange', 6000),
('2020-07-01', 'banana', 7200),('2020-08-01', 'apple', 9000),
('2020-08-01', 'banana', 6500),('2020-09-01', 'apple', 7000),
('2020-09-01', 'banana', 7000),('2020-10-01', 'apple', 9000),
('2020-10-01', 'banana', 7800),('2020-11-01', 'apple', 7000),
('2020-11-01', 'banana', 7400),('2020-12-01', 'apple', 8000),
('2020-12-01', 'banana', 7500),
('2021-01-01', 'apple', 9000),('2021-01-01', 'orange', 8000),
('2021-01-01', 'banana', 8500),('2021-02-01', 'apple', 9500),
('2021-02-01', 'orange', 9000),('2021-02-01', 'banana', 9500),
('2021-03-01', 'apple', 9500),('2021-03-01', 'orange', 8000),
('2021-03-01', 'banana', 9500),('2021-04-01', 'apple', 9000),
('2021-04-01', 'orange', 8000),('2021-04-01', 'banana', 7500),
('2021-05-01', 'apple', 10000),('2021-05-01', 'orange', 9000),
('2021-05-01', 'banana', 8500),('2021-06-01', 'apple', 10000),
('2021-06-01', 'orange', 9000),('2021-06-01', 'banana', 9000),
('2021-07-01', 'apple', 11000),('2021-07-01', 'orange', 10000),
('2021-07-01', 'banana', 9500)
- 查询样例数据
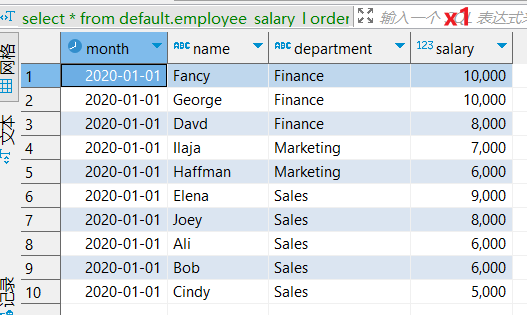
select * from default.employee_salary_l;
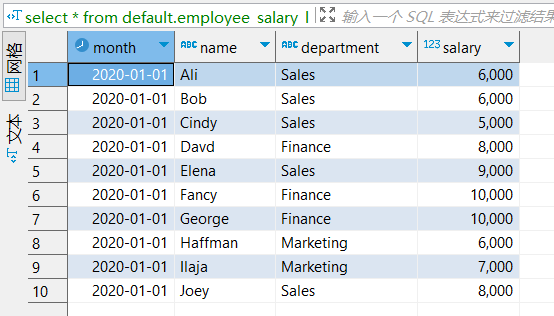
/month /name /department /salary
2020-01-01 Ali Sales 6000
2020-01-01 Bob Sales 6000
2020-01-01 Cindy Sales 5000
2020-01-01 Davd Finance 8000
2020-01-01 Elena Sales 9000
2020-01-01 Fancy Finance 10000
2020-01-01 George Finance 10000
2020-01-01 Haffman Marketing 6000
2020-01-01 Ilaja Marketing 7000
2020-01-01 Joey Sales 8000
2 开窗函数的实验
2.0 基础/常规 : range between
不设置order by
- CASE1 : 首先,看一个简单的例子,开窗求和,但窗范围限制在当前行,结果如下:
SELECT
goods,
month,
sales,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods RANGE BETWEEN CURRENT ROW AND CURRENT ROW) AS sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
output
/goods /month /sales /sum_sales
orange 2021-06-01 9000 102700
orange 2021-04-01 8000 102700
orange 2021-02-01 9000 102700
orange 2021-01-01 8000 102700
orange 2020-03-01 5000 102700
orange 2020-04-01 6000 102700
orange 2020-02-01 5000 102700
orange 2020-07-01 6000 102700
orange 2020-01-01 7000 102700
orange 2021-07-01 10000 102700
orange 2020-05-01 6000 102700
orange 2021-05-01 9000 102700
orange 2020-06-01 6700 102700
orange 2021-03-01 8000 102700
【结果分析】
从结果可见,实际上是对所有行求和,并没有受参数影响。
这其实是因为range between在未指定order by列时,默认在【开窗分组】中对所有行进行统计。
- CASE2 : 下面是指定了order by的结果,看起来确实和预想的一致:
SELECT
goods,
month,
sales,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY month ASC RANGE BETWEEN CURRENT ROW AND CURRENT ROW) AS sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
output
/goods /month /sales /sum_sales
orange 2020-01-01 7000 7000
orange 2020-02-01 5000 5000
orange 2020-03-01 5000 5000
orange 2020-04-01 6000 6000
orange 2020-05-01 6000 6000
orange 2020-06-01 6700 6700
orange 2020-07-01 6000 6000
orange 2021-01-01 8000 8000
orange 2021-02-01 9000 9000
orange 2021-03-01 8000 8000
orange 2021-04-01 8000 8000
orange 2021-05-01 9000 9000
orange 2021-06-01 9000 9000
orange 2021-07-01 10000 10000
设置order by
时间列排序
- 有的时候,我们可能需要对时间列进行排序,同时也要对指定行范围进行求和。这时在
range between中,如果没有使用固定的关键字(如unbounded preceding,current row),而是指定了数值行,那么结果并不会像我们想象的那样。
具体可以先看下面例子:
SELECT
goods,
month,
sales,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY month ASC RANGE BETWEEN 31 PRECEDING AND 31 FOLLOWING) AS sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
本例子中,指定了
BETWEEN 31 PRECEDING AND 31 FOLLOWING,看起来好像是前面31行后面31行,实际上并不是。
因为在order by中使用了时间列。因此,这个数值是和时间有关的。
在本例中31指的是天,也就是前面31天到后面31天的范围来求和。结果也符合预期,是在前后三行进行求和。
output
/goods /month /sales /sum_sales
orange 2020-01-01 7000 12000
orange 2020-02-01 5000 17000
orange 2020-03-01 5000 16000
orange 2020-04-01 6000 17000
orange 2020-05-01 6000 18700
orange 2020-06-01 6700 18700
orange 2020-07-01 6000 12700
orange 2021-01-01 8000 17000
orange 2021-02-01 9000 25000
orange 2021-03-01 8000 25000
orange 2021-04-01 8000 25000
orange 2021-05-01 9000 26000
orange 2021-06-01 9000 28000
orange 2021-07-01 10000 19000
数值列排序
- 回到正常对数值列排序的场景中,我们需要在排序后进行求和。而在指定行范围时,需要注意的是,如果不是使用固定的关键字(如
unbounded preceding,current row),而是使用数值时,实际上数值并不是指定行范围,而是指定数值范围。
看如下例子:
SELECT
goods,
month,
sales,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales DESC RANGE BETWEEN 500 PRECEDING AND 500 FOLLOWING) AS sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
该例子中
BETWEEN 500 PRECEDING AND 500 FOLLOWING,就是指当前行数值减500得到左区间,加500得到右区间,例如对于10000来说,得到的区间范围就是[9500, 10500],结果如下:
┌─goods──┬──────month─┬─sales─┬─sum_sales─┐
│ orange │ 2021-07-01 │ 10000 │ 10000 │
│ orange │ 2021-06-01 │ 9000 │ 27000 │
│ orange │ 2021-05-01 │ 9000 │ 27000 │
│ orange │ 2021-02-01 │ 9000 │ 27000 │
│ orange │ 2021-04-01 │ 8000 │ 24000 │
│ orange │ 2021-03-01 │ 8000 │ 24000 │
│ orange │ 2021-01-01 │ 8000 │ 24000 │
│ orange │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 13700 │
│ orange │ 2020-06-01 │ 6700 │ 13700 │
│ orange │ 2020-05-01 │ 6000 │ 18000 │
│ orange │ 2020-07-01 │ 6000 │ 18000 │
│ orange │ 2020-04-01 │ 6000 │ 18000 │
│ orange │ 2020-02-01 │ 5000 │ 10000 │
│ orange │ 2020-03-01 │ 5000 │ 10000 │
└────────┴────────────┴───────┴───────────┘
拿其中
9000来看,区间范围应该是[8500, 9500],而在这个范围内的仅有三个9000是符合的,因此结果就是他们三个数值相加,得到的就是27000。
累计
按月实现累计
SELECT
goods, month, sales,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY month desc range BETWEEN unbounded preceding and current row) as sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
output
┌─goods──┬──────month─┬─sales─┬─sum_sales─┐
│ orange │ 2021-07-01 │ 10000 │ 10000 │
│ orange │ 2021-06-01 │ 9000 │ 19000 │
│ orange │ 2021-05-01 │ 9000 │ 28000 │
│ orange │ 2021-04-01 │ 8000 │ 36000 │
│ orange │ 2021-03-01 │ 8000 │ 44000 │
│ orange │ 2021-02-01 │ 9000 │ 53000 │
│ orange │ 2021-01-01 │ 8000 │ 61000 │
│ orange │ 2020-07-01 │ 6000 │ 67000 │
│ orange │ 2020-06-01 │ 6700 │ 73700 │
│ orange │ 2020-05-01 │ 6000 │ 79700 │
│ orange │ 2020-04-01 │ 6000 │ 85700 │
│ orange │ 2020-03-01 │ 5000 │ 90700 │
│ orange │ 2020-02-01 │ 5000 │ 95700 │
│ orange │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 102700 │
└────────┴────────────┴───────┴───────────┘
按数量大小实现累计
SELECT
goods, month, sales,
rank() over (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc) as rank,
row_number() over (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc) as row,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc range BETWEEN unbounded preceding and current row) as sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
output
┌─goods──┬──────month─┬─sales─┬─rank─┬─row─┬─sum_sales─┐
│ orange │ 2021-07-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │ 1 │ 10000 │
│ orange │ 2021-06-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 2 │ 37000 │
│ orange │ 2021-05-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 3 │ 37000 │
│ orange │ 2021-02-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 4 │ 37000 │
│ orange │ 2021-04-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 5 │ 61000 │
│ orange │ 2021-03-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 6 │ 61000 │
│ orange │ 2021-01-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 7 │ 61000 │
│ orange │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 8 │ 8 │ 68000 │
│ orange │ 2020-06-01 │ 6700 │ 9 │ 9 │ 74700 │
│ orange │ 2020-05-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 10 │ 92700 │
│ orange │ 2020-07-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 11 │ 92700 │
│ orange │ 2020-04-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 12 │ 92700 │
│ orange │ 2020-02-01 │ 5000 │ 13 │ 13 │ 102700 │
│ orange │ 2020-03-01 │ 5000 │ 13 │ 14 │ 102700 │
└────────┴────────────┴───────┴──────┴─────┴───────────┘
会发现: 累计和是按照sales的大小序号进行求和的,存在并列的情况,这种情况下,还是需要用
rows between来实现,如下所示:
SELECT
goods, month, sales,
rank() over (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc) as rank,
row_number() over (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc) as row,
sum(sales) OVER (PARTITION BY goods ORDER BY sales desc rows BETWEEN unbounded preceding and current row) as sum_sales
FROM commodity_sales
WHERE goods = 'orange'
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
-- FORMAT PrettyCompactMonoBlock
output
┌─goods──┬──────month─┬─sales─┬─rank─┬─row─┬─sum_sales─┐
│ orange │ 2021-07-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │ 1 │ 10000 │
│ orange │ 2021-02-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 2 │ 19000 │
│ orange │ 2021-06-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 3 │ 28000 │
│ orange │ 2021-05-01 │ 9000 │ 2 │ 4 │ 37000 │
│ orange │ 2021-01-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 5 │ 45000 │
│ orange │ 2021-04-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 6 │ 53000 │
│ orange │ 2021-03-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 7 │ 61000 │
│ orange │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 8 │ 8 │ 68000 │
│ orange │ 2020-06-01 │ 6700 │ 9 │ 9 │ 74700 │
│ orange │ 2020-05-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 10 │ 80700 │
│ orange │ 2020-07-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 11 │ 86700 │
│ orange │ 2020-04-01 │ 6000 │ 10 │ 12 │ 92700 │
│ orange │ 2020-02-01 │ 5000 │ 13 │ 13 │ 97700 │
│ orange │ 2020-03-01 │ 5000 │ 13 │ 14 │ 102700 │
└────────┴────────────┴───────┴──────┴─────┴───────────┘
2.1 开窗排序
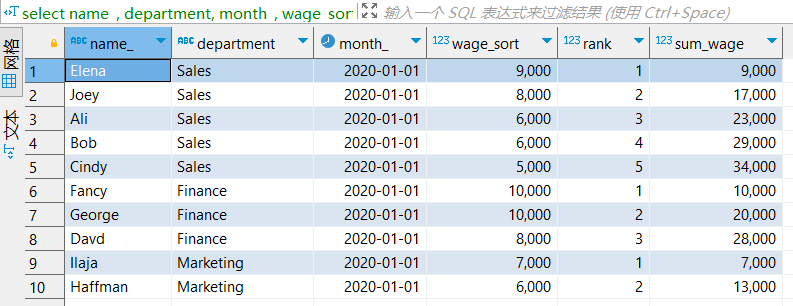
rank() 函数 : 分组排序(允许并列排名、序号顺延)
rank方法允许并列排名,后续排名序号往后顺延。比如,有两个第一,则接着后面就是第三了。我们先看一下下面的sql语句:
- 方式1:
select
name, department, month, salary,
rank() OVER (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc) AS rank
from default.employee_salary_l
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 方式2:
select
name, department, month, salary,
rank() OVER w AS rank
from default.employee_salary_l
