零基础学习java------22----------社交用户分析案例,反射(概念,获取配置文件的3种方式),手机号段上网日志流量统计
1. 社交用户关系数据分析案例
数据样例:

需求:
1. 获取每个人的好友个数,并按照好友数量排序
2. 获取任意两个人的共同好友
3.获取所有人两两共同好友
1.
public class SimpleFriendsDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); try ( // 获取缓冲字符流,读取并切割数据 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\javafile\\simpleFriend.txt")); ){ String line = null; while((line = br.readLine())!= null) { String[] split = line.split(":"); String uid = split[0]; String[] fsn = split[1].split(","); // 以uid为key,好友数量为value存入map map.put(uid,fsn.length); } // 获取每个人的好友数量 Set<Entry<String, Integer>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Entry<String, Integer> entry : entrySet) { System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"好友的个数为"+entry.getValue()); } // 安好友数量进行排序(降序) ArrayList<Entry<String, Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>(entrySet); Collections.sort(list,(o1,o2)->o2.getValue()-o1.getValue()); System.out.println(list); // [F=7, A=6, E=5, G=5, H=5, B=4, C=4, D=4, O=4, K=3, L=3, M=3, I=2, J=2] } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2.
错误代码:
public class SimpleFriendsDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try ( // 获取缓冲字符流,读取并切割数据 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\javafile\\simpleFriend.txt")); ){ String line1 = br.readLine(); String line2 = br.readLine(); String uid1 = line1.split(":")[0]; String[] fs1 = line1.split(":")[1].split(","); String uid2 = line2.split(":")[0]; String[] fs2 = line2.split(":")[1].split(","); List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList(fs1); List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList(fs2); list1.retainAll(list2); System.out.println(uid1+"和"+uid2+"的共同好友是:"+list1); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
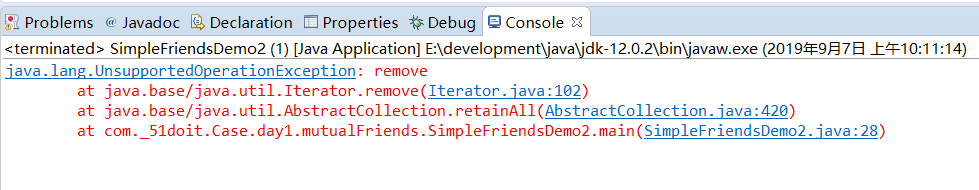
原因:由asList得到的集合是不能进行增删操作的,即数据不能更改,而retainAll方法对list1中的元素是进行了操作的,所以此处要创建一个新的集合将list1中的数据传进去,正确代码如下
public class SimpleFriendsDemo2 { public static void main(String[] args) { try ( // 获取缓冲字符流,读取并切割数据 BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("E:\\javafile\\simpleFriend.txt")); ){ String line1 = br.readLine(); String line2 = br.readLine(); String uid1 = line1.split(":")[0]; String[] fs1 = line1.split(":")[1].split(","); String uid2 = line2.split(":")[0]; String[] fs2 = line2.split(":")[1].split(","); List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList(fs1); List<String> list2 = Arrays.asList(fs2); List<String> list11 = new ArrayList<>(list1); list11.retainAll(list2); if(list11 != null && list11.size()>0) { System.out.println(uid1+"和"+uid2+"的共同好友是:"+list11); //A和B的共同好友是:[C, E] } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } }
方法封装形式的代码

