一、连接池的描述图片如下:
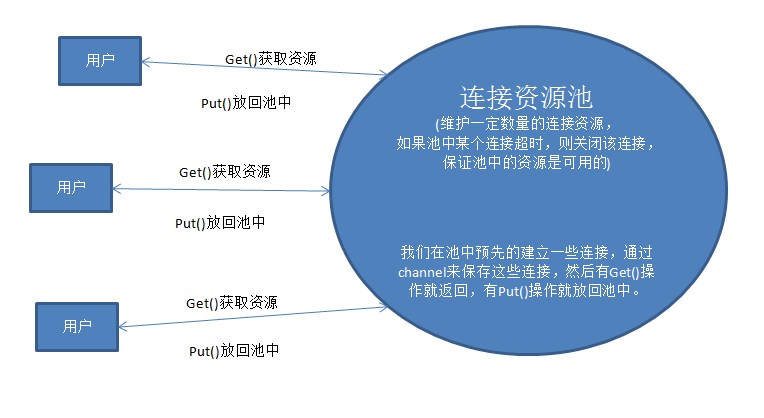
二、连接池代码如下:
package main;
import (
"time"
"sync"
"errors"
"net"
"fmt"
)
//频繁的创建和关闭连接,对系统会造成很大负担
//所以我们需要一个池子,里面事先创建好固定数量的连接资源,需要时就取,不需要就放回池中。
//但是连接资源有一个特点,我们无法保证连接长时间会有效。
//比如,网络原因,人为原因等都会导致连接失效。
//所以我们设置一个超时时间,如果连接时间与当前时间相差超过超时时间,那么就关闭连接。
//只要类型实现了ConnRes接口中的方法,就认为是一个连接资源类型
type ConnRes interface {
Close() error;
}
//工厂方法,用于创建连接资源
type Factory func() (ConnRes, error)
//连接
type Conn struct {
conn ConnRes;
//连接时间
time time.Time;
}
//连接池
type ConnPool struct {
//互斥锁,保证资源安全
mu sync.Mutex;
//通道,保存所有连接资源
conns chan *Conn;
//工厂方法,创建连接资源
factory Factory;
//判断池是否关闭
closed bool;
//连接超时时间
connTimeOut time.Duration;
}
//创建一个连接资源池
func NewConnPool(factory Factory, cap int, connTimeOut time.Duration) (*ConnPool, error) {
if cap <= 0 {
return nil, errors.New("cap不能小于0");
}
if connTimeOut <= 0 {
return nil, errors.New("connTimeOut不能小于0");
}
cp := &ConnPool{
mu: sync.Mutex{},
conns: make(chan *Conn, cap),
factory: factory,
closed: false,
connTimeOut: connTimeOut,
};
for i := 0; i < cap; i++ {
//通过工厂方法创建连接资源
connRes, err := cp.factory();
if err != nil {
cp.Close();
return nil, errors.New("factory出错");
}
//将连接资源插入通道中
cp.conns <- &Conn{conn: connRes, time: time.Now()};
}
return cp, nil;
}
//获取连接资源
func (cp *ConnPool) Get() (ConnRes, error) {
if cp.closed {
return nil, errors.New("连接池已关闭");
}
for {
select {
//从通道中获取连接资源
case connRes, ok := <-cp.conns:
{
if !ok {
return nil, errors.New("连接池已关闭");
}
//判断连接中的时间,如果超时,则关闭
//继续获取
if time.Now().Sub(connRes.time) > cp.connTimeOut {
connRes.conn.Close();
continue;
}
return connRes.conn, nil;
}
default:
{
//如果无法从通道中获取资源,则重新创建一个资源返回
connRes, err := cp.factory();
if err != nil {
return nil, err;
}
return connRes, nil;
}
}
}
}
//连接资源放回池中
func (cp *ConnPool) Put(conn ConnRes) error {
if cp.closed {
return errors.New("连接池已关闭");
}
select {
//向通道中加入连接资源
case cp.conns <- &Conn{conn: conn, time: time.Now()}:
{
return nil;
}
default:
{
//如果无法加入,则关闭连接
conn.Close();
return errors.New("连接池已满");
}
}
}
//关闭连接池
func (cp *ConnPool) Close() {
if cp.closed {
return;
}
cp.mu.Lock();
cp.closed = true;
//关闭通道
close(cp.conns);
//循环关闭通道中的连接
for conn := range cp.conns {
conn.conn.Close();
}
cp.mu.Unlock();
}
//返回池中通道的长度
func (cp *ConnPool) len() int {
return len(cp.conns);
}
func main() {
cp, _ := NewConnPool(func() (ConnRes, error) {
return net.Dial("tcp", ":8080");
}, 10, time.Second*10);
//获取资源
conn1, _ := cp.Get();
conn2, _ := cp.Get();
//这里连接池中资源大小为8
fmt.Println("cp len : ", cp.len());
conn1.(net.Conn).Write([]byte("hello"));
conn2.(net.Conn).Write([]byte("world"));
buf := make([]byte, 1024);
n, _ := conn1.(net.Conn).Read(buf);
fmt.Println("conn1 read : ", string(buf[:n]));
n, _ = conn2.(net.Conn).Read(buf);
fmt.Println("conn2 read : ", string(buf[:n]));
//等待15秒
time.Sleep(time.Second * 15);
//我们再从池中获取资源
conn3, _ := cp.Get();
//这里显示为0,因为池中的连接资源都超时了
fmt.Println("cp len : ", cp.len());
conn3.(net.Conn).Write([]byte("test"));
n, _ = conn3.(net.Conn).Read(buf);
fmt.Println("conn3 read : ", string(buf[:n]));
//把三个连接资源放回池中
cp.Put(conn1);
cp.Put(conn2);
cp.Put(conn3);
//这里显示为3
fmt.Println("cp len : ", cp.len());
cp.Close();
}
三、8080服务端代码如下:
package main;
import (
"net"
"io"
"log"
)
func handler(conn net.Conn) {
for {
io.Copy(conn, conn);
}
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", ":8080");
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err);
}
for {
conn, err := lis.Accept();
if err != nil {
continue;
}
go handler(conn);
}
}
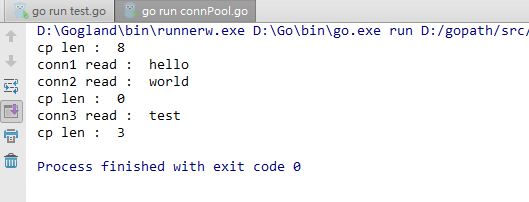
测试结果如下:
版权声明:博主文章,可以不经博主允许随意转载,随意修改,知识是用来传播的。


