MySQL常用代码片段
概述
每次想要实现一个功能时,总是百度Google,挺浪费时间的,于是整理得到此文。持续更新中。
字符串截取函数
length
length(str):返回str的长度,如果是中文,一个字符会当作3个字符长度
char_length
length(str):返回str的长度,一个字符就是一个字符长度,不管是否为中英文
select length('2022-核心KPI-签约成交vintage') l1, char_length('2022-核心KPI-签约成交vintage') l2;
-- 输出:
-- l1, l2
-- 34, 22
left
left(str, length),根据length指定的长度取str从第一个字符开始的子串,length不能为负数。
select left('www.google.com', 3);-- www
right
right(str, length),根据length指定的长度取str从最后一个字符开始的子串,length不能为负数。
select right('www.google.com', 3);-- com
substring
substring(str, pos, [len]):从str的第pos个字符开始,取len个字符;len如果不指定,则取第pos个字符开始的所有字符;pos如果为负数,则表示倒数。
select substring('www.google.com', 5);-- google.com
select substring('www.google.com', 5, 6);-- google
select substring('www.google.com', -3, 3);-- com
mid
等价于substring。
substr
等价于substring。
locate
locate(substr, str),返回子串substr在字符串str第一个出现的位置,如果substr不是在str里面,返回0。
select locate('google', 'www.google.com');-- 4
select locate('baidu', 'www.google.com');-- 0
position
position(substr IN str)等价于locate(substr, str)。
select position('google' in 'www.google.com');--5
substring_index
用于截取字符串:substring_index(str, delim, count)
- str:要处理的字符串
- delim:分隔符
- count:计数
实例:
count是正数,从左往右,第N个分隔符的左边的全部内容
select substring_index('www.google.com', '.', 1);-- www
select substring_index('www.google.com', '.', 2);-- www.google
count是负数,从右往左,第N个分隔符的右边的全部内容
select substring_index('www.google.com', '.', -1);-- com
select substring_index('www.google.com', '.', -2);-- google.com
怎么取中间的google?从两个方向截取:
select substring_index(substring_index('www.google.com', '.', -2), '.', 1);-- google
concat
concat(str1, str2, ...):将若干个字符串按照顺序拼接起来
常用于like查询:select user_id from user where username like concat('%', 'johnny', '%');
SELECT concat('My', NULL, 'QL');-- null
concat_ws
concat_ws(separator, str1, str2, ...):将若干个字符串按照顺序通过separator拼接起来
SELECT concat_ws(',', 'My', 'SQL');-- My,SQL
group_concat
group_concat():用于将若干行结果集合并输出为一行字符串,separator默认是,,可替换为指定的分隔符:
select group_concat(login_name) from user;--aa,bb
select group_concat(login_name SEPARATOR ';') from user;--aa;bb
如果想要对输出的结果进行排序和去重咋处理:
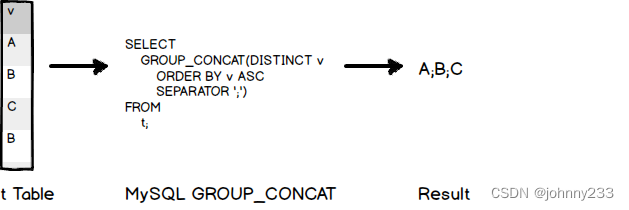
- DISTINCT子句用于在连接分组之前消除组中的重复值
- ORDER BY子句允许在连接之前按升序或降序排序值,默认升序
- SEPARATOR指定在组中的值之间插入的文字值
GROUP_CONCAT函数忽略NULL值,如果找不到匹配的行,或所有参数都为NULL值,则返回NULL;GROUP_CONCAT函数返回二进制或非二进制字符串,这取决于参数。 默认情况下,返回字符串的最大长度为1024。如果您需要更多的长度,可以通过在SESSION或GLOBAL级别设置group_concat_max_len系统变量来扩展最大长度。
其他
重置自增ID最大值
MySQL的表的主键ID可以手动更改(登录用户有权限的条件下)
为了让主键ID不出现大片的空缺,可以更改主键自增ID,前提是表里面不能有大于这个主键ID的记录,如果有,需要先删除才能执行成功:
alter table dataset auto_increment = 20315;
统计字段中某一字符串出现的次数
统计MySQL表某个字段里某个字符串关键词出现的次数,比如数据集执行SQL里sum出现的次数:
SELECT (LENGTH(json_extract(`data_json`, '$.query.sql')) -
LENGTH(REPLACE(json_extract(`data_json`, '$.query.sql'), 'sum', ''))) / LENGTH('sum') AS count
FROM dataset where dataset_id = 8432;
思路:先计算原始执行SQL,即$.query.sql的长度,再统计替换掉关键词sum后执行SQL的长度,两者相减,除以sum的长度,就得到字符串出现的次数。
查询字段里含有大(小)写字母的记录
select loginName from user WHERE CAST(loginName AS BINARY) RLIKE '[A-Z]';
字段类型不一致时join查询
在表里用户ID定义为varchar类型,在另一个表里面定义为int类型。两个表之间如何join关联查询?
