[hdu4498]离散化,simpson求积分
题意: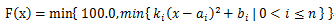 ,求这个函数在[0,100]上的图像的长度。
,求这个函数在[0,100]上的图像的长度。
思路:采用离散化的思想,求出所有交点 ,把交点排序,把[0,100]分成若干个小区间,这样原函数在每个小区间上的图像属于某一个二次函数或者是一条直线。如何确定属于哪个呢?比如对于某个区间,令m为这个小区间的中点,求出所有的函数在m点的函数值的最小值,对应的那个函数就是答案。如果最小值>=100则说明是直线。那么问题就变成了求二次函数曲线在区间[L,R]上的长度。这个可以转化为积分来算,令f(x)为原函数的倒数,则答案就是sqrt(1+f(x)*f(x))在[L,R]上的积分了。求积分可以用自适应辛普森法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 | #include <iostream>#include <cstdio>#include <cstring>#include <cstdlib>#include <queue>#include <cmath>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int maxn = 123;#define _x2(a) (a) * (a)namespace Integral { double (*func)(double); double simpson(double a, double b) { double c = a + (b - a) / 2; return (func(a) + func(c) * 4 + func(b)) * (b - a) / 6; } double asr(double a, double b, double eps, double A) { double c = a + (b - a) / 2; double L = simpson(a, c), R = simpson(c, b); if (fabs(L + R - A) < 15 * eps) return L + R + (L + R - A) / 15; return asr(a, c, eps / 2, L) + asr(c, b, eps / 2, R); } double getans(double a, double b, double eps, double (*f)(double)) { func = f; return asr(a, b, eps, simpson(a, b)); }};int k[maxn], a[maxn], b[maxn];int A[maxn], B[maxn], C[maxn];int ga, gb, gc, cnt;double pos[12345];double F(double x) { return ga * x * x + gb * x + gc;}double f(double x) { return sqrt(1.0 + _x2(2.0 * ga * x + gb));}void add(double x) { if (x > 0 && x < 100) pos[cnt ++] = x;}int main() {#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);#endif // ONLINE_JUDGE int T, n; cin >> T; while (T --) { cnt = 0; pos[cnt ++] = 0; pos[cnt ++] = 100; cin >> n; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { cin >> k[i] >> a[i] >> b[i]; A[i] = k[i]; B[i] = -2 * k[i] * a[i]; C[i] = k[i] * a[i] * a[i] + b[i]; if (b[i] < 100) { double buf = sqrt((100.0 - b[i]) / k[i]); add(a[i] + buf); add(a[i] - buf); } } for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j ++) { ga = A[i] - A[j]; gb = B[i] - B[j]; gc = C[i] - C[j]; if (ga == 0) { if (gb != 0) add(-1.0 * gc / gb); continue; } int d = gb * gb - 4 * ga * gc; if (d >= 0) { add((-gb - sqrt(1.0 * d)) / 2.0 / ga); if (d) add((-gb + sqrt(1.0 * d)) / 2.0 / ga); } } } sort(pos, pos + cnt); double ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i ++) { double L = pos[i - 1], R = pos[i]; if (R - L < 1e-10) continue; double M = (L + R) / 2, minval = 100; int target = -1; for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) { ga = A[i]; gb = B[i]; gc = C[i]; if (F(M) < minval) { minval = F(M); target = i; } } if (~target) { ga = A[target]; gb = B[target]; gc = C[target]; ans += Integral::getans(L, R, 1e-8, f); } else ans += R - L; } printf("%.2f\n", ans); } return 0;} |


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号