SpringBoot(四):java从配置文件中取值的方式
一、SpringBoot项目中取yaml配置文件中的值
application.yaml
test:
url: localhost:8080
name: root
password: 123456
val:
a: 1
b: 2
c: 3
TestConfig.class
@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "test") public class TestConfig { private String url; private String name; private String password; private Map<String, Object> val; public TestConfig() { } public TestConfig(String url, String name, String password, Map<String, Object> val) { this.url = url; this.name = name; this.password = password; this.val = val; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Map<String, Object> getVal() { return val; } public void setVal(Map<String, Object> val) { this.val = val; } @Override public String toString() { return "TestConfig{" + "url='" + url + '\'' + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", val=" + val + '}'; } }
测试类:
@SpringBootTest class Springboot02ConfigApplicationTests { private TestConfig testConfig; @Autowired public void setTestConfig(TestConfig testConfig) { this.testConfig = testConfig; } @Test void contextLoads() { System.out.println(testConfig); } }
测试结果:

在SpringBoot项目中取得yaml配置文件的内容,核心就是@ConfigurationProperties注解。
二、取properties配置文件中的值
jms.properties
url=localhost:8081
name=root1
password=1234567
TestConfig.class
@Component @PropertySource("classpath:jms.properties") public class TestConfig { @Value("${url}") private String url; @Value("${name}") private String name; @Value("${password}") private String password; private Map<String, Object> val; public TestConfig() { } public TestConfig(String url, String name, String password, Map<String, Object> val) { this.url = url; this.name = name; this.password = password; this.val = val; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public Map<String, Object> getVal() { return val; } public void setVal(Map<String, Object> val) { this.val = val; } @Override public String toString() { return "TestConfig{" + "url='" + url + '\'' + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", password='" + password + '\'' + ", val=" + val + '}'; } }
测试结果:
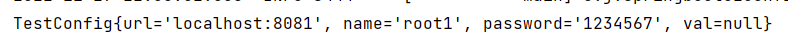
核心注解@Value,这里用到@propertySource是为了不不使用默认的application配置文件,若为application.properties,可不使用此注解。
三、普通项目中得到properties配置文件中的值
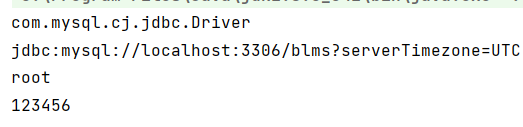
jdbc.properties
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blms?serverTimezone=UTC
name=root
password=123456
测试类
public class test { public static void main(String[] args) { ResourceBundle bundle = ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc"); String driver = bundle.getString("driver"); String url = bundle.getString("url"); String name = bundle.getString("name"); String password = bundle.getString("password"); System.out.println(driver + "\n" + url + "\n" + name + "\n" + password); } }
(本文仅作个人学习用,如有纰漏敬请指正)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号