springBoot入门和web开发例子
一、SpringBoot的主要优点:
1.快速整合第三方框架,无需配置文件。几乎可以是零配置的开箱即用(out-of-the-box)。开发者能够更加专注于业务逻辑
2.内置http容器(Tomcat、Jetty),最终以java应用程序进行执行
二、实现原理:
1.Maven依赖传递

<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies>
2.SpringBoot的Web组件,默认集成的是SpringMVC框架。SpringMVC是控制层。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController // @EnableAutoConfiguration 作用 开启自动装备(默认是true) public class IndexController { // 1.在微服务情况,基本上都在类上加上@RestController 目的?返回json格式。
//2.@RestController注解相当于@ResponseBody + @Controller合在一起的作用。如果只是使用@RestController注解Controller,则Controller中的方法无法返回jsp页面,或者html,配置的视图解析器 InternalResourceViewResolver不起作用,返回的内容就是Return 里的内容。使用传统方式返回json //@RestController 修饰的类下的所有方法,全部都是返回josn格式,这样的话不用在方法上加上@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/index1") public String index() throws InterruptedException { return "v6.0"; } // // 思考:如何启动? 使用main启动 // public static void main(String[] args) { // // 告诉SpringBoot 程序入口 默认端口号是8080 // SpringApplication.run(IndexController.class, args); // } }
3.内置Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat() 对象

@RestController @EnableAutoConfiguration public class HelloController { @RequestMapping("/hello") public String index() { return "Hello World"; } public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(HelloController.class, args); } }
三、StringMVC
@Controller:表示这个类是SpringMVC 里的Controller,DispatchServlet会自动扫面这个类。效果:用这个注解,通过return的String类型的数据,视图解析器可以解析jsp,html页面,并且跳转到相应页面。目的就是为了能访问,所以是必须的。
@ResponseBody :可作用于类或者方法,表示该方法的返回结果直接写入 HTTP response body 中,适用于返回JSON,XML。无法返回jsp页面,或者html。一般通过Ajax程序来获取数据。一般只写在方法上面,因为这个注解是为了,区别同一个类,不同的方法到底是返回页面还是返回数据!
@RestController: 表示 Controller+ ResponseBody(类上只用ResponseBody是不能被访问的,必须要有Controller),同样不能返回jsp和html。如果是只用于返回json的类,一般用这种。
@RequestMapping(“/url”):作用在 Controller的方法,表示映射地址
四、实践
资源访问
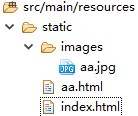
Springboot 的工作目录resources下面有两个文件夹,static 和 templates。
1.Static 文件夹下面放静态资源
可以直接访问(默认页面index.html)可以用浏览器直接访问,localhost:81默认页面 为 static/index.html。
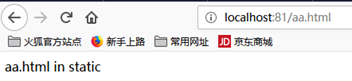
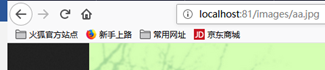 http://localhost:81/images/aa.jpg http://localhost:81/aa.html
http://localhost:81/images/aa.jpg http://localhost:81/aa.html
2.templates 文件夹下面放动态页面(使用Freemarker模板引擎渲染web视图)

<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
加入thymeleaf依赖,就可以通过java代码转发到目录下面的页面。
Java代码如下:
@Controller //表示转发到页面 public class TTController { @RequestMapping("/test") public String test() { return "test";//访问的是templates下面的test.html } }

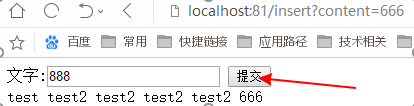
下面是动态页面演示:
java代码
@Controller public class TextController { @Autowired private TextServiceImpl textServiceImpl; @RequestMapping("/text") public String text(Model model,HttpServletRequest request){ List<Text> textList = textServiceImpl.findAll(); model.addAttribute("textList",textList); return "text"; } @RequestMapping("/insert") public String insert(String content,Model model,HttpServletRequest request){ Text text = new Text(); text.setContent(content); Integer i = textServiceImpl.insert(text); if(i==1){ System.out.println("插入成功"); } List<Text> textList = textServiceImpl.findAll(); model.addAttribute("textList",textList); return "text"; } }
@Service //自动注册到Spring容器,不需要再在applicationContext.xml配置 public class TextServiceImpl implements TextService{ @Autowired private TextMapper textMapper; public List<Text> findAll(){ return textMapper.findAll(); } @Transactional public Integer insert(Text text) { int insertResult = textMapper.insert(text.getContent()); System.out.println("insertResult="+insertResult); return insertResult; } }
public interface TextService { public Integer insert(Text text); public List<Text> findAll(); }
@Repository //用于标注数据访问组件 public interface TextMapper { @Select("SELECT * FROM TEXT") List<Text> findAll(); /* @Select("SELECT * FROM USER WHERE NAME = #{name}") User findByName(@Param("name") String name); */ @Insert("INSERT INTO TEXT (content) VALUE(#{content})") int insert(@Param("content") String content); }
src\main\resources\templates\text.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title>文本显示</title> <script type="text/javascript"></script> <body > <form action="/insert"> 文字:<input type="text" name="content"/> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> <thead> <tr th:each="text:${textList}"> <td th:text="${text.content}"></td> </tr> </thead> </body> </html>
main方法
//@EnableAutoConfiguration 作用在于让 Spring Boot 根据应用所声明的依赖来对 Spring 框架进行自动配置 //@ComponentScan(basePackages = "wull.tool.*") 控制器扫包范围 @SpringBootApplication //这个表示上面两行 //@ComponentScan("/") @MapperScan("wull.*") public class ToolApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(ToolApplication.class, args); System.out.println("启动成功" ); } }





【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步