java基础之HashMap
一、
public class HashMap<K,V> extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable {
//数组的默认初始化容量为:16
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 1 << 4; // aka 16
//数组的最大扩容到:2的30次方
static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;
//默认的扩容因子0.75
static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;
//当链表上节点数大于8时,将链表转为红黑树----因为链表节点数大于8时,会影响其查询效率
static final int TREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 8;
//当红黑树上节点数小于6时,将红黑树转为链表
static final int UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD = 6;
//存储节点元素的数组
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
//数组元素个数
transient int size;
//每次扩容和更改map结构的次数
transient int modCount;
//需要扩容的临界值:当大于(初始化容量*0.75)【临界值时】,以2倍进行扩容
int threshold;
}
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash; // 哈希值
final K key; // 键
V value; // 值
Node<K,V> next; // 下一个节点地址
}
//计算哈希值 = key(键).hashCoder()
putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
//核心代码
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//可以对数组进行初始化和扩容操作
n = (tab = resize()).length;
//通过(n - 1) & hash找到所在数组相应位置
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
//当hash值和key都相等时,会将链表中第一个元素(数组中的结点)的内容进行覆盖
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p; //内容覆盖
//黑红数结构
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
//链表结构
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
//当链表的节点数超过8时,将链表转为红黑树
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
if (++size > threshold)
//数组扩容
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
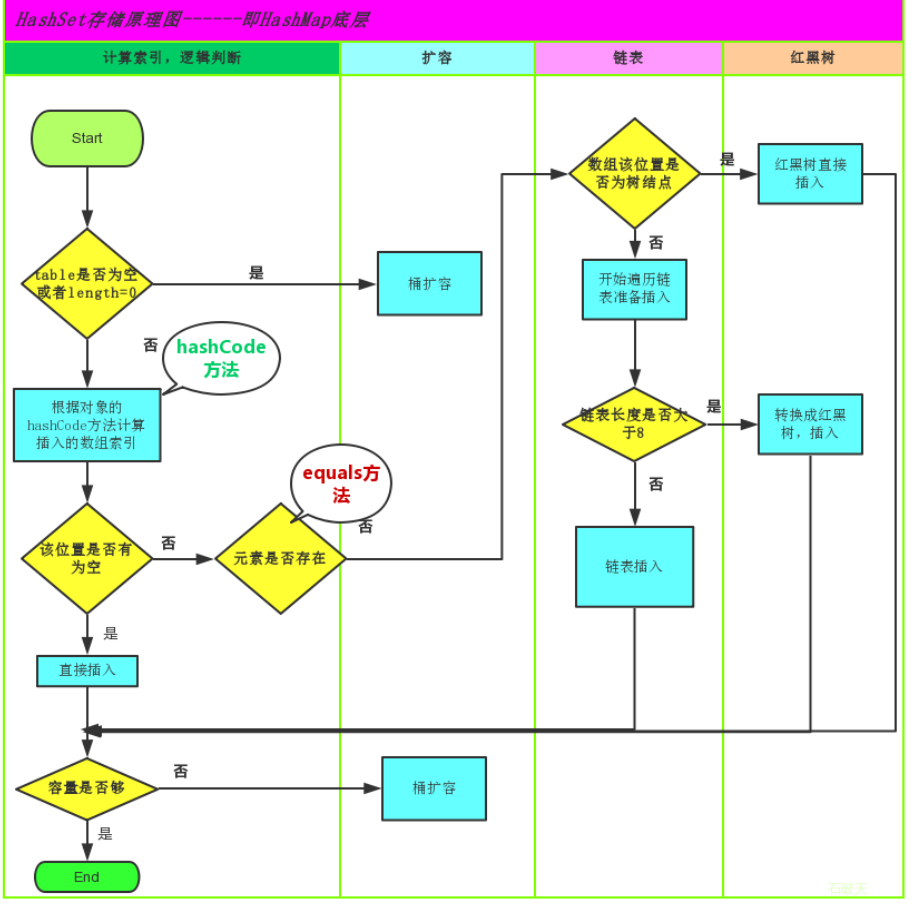
计算 key.hashCode(),得到原始哈希值 h(32位整数)。
将 h 无符号右移 16 位(h >>> 16),相当于将高 16 位移动到低 16 位,高 16 位补 0。
将原始哈希值 h(高位hash值) 和 右移后的值(低位hash值)进行 异或运算(^),得到最终哈希值。
注意:
-
(1)数组原本的位置为空时
-
(2)数组原本的位置为不为空时,且下面是链表的结构
-
(3)数组原本的位置为不为空时,且下面是红黑树的结构
-
(4)若是key,hash值均相同时,进行内容的覆盖
图表:
二、
Map集合的特点:
1.Map集合是一个双列集合,一个元素包含两个值(一个Key,一个Value)
2.Map集合元素中,Key和value的数据类型可以相同,也可以不同
3.Map集合元素中,Key不允许重复,Value可以重复
4.Map集合元素中,Key与Value是一一对应的
Map集合的方法:
public V put(K key, V value) : 把指定的键与指定的值添加到Map集合中。
public V remove(Object key) : 把指定的键 所对应的键值对元素 在Map集合中删除,返回被删除元素的值。
boolean containsKey(Object key) 判断集合中是否包含指定的键。
public V get(Object key) 根据指定的键,在Map集合中获取对应的值。
public Set<K> keySet() : 获取Map集合中所有的键,存储到Set集合中。
public Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet() : 获取到Map集合中所有的键值对对象的集合(Set集合)。
java.utils.HashMap<k,v>集合 implements Map<k,v>接口
HashMap的特点:
1.HashMap集合底层是哈希表,查询速度相当快
JDK1.8前:数组 + 链表
JDK1.8后:数组 + 链表/红黑树(链表的长度超过8),提高查询效率
2.HashMap集合是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致
java.utils.LinkeHashMap<k,v>集合 extends HashMap<k,v>集合
LinkeHashMap的特点:
1.LinkeHashMap集合底层是哈希表 + 链表(保证迭代的顺序)
2.LinkeHashMap集合是一个有序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序一致
java.utils.Hashtable<k,v>集合 implements Map<k,v>接口
Hashtable的特点:
1.Hashtable集合底层是哈希表
2.Hashtable集合是一个无序的集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序有可能不一致
HashMap与Hashtable区别:
1.HashMap可以存储null键,null值,Hashtable不允许存null键,null值
2.HashMap线程不安全,Hashtable方法使用synchronized修饰,线程安全的
三、
Map集合例子:
public class MapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,String> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put("秦问天","莫倾城");
hashMap.put("莫凡","书音");
hashMap.put("张小凡","碧瑶");
hashMap.put("唐三","小舞");
System.out.println(hashMap.containsKey("莫凡"));
System.out.println(hashMap.get("张小凡"));
System.out.println("..............");
System.out.println(hashMap.remove("唐三"));
System.out.println("..............");
for (String key : hashMap.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
System.out.println(hashMap.get(key));
System.out.println("..............");
}
System.out.println("..............");
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : hashMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println("key:"+entry.getKey()+"......"+"value:"+entry.getValue());
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号