WINDOW w AS (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc)
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 【解释】:在该sql语句中
WINDOW w AS (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc)这一行就是定义一个分组窗partition by department是指按照部门进行分组ORDER BY salary desc则是在分组内对salary按照从大到小进行排序,这个排序主要是为了让rank()函数依据该结果得到排序后的序号
- 排序后的查询结果:
┌─name────┬─department─┬──────month─┬─salary─┬─rank─┐
│ Fancy │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │
│ George │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │
│ Davd │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 3 │
│ Ilaja │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 1 │
│ Haffman │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 2 │
│ Elena │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 9000 │ 1 │
│ Joey │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 2 │
│ Ali │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │
│ Bob │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │
│ Cindy │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 5000 │ 5 │
└─────────┴────────────┴────────────┴────────┴──────┘
从结果可以看到,rank函数得到的就是每个成员在各自部门分组内的排序序号,而序号也是不连续的。
dense_rank() 函数 : 分组排序(允许并列排名、序号不顺延)
dense_rank()方法允许出现并列排名,但是后续排名序号不顺延,也就是会出现连续的序号。
如下所示为dense_rank的排序sql语句和结果:
- 方法1:
select
name, department, month, salary,
dense_rank() OVER (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc) AS dense_rank
from default.employee_salary_l
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 方法2:
select
name, department, month, salary,
dense_rank() OVER w AS dense_rank
from default.employee_salary_l
WINDOW w AS (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc)
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 查询结果
┌─name────┬─department─┬──────month─┬─salary─┬─dense_rank─┐
│ Fancy │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │
│ George │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │
│ Davd │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 2 │
│ Ilaja │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 1 │
│ Haffman │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 2 │
│ Elena │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 9000 │ 1 │
│ Joey │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 2 │
│ Ali │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │
│ Bob │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │
│ Cindy │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 5000 │ 4 │
└─────────┴────────────┴────────────┴────────┴────────────┘
row_number() : 分组排序(不允许并列排名:=排序行号)
row_number()不允许并列排名,所有序号需连续排列。
其实准确的说,
row_number()方法并不是一个严格意义的排序方法,它的本质是获得每一行的行号,但在某些排序场景中还是可以用到该方法的。
比如,当常规排序后只想要保留第一条数据(并列的也只取一个),那么就可以用row_number()来解决这样的问题了。
需要注意的是由于row_number()不允许出现并列的序号,那么:对于并列的两行数据,重复执行的话结果行号可能会不一样。
- 方法1:
select
name, department, month, salary,
row_number() OVER (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc) AS row_number
from default.employee_salary_l
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 方法2:
select
name, department, month, salary,
row_number() OVER w AS row_number
from default.employee_salary_l
WINDOW w AS (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc)
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
- 查询结果:
┌─name────┬─department─┬──────month─┬─salary─┬─row_number─┐
│ Fancy │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │
│ George │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 2 │
│ Davd │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 3 │
│ Ilaja │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 1 │
│ Haffman │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 2 │
│ Elena │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 9000 │ 1 │
│ Joey │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 2 │
│ Ali │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │
│ Bob │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 4 │
│ Cindy │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 5000 │ 5 │
└─────────┴────────────┴────────────┴────────┴────────────┘
2.2 开窗聚合
- 开窗功能除了用来进行组内排序,还经常用来进行组内的数据统计,比如求和、均值、最大值等。下面我们按部门对薪资进行统计分析。
常规聚合
- 常规聚合一般包含计算数据条数、最小值、最大值、总数、平均值等。
实现如下:
- 使用方法
select
name, department, month, salary,
count(*) OVER w AS count,
sum(salary) OVER w AS sum_wage,
avg(salary) OVER w AS avg_wage,
max(salary) OVER w AS max_wage,
min(salary) OVER w AS min_wage
from default.employee_salary_1
WINDOW w AS (partition by department)
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
观察一下sql语句我们会发现,在分组窗的定义语句中,只有partition by,却没有了刚刚说的order by。这是因为在统计聚合中,我们无需用到排序方法,因此在分组窗中也就无需对指定列排序了。
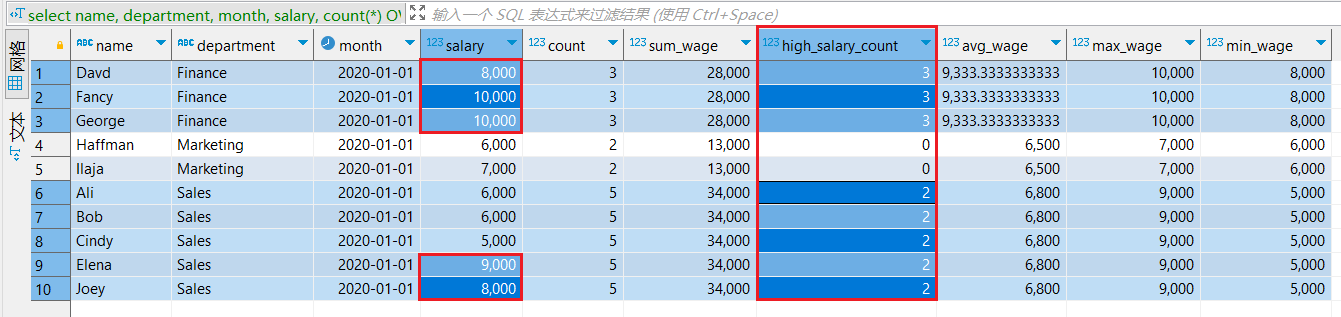
- 统计结果:
为了结果看起来规整删掉了部分小数。
┌─name────┬─department─┬──────month─┬─salary─┬─count─┬─sum_wage─┬─avg_wage─┬─max_wage─┬─min_wage─┐
│ Davd │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 3 │ 28000 │ 9333 │ 10000 │ 8000 │
│ Fancy │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 3 │ 28000 │ 9333 │ 10000 │ 8000 │
│ George │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 3 │ 28000 │ 9333 │ 10000 │ 8000 │
│ Haffman │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 2 │ 13000 │ 6500 │ 7000 │ 6000 │
│ Ilaja │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 2 │ 13000 │ 6500 │ 7000 │ 6000 │
│ Ali │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 6800 │ 9000 │ 5000 │
│ Bob │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 6800 │ 9000 │ 5000 │
│ Cindy │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 5000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 6800 │ 9000 │ 5000 │
│ Elena │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 9000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 6800 │ 9000 │ 5000 │
│ Joey │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 6800 │ 9000 │ 5000 │
└─────────┴────────────┴────────────┴────────┴───────┴──────────┴──────────┴──────────┴──────────┘
- 扩展:统计各部门内高收入员工人数
select
name, department, month, salary,
count(*) OVER w AS count,
sum(salary) OVER w AS sum_wage,
sum( is_high_salary ) OVER w AS high_salary_count, -- 窗口内,高收入的总人数
avg(salary) OVER w AS avg_wage,
max(salary) OVER w AS max_wage,
min(salary) OVER w AS min_wage
from (
select
*
, if(salary>= 8000, 1, 0) as is_high_salary -- 是否为高收入
from default.employee_salary_l
)
WINDOW w AS (partition by department)
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
开窗累计
除了常规的统计值,在实际工作中,可能会碰到需要计算累计和的场景,例如计算累计分布。这时,我们就需要按行去累计某个指定指标值了。
- 窗口参数设置实现累计
分区内累计(求和)
SELECT
name,
department,
month,
salary,
row_number() OVER w AS row,