表t_role_user定义如下:
create table t_role_user (
id int identity (10) not null primary key nonclustered,
role_id int not null,
user_id int not null constraint idx_nonclustered unique comment '用户ID'
)
表t_user定义如下:
create table t_user
(
id2 int identity (10) not null primary key nonclustered,
user_name varchar(50),
id varchar(100) comment '用户ID'
)
如上两张表就是之前的开发人定义的表结构。
现在需要join查询具有某个角色的全部用户,常规思路:
select tu.user_name from t_user tu
left join t_role_user tru on tu.id = tru.user_id
where tru.role_id = 905405;
但是由于两个表的字段类型不一致,这样join是查询不到数据的。注:SQL Server会自动进行类型转换处理,可以查询。
解决方法不难想到,或者稍微Google一下,就知道可以通过cast函数来实现。至于类型转换,有2个思路:
int转成varchar:
select tu.user_name from t_user tu
left join t_role_user tru ON right('000000' + cast(tru.user_id as varchar(6)), 6) = tu.id
where tru.role_id = 905405;
varchar转换成int:
select tu.user_name from t_user tu
left join t_role_user tru ON cast(tu.id as int) = tru.user_id
where tru.role_id = 905405;
注:user_id是6位数字,且是唯一值,业务意义:员工工号。
列更新
如,http更新为https:
UPDATE <table> SET <field> = replace(field, 'http://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.baidu.com');
常用于批量更新数据,洗数据:
// 优化字段命名方式为驼峰命名
UPDATE dataset SET data_json = replace(data_json, 'mongokey', 'mongoKey');
// data_json见名知义是json string,其中sql字段为多段SQL,以`;`分隔,删除多余空SQL子句,查询时无需转义,update洗数据时需要加上转义字符
UPDATE dataset SET data_json = replace(data_json, ';\\n;', ';')
where json_unquote(json_extract(data_json, '$.query.sql')) like '%;\n;%';
列统计
有如下经过简化的建表语句:
create table execlog
(
id bigint(11) auto_increment primary key,
model_id bigint(11) null comment '任务Id',
model_type tinyint(2) not null comment '任务类型',
exec_status tinyint(2) null comment '执行状态0-失败,1-成功,2-处理中, 3-延时'
);
用于记录若干个任务执行结果,任务Id即为model_id字段,exec_status表示执行结果。
现在想要统计全部任务执行失败率降序情况:
select model_id,
count(*) as cnt,
count(case when exec_status = 0 then model_id end) as failed_cnt,
count(case when exec_status = 0 then model_id end) / count(*) * 100 as failed_rate
from execlog e
group by model_id
order by failed_rate desc;
统计最近20次连续执行未成功过一次的情况:
select model_id, group_concat(e.exec_status) as totalStatus
from execlog e
left join dataset d on e.model_id = d.dataset_id
where d.isactive = 1
and d.cron_exp_status = 1
and e.model_type = 2
group by e.model_id
HAVING totalStatus not LIKE '%1%'
and length(totalStatus) > 40
;
查询重复数据取其中一条
SELECT a.*
FROM channle_sourceid a,
(
SELECT MAX(id) as id
FROM channle_sourceid
GROUP BY channel_id, source_id, id) b
WHERE a.id = b.id
ORDER BY a.id DESC
删除重复数据,仅保留索引(id)最小的一条数据
硬删除:
delete
from role_res
where role_res_id in (
select role_res_id
from (
select max(role_res_id) as role_res_id
from role_res
group by role_id, res_type, res_id, permission
having count(*) > 1
) dt
);
逻辑删除:
update role_res set is_active = 0
where role_res_id in (
select role_res_id
from (
select max(role_res_id) as role_res_id
from role_res
group by role_id, res_type, res_id, permission
having count(*) > 1
) dt
);
备注:
网络上流传着另一种写法:上面的in改为not in,max改为min,这种写法其实是有问题的,那些没有重复的数据也会被删除。
但是这种方法,也不是没有毛病,如果有3条以上的重复记录,上面的in ... max写法需要多次执行才能将重复的数据删除。
结论:使用in ... max方式。至少目前没有找到更好的写法。
添加constraint限制
alter table role_res add constraint uniq_role_res_type_id unique (role_id, res_type, res_id);
指定字段加前缀
加前缀000:
update user_role set user_id = concat('000', user_id) where length(user_id) = 3;
指定字段加后缀
加后缀000:
update user_role set user_id = concat(user_id, '000') where length(user_id) = 3;
指定字段去掉前缀
从左数第二位之前的字符去掉;包括第二位:
update user_role set user_id = right(user_id , length(user_id ) - 2) where length(user_id) = 3;
指定字段去掉后缀
从右数第二位之后的字符去掉;包括第二位:
update user_role set user_id = left(user_id , length(user_id ) - 2) where length(user_id) = 3;
获取时间毫秒数
MySQL表字段定义:
inserttime datetime default CURRENT_TIMESTAMP not null comment '插入时间',
-- 取秒则无需乘以1000
select ROUND(UNIX_TIMESTAMP(inserttime) * 1000) from tb1;
更新cron+3小时
背景,有这么一张数据集定时调度执行表(省略其他字段):
create table iview_new.dataset
(
dataset_id bigint auto_increment primary key comment '主键,数据集ID',
datasource_id bigint not null comment '数据集依赖的数据源ID',
dataset_name varchar(100) not null comment '数据集名称',
cron_exp varchar(200) not null comment 'cron表达式'
);
需求,对数据表里面的cron表达式hour数批量增加3小时,即延后3小时执行。
洗数据脚本如下:
UPDATE dataset SET cron_exp = CONCAT(
substring_index(cron_exp, ' ', 2),
' ',
substring_index(substring_index(cron_exp, ' ', 3), ' ', -1) + 3,
' ',
substring_index(cron_exp, ' ', -3)
)
where dataset_id = 8429
-- hour小于12
and substring_index(substring_index(cron_exp, ' ', 3), ' ', -1) < 12;
参考
- search-group-concat-using-like
- string-functions
- group_concat
- Java解析cron表达式
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/21303189/can-i-left-join-between-column-types-int-and-varchar
- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2397161/how-to-convert-int-to-char-with-leading-zeros





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix