java基础之集合(List)、Properties集合
一、ArrayList集合的方法
1、public void add(int index, E element) : 将指定的元素,添加到该集合中的指定位置上。
2、public E get(int index) :返回集合中指定位置的元素。
3、public E remove(int index) : 移除列表中指定位置的元素, 返回的是被移除的元素。
4、public E set(int index, E element) :用指定元素替换集合中指定位置的元素,返回值的更新前的元素
AarrayList方法中add()方法添加元素时的扩容源码
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //扩容倍数:new = old + old/2
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
例子:
public class ListTest {
// private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; 长度为0的空数组
// private int size; 集合的长度
// transient Object[] elementData 集合存储元素的数组
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> array = new ArrayList<>();
array.add(1);
array.add(4);
array.add(2);
array.add(7);
System.out.println(array.get(3));
System.out.println(array.set(1,8));
System.out.println("排序....");
/*
array.sort(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
*/
//使用lambda表达式简写
array.sort((a,b)->{
return b-a;
});
System.out.println(array);
}
}
二、linkeList集合的add()方法的源码
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //数据
Node<E> next; //前一个节点
Node<E> prev; //后一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
transient int size = 0; //集合元素个数
transient Node<E> first; //第一个节点
transient Node<E> last; //最后一个节点
例如:集合已有 a、b两个节点,现在添加 c节点
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last; //没有new c节点前,b为last 节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //先在new c节点,那么相对c节点而言,b节点为则为前节点
last = newNode; //然后将c节点视为最后节点
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode; //那么相对b节点而言,c节点为则为后节点
size++;
modCount++;
}
}
linkeList自身特有的方法:
public void addFirst(E e) :将指定元素插入此列表的开头。
public void addLast(E e) :将指定元素添加到此列表的结尾。
public E getFirst() :返回此列表的第一个元素。
public E getLast() :返回此列表的最后一个元素。
public E removeFirst() :移除并返回此列表的第一个元素。
public E removeLast() :移除并返回此列表的最后一个元素。
public E pop() :从此列表所表示的堆栈处弹出一个元素。
public void push(E e) :将元素推入此列表所表示的堆栈。
public boolean isEmpty() :如果列表不包含元素,则返回true
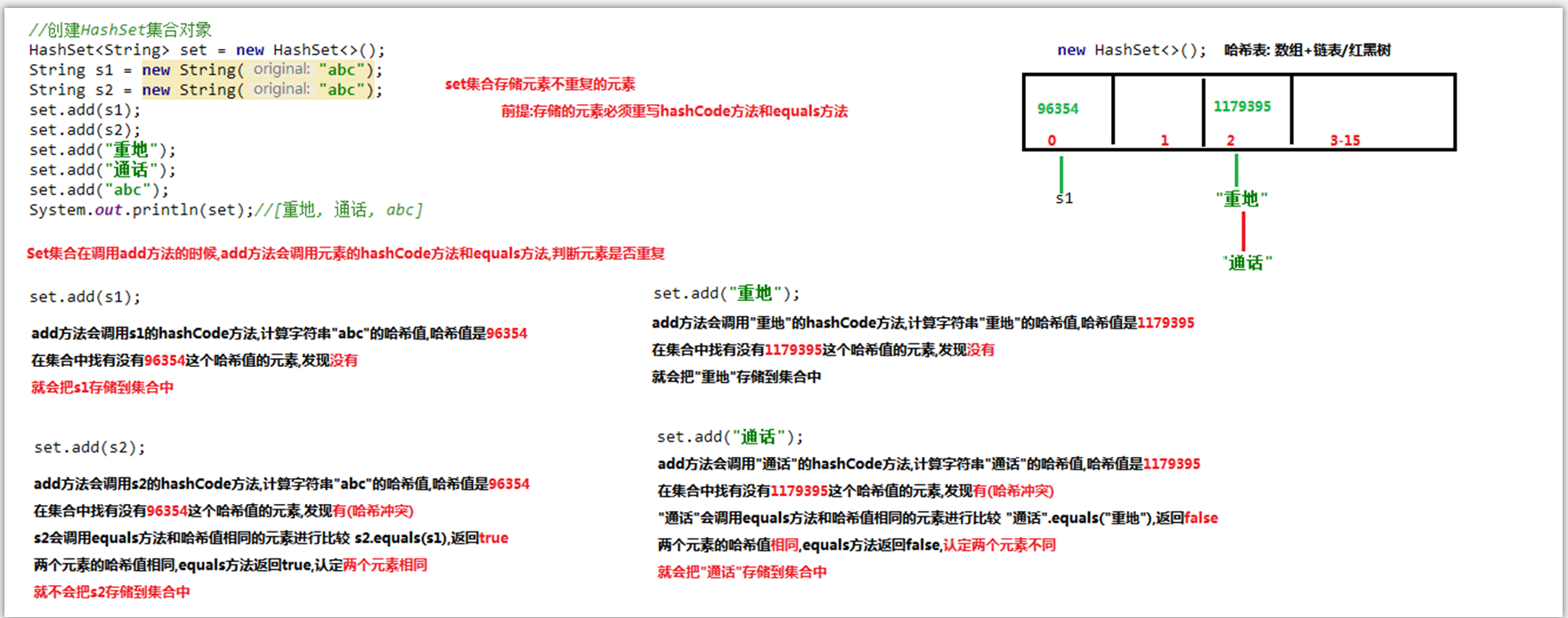
三、Set集合中HashSet集合
java.util.HashSet<E> implements Set<E>
HashSet特点:
1.不允许存储重复元素
2.没有索引,所以不能使用普通的for循环遍历
3.无序集合,存储元素和取出元素的顺序不一致
4.底层是一个哈希表,查询效率快
JDK1.8前:组数 + 链表
JDK1.8后:组数 + 链表/红黑树(链表节点数超过8时),为了提高查询效率
哈希值:是一个十进制的整数,(就是对象的一个临时逻辑虚拟地址,不是真实的物理地址)
在object类有一个方法,可以获取哈希值
int hashCode():返回对象的哈希值,不重写的情况下是由系统自动分配的
例子:
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashSet hashSet = new HashSet();
Student stu1 = new Student("ab");
Student stu2 = new Student("ab");
hashSet.add(stu1);
hashSet.add(stu2);
hashSet.add("ab");
System.out.println(stu1.hashCode());
System.out.println(stu2.hashCode());
System.out.println(hashSet);
}
}
图解:
四、Set集合中LinkeHashSet集合
java.util.LinkeHashSet<E> extends HashSet<E>
LinkeHashSet特点:
1.LinkeHashSet集合底层哈希表 + 链表(保证迭代顺序)
1.LinkeHashSet集合:有序,不可重复
例子:
public class LinkeHashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashSet<Integer> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
linkedHashSet.add(2);
linkedHashSet.add(4);
linkedHashSet.add(6);
linkedHashSet.add(2);
System.out.println(linkedHashSet);
}
}
五、Properties集合
java.util.Properties集合 extends Hashtable<k,v> implements Map<k,v>
Properties 类表示了一个持久的属性集。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。
Properties集合是一个唯一和IO流相结合的集合
可以使用Properties集合中的方法store,把集合中的临时数据,持久化写入到硬盘中存储
可以使用Properties集合中的方法load,把硬盘中保存的文件(键值对),读取到集合中使用
属性列表中每个键及其对应值都是一个字符串。
Properties集合是一个双列集合,key和value默认都是字符串
使用Properties集合存储数据,遍历取出Properties集合中的数据
Properties集合是一个双列集合,key和value默认都是字符串
Properties集合有一些操作字符串的特有方法
Object setProperty(String key, String value) 调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。
String getProperty(String key) 通过key找到value值,此方法相当于Map集合中的get(key)方法
Set<String> stringPropertyNames() 返回此属性列表中的键集,其中该键及其对应值是字符串,此方法相当于Map集合中的keySet方法
例子:
public class PropertiesTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties prop = new Properties();
//使用setProperty往集合中添加数据
prop.setProperty("赵丽颖","168");
prop.setProperty("迪丽热巴","165");
prop.setProperty("古力娜扎","160");
//使用stringPropertyNames把Properties集合中的键取出,存储到一个Set集合中
Set<String> set = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for (String s : set) {
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(prop.getProperty(s));
}
}
}