sum(salary) OVER w AS sum_wage,
sum(salary) over (partition by department ORDER BY salary DESC rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as sum_wage_2
FROM default.employee_salary_l
WINDOW w AS (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY salary DESC )
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
sum(salary) over (partition by department ORDER BY salary DESC rows between unbounded preceding and current row) as sum_wage_2。
在该代码中,多了一个rows between unbounded preceding and current row,意思是:从该分组内的第一行开始到当前行都纳入到计算中,那么在指定求和的话,该代码得到的就是一个累计值。
而为什么不直接使用整段代码最后的分组窗,而要自己额外定义一个分组窗呢?这是因为在本段代码中还有其他统计值,他们是不需要进行累计的因此也不需要定义窗口范围(默认就是组内所有行)。
有感兴趣的朋友可以自己试一下将其他统计值去掉,然后把实现累计功能的窗口定义放到WINDOW那一行去看下结果如何。为了进行对比,笔者也将普通的求和结果放上去了,看下结果:
┌─name────┬─department─┬──────month─┬─salary─┬─row─┬─sum_wage─┬─sum_wage_2─┐
│ Fancy │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 1 │ 20000 │ 10000 │
│ George │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 10000 │ 2 │ 20000 │ 20000 │
│ Davd │ Finance │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 3 │ 28000 │ 28000 │
│ Ilaja │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 7000 │ 1 │ 7000 │ 7000 │
│ Haffman │ Marketing │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 2 │ 13000 │ 13000 │
│ Elena │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 9000 │ 1 │ 9000 │ 9000 │
│ Joey │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 8000 │ 2 │ 17000 │ 17000 │
│ Ali │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 3 │ 29000 │ 23000 │
│ Bob │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 6000 │ 4 │ 29000 │ 29000 │
│ Cindy │ Sales │ 2020-01-01 │ 5000 │ 5 │ 34000 │ 34000 │
└─────────┴────────────┴────────────┴────────┴─────┴──────────┴────────────┘
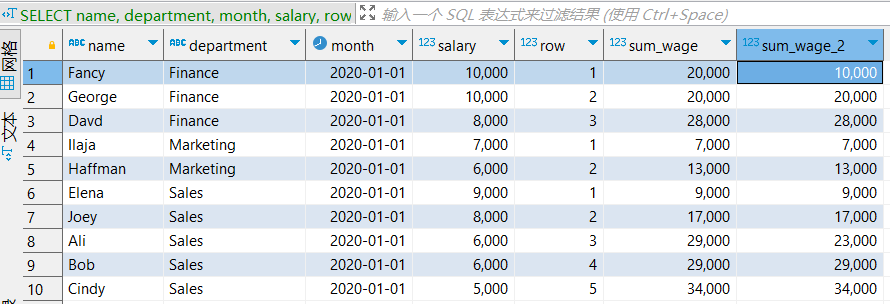
从结果我们可以看到,sum_wage_2确实是在分组内进行累计求和,而与之对应的,sum_wage很奇怪,看起来似乎是累计,但是又出现有并列的结果。
推测应该是因为ORDER BY salary DESC之后,默认是并列排序。因此,同样序号的结果就被计算到同一个累计值中了。
这也提醒大家注意在实际求和时,可千万别随便使用order by。
array join实现累计(求和)
在开窗函数出现之前对于累计功能,我们使用的是array join来实现,也将这种方法放在这里。
方法1 : 先排序后累计(求和)
- 这种方式比较繁琐,有好几层嵌套查询,先要进行排序,然后使用groupArray将列数据放到一个数组中,之后再用array join进行展开,展开的同时用arrayCumSum来获取数组中每个位置的累计值。
具体大家看下代码研究下:
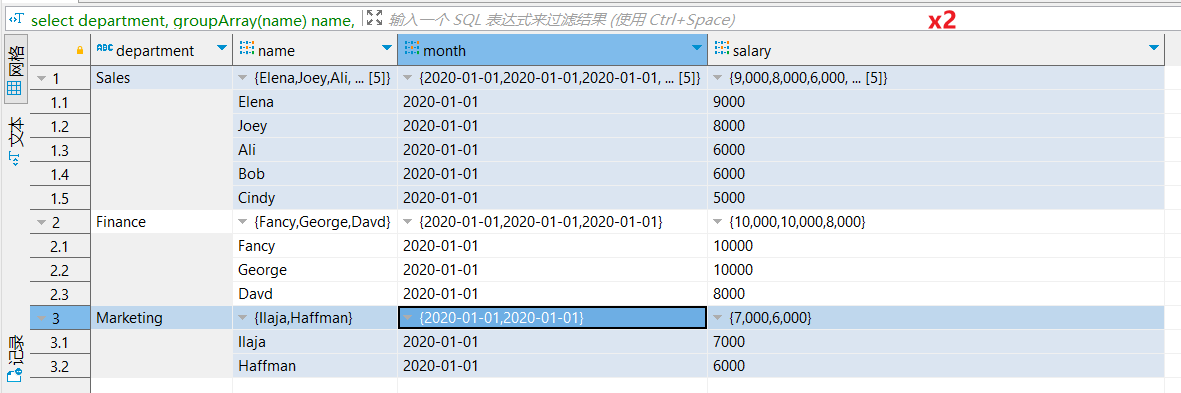
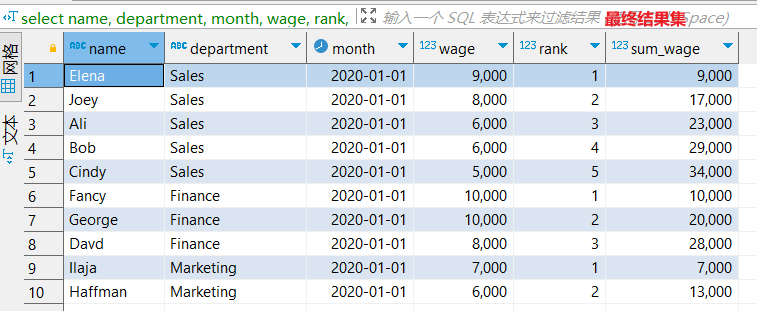
select
name, department, month, wage, rank, sum_wage
from (
select
department,
groupArray(name) name,
groupArray(month) month,
groupArray(salary) salary
from (
select
*
from default.employee_salary_l
order by department, salary desc
) x1
group by department
) x2
array join
name, month, salary as wage
, arrayCumSum(salary) as sum_wage
, arrayEnumerate(salary) AS rank
x1
x2
最终结果集
方法2 : arraySort实现累计(求和)
这种方式其实类似,但是可以减少一层查询,具体做法是在对数组进行展开的时候按照指定方式进行排序,这样就避免了一开始的内层嵌套排序查询。
因为涉及到好几个array函数,可以先去看下官方文档中关于这些函数的用法。
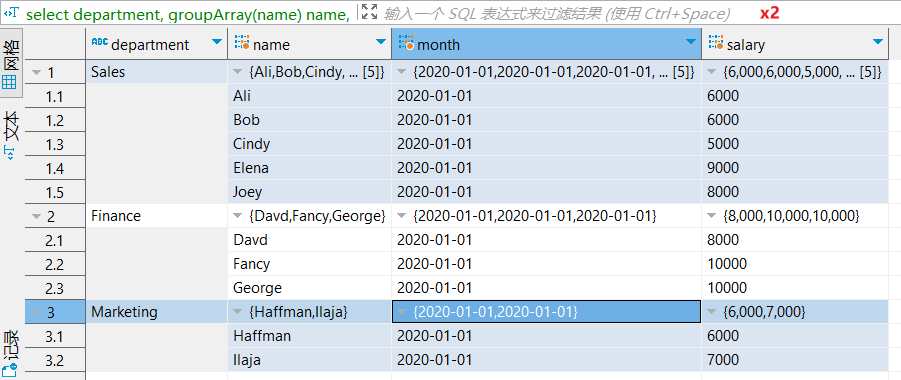
select
name_, department, month_, wage_sort, rank, sum_wage
from (
select
department,
groupArray(name) name,
groupArray(month) month,
groupArray(salary) salary
from default.employee_salary_l
group by department
) x2
array join
arraySort((x, y) -> -y, name, salary) as name_,
arraySort((x, y) -> -y, month, salary) as month_,
arraySort((x) -> -x, salary) as wage_sort,
arrayCumSum(arraySort((x) -> -x, salary)) as sum_wage,
arrayEnumerate(arraySort((x) -> -x, salary)) AS rank
x2
最终结果集
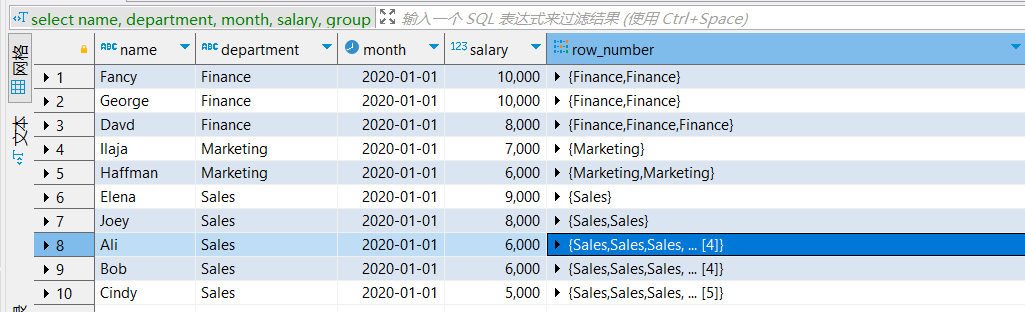
groupArray(field)
- 使用方法
select
name, department, month, salary,
groupArray( department ) OVER (partition by department ORDER BY salary desc) AS row_number
from default.employee_salary_l
SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1;
2.3 同比/环比
J 经典场景
CASE : 基于开/关事件明细表对设备分组、并基于事件时间动态分段,统计设备动态分段内时长(最大事件时间-最小事件时间)
- 原理: 利用SUM开窗函数 对0/1的累计,实现动态分段
SUM(segement_flag) over (partition by device_id order by event_time asc) as segement
- 具体应用:
- 基于开/关事件,计算照明时长
- 基于上线/下线事件,计算用户在线时长、设备联网时长
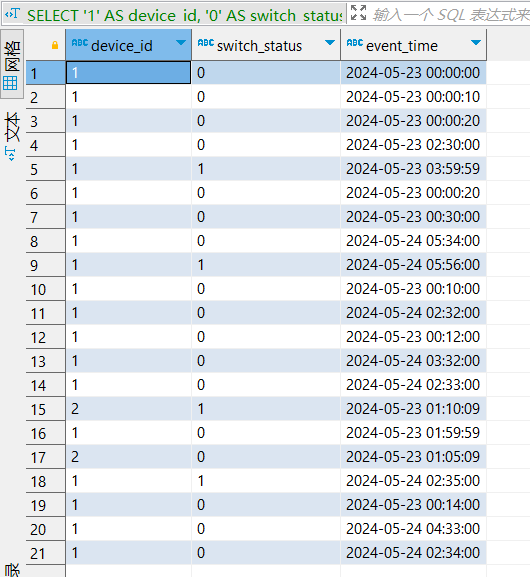
样例数据集
-- ods_device_switch_event
SELECT '1' AS device_id, '0' AS switch_status, toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:00')) AS event_time
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:10'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:20'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:20'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:10:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:12:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:14:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:30:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:59:59'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 02:30:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 03:59:59'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:32:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:33:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:34:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:35:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 03:32:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 04:33:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 05:34:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 05:56:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '2', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:05:09'))
UNION ALL SELECT '2', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:10:09'))
- ods_device_switch_event
实现SQL
WITH
ods_device_switch_event AS (
SELECT '1' AS device_id, '0' AS switch_status, toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:00')) AS event_time
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:10'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:20'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:00:20'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:10:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:12:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:14:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 00:30:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:59:59'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 02:30:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 03:59:59'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:32:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:33:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:34:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 02:35:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 03:32:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 04:33:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 05:34:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '1', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-24 05:56:00'))
UNION ALL SELECT '2', '0', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:05:09'))
UNION ALL SELECT '2', '1', toString(toDateTime('2024-05-23 01:10:09'))
)
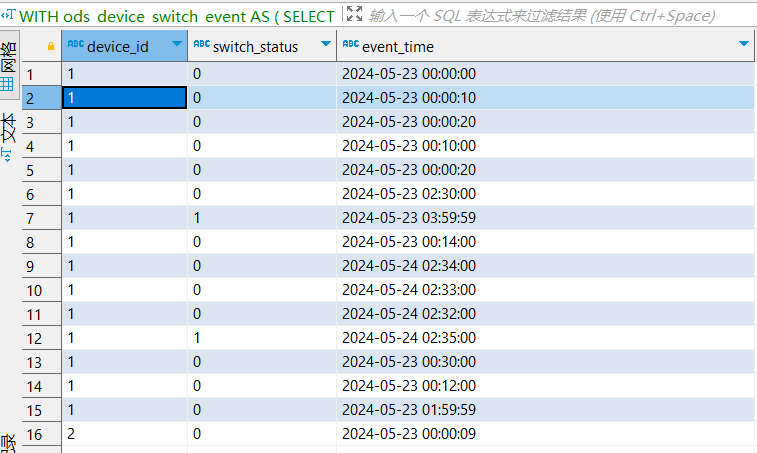
, tmp_x1 as (
select
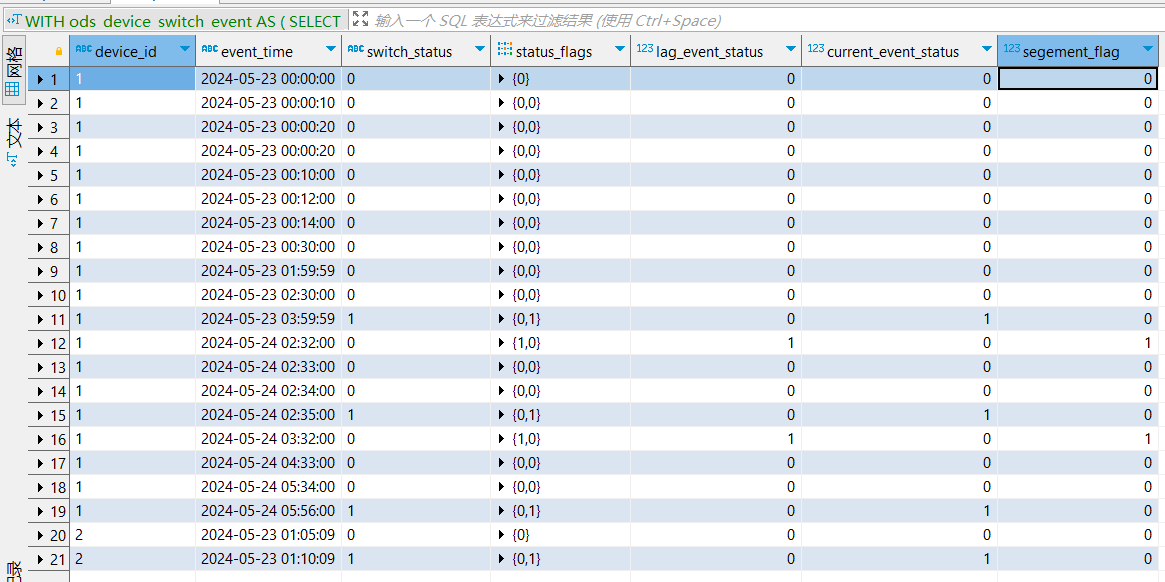
device_id,event_time,switch_status -- switch_status : 事件类型/事件状态(0:开事件、1:关事件)
,groupArray(toInt8(switch_status)) over (PARTITION BY device_id ORDER BY event_time ASC Rows BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND current row) as status_flags
-- 第1个元素: 最近1次事件(上一条事件)的事件状态,第2个元素:当前事件的事件状态
from ods_device_switch_event
-- WINDOW w1 as (PARTITION BY device_id ORDER BY event_time ASC Rows BETWEEN 1 PRECEDING AND current row)
order by device_id,event_time asc
)
, tmp_x2 as (
select
device_id,event_time,switch_status,status_flags
,arrayElement(status_flags,1) as lag_event_status -- 数组内第1个元素
,arrayElement(status_flags,2) as current_event_status -- 数组内第2个元素
,if((current_event_status - lag_event_status) >= 0, 0, 1) as segement_flag -- 动态分段的标志位(值为1,即 当前动态段的第1个元素,但后续其他元素为0)
from tmp_x1
)
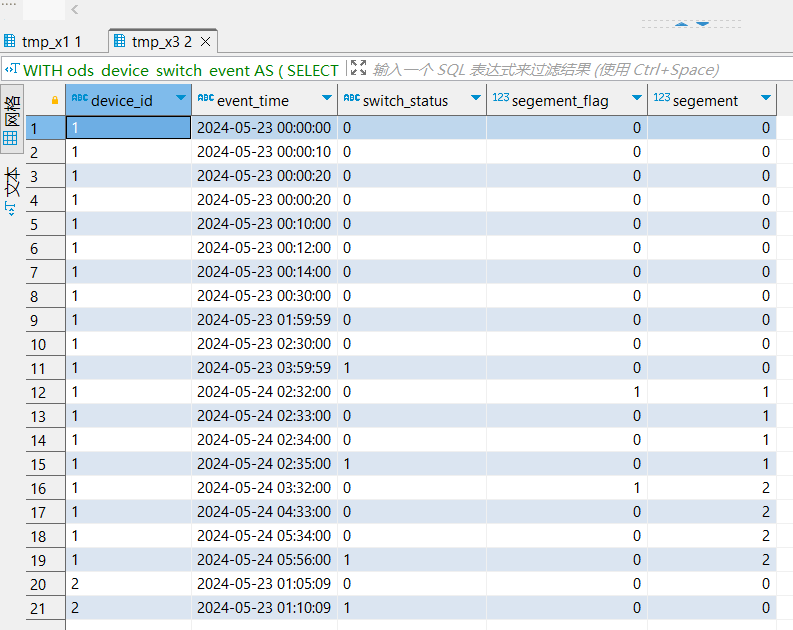
, tmp_x3 as (
select
device_id,event_time , switch_status
, segement_flag
, SUM(segement_flag) over (partition by device_id order by event_time asc) as segement
-- 动态分段的划分结果 (属于本段内的元素,要么全部为0,要么全部为1; 若动态段内全0,则:各元素始终累计为0;若动态段内首个元素为个1、其他元素必为0,则:各元素始终累计为1)
from tmp_x2
)
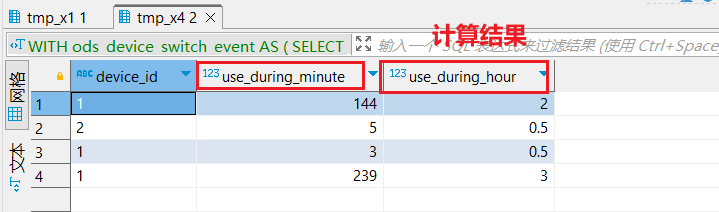
, tmp_x4 as (
select
device_id
, dateDiff('minute',toDateTime(min(event_time)), toDateTime(max(event_time))) as use_during_minute -- 使用时长(单位:分钟)
, multiIf(
use_during_minute >= 0 and use_during_minute < 30,0.5,use_during_minute >= 31 and use_during_minute < 60, 1
,use_during_minute >= 360,6
,FLOOR(use_during_minute/60)
) as use_during_hour -- 使用时长(单位:小时)
from tmp_x3
group by device_id,segement
)
-- select * from ods_device_switch_event
-- select * from tmp_x1 SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
-- select * from tmp_x2 SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
-- select * from tmp_x3 SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
select * from tmp_x4 SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1
-- 注: SETTINGS allow_experimental_window_functions = 1 | clickhouse 21.3 开启试验特性 : 开窗函数
-
tmp_x1
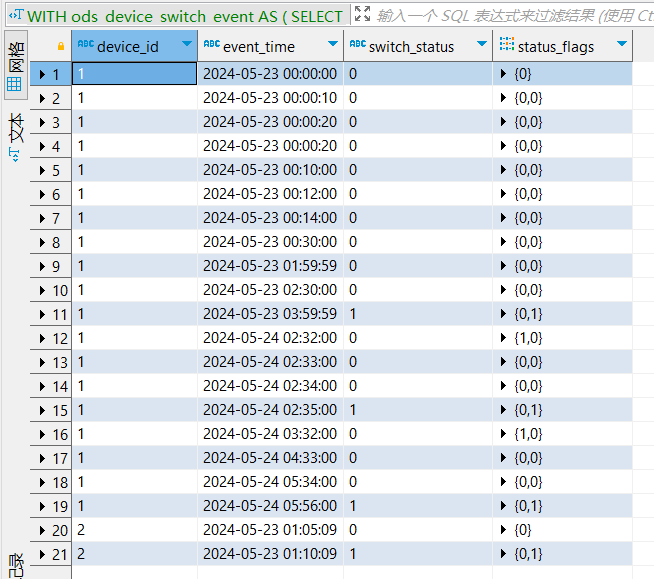
-
tmp_x2
-
tmp_x3
-
tmp_x4
X 参考文献
- windows functions - clickhouse
- clickhouse--开窗函数(window function)的用法 - CSDN 【推荐】
- clickhouse--Window Functions 窗口函数概念讲解及实际使用示例 - CSDN
- SQL窗口函数的使用 - CSDN
- Hive--开窗函数--窗口聚合函数:SUM、AVG、COUNT、MAX、MIN - CSDN
- SQL知识补充:窗口函数 - CSDN
- clickhouse--Window Functions 窗口函数概念讲解及实际使用示例 - CSDN 【推荐】
- SQL窗口函数的使用 - CSDN 【推荐】
- 【SQL】使用SQL查询制作分区间/分段统计的思路 - CSDN
- 使用SQL查询实现分区间/分段统计。该sql使用常存在于报表的制作,统计数据的计算,大屏数据展示等场景。通常我们会面对一类需求,将一组或一批或一张表的数据,根据某一字段按照分段、分区间(有时是自定义区间)的形式,进行汇总统计,计算相关数值、占比等。
- 这些场景的特点是:不同于常规的分组统计,可以根据某一字段直接使用group by进行分组统计,而是一个区间范围,且区间范围可能大小不一(需动态划分)。无法直接使用group by分组统计。

本文链接: https://www.cnblogs.com/johnnyzen
关于博文:评论和私信会在第一时间回复,或直接私信我。
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
日常交流:大数据与软件开发-QQ交流群: 774386015 【入群二维码】参见左下角。您的支持、鼓励是博主技术写作的重要动力!