/** * 获取两个人的共同好友 数据 文件 * 获取 Map<String,List<String>> * 方法的封装 获取一个数据 传递 返回数据 void * @author hang */ public class TestDemo2 { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { //Map<String, List<String>> map = getUserFsInfo(); getSameFriends("A", "B"); } /** * 获取任意两个人的共同好友 * @param uid1 好友1 id * @param uid2 好友2 id * @return 返回这两个人的好友列表数据 */ public static List<String> getSameFriends(String uid1 , String uid2){ //map 获取map Map<String, List<String>> map = getUserFsInfo(); // 分别获取两个人的好友列表信息 List<String> list1 = map.get(uid1); List<String> list2 = map.get(uid2); //获取两个人的共同好友 将两个集合的共同数据存储在前面集合中 list1.retainAll(list2); //如果两个人的好友存在交集 返回 if(list1!=null && list1.size()>0){ // 说明有数据 两个好友有交集 System.out.println(uid1 +"和" + uid2 +"的共同好友是"+list1); return list1; } return null; } /** * 获取存储用户以及用户好友列表的map数据 * @return */ private static Map<String, List<String>> getUserFsInfo() { Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); try (BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/好友.txt"));) { String line = null; while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) { String[] split = line.split(":"); String uid = split[0]; String fsstr = split[1]; String[] arr = fsstr.split(","); // 将数组 长度 list长度固定 元素不允许修改 List<String> list = Arrays.asList(arr); // 创建新的list存储数据 ArrayList<String> fsList = new ArrayList<>(list); //强每个人对应的好友列表存储在map集合中 map.put(uid, fsList); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } //调用方法返回 一个存储每个人和其对应的每个人的好友列表的map集合 return map; } }
3.

public class TestDemo3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //每个人所对应的好友列表 Map<String, List<String>> map = getUserFsInfo(); //获取所有的用户uid List<String> list = getAllUsers(); //嵌套循环 获取前一个和后一个人的用户uid for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) { // 第一个遍历到倒数第二个 String uid1 = list.get(i);// A List<String> fs1 = map.get(uid1); for (int j = i + 1; j < list.size(); j++) { // 从第二个遍历到最后同一个 String uid2 = list.get(j); // B c d e f List<String> fs2 = map.get(uid2); //由于 交集的方法会对源集合的数据发生改变 所以要创建新的集合 List<String> fs = new ArrayList<>(fs2); // 交集 fs.retainAll(fs1); if (fs != null && fs.size() > 0) { System.out.println(uid1 + "和" + uid2 + "的好友是" + fs); } } } // list遍历方式1 /* * for (String string : list) { System.out.println(string); List<String> * fs = map.get(string); } */ } /** * 获取所有的用户列表 * * @return */ private static List<String> getAllUsers() { //创建list集合存储所欲的用户的uid List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); // 读取数据 将 uid 放在list中 try (BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/好友.txt"));) { String line = null; while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) { String[] split = line.split(":"); String uid = split[0]; //将所有的用户存储在list集合中 list.add(uid); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } return list; } /** * 获取存储用户以及用户好友列表的map数据 * * @return */ private static Map<String, List<String>> getUserFsInfo() { Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>(); try (BufferedReader bfr = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/好友.txt"));) { String line = null; while ((line = bfr.readLine()) != null) { String[] split = line.split(":"); String uid = split[0]; String fsstr = split[1]; String[] arr = fsstr.split(","); // 将数组 长度 list长度固定 元素不允许修改 List<String> list = Arrays.asList(arr); // 创建新的list存储数据 ArrayList<String> fsList = new ArrayList<>(list); // 强每个人对应的好友列表存储在map集合中 map.put(uid, fsList); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } // 调用方法返回 一个存储每个人和其对应的每个人的好友列表的map集合 return map; } }
2. 反射(此处结合day20的内容一起看)
2.1 一些概念
反射是一种动态获取类信息的技术,可以根据类的全类型,类的字节码,class属性获取所有字节码的Class类,在java的高级编程和javaee框架中应用广泛
获取到字节码对象以后,可以获取类的任意内容,可以操作类中的任意方法、属性和构造方法等等
对于动态获取类信息的理解:此处的动态体现在使用字符串获取对象(全类名的形式),字符串可以从文件里读取,那么修改文件内容字符串会变化,跟着对象也就变化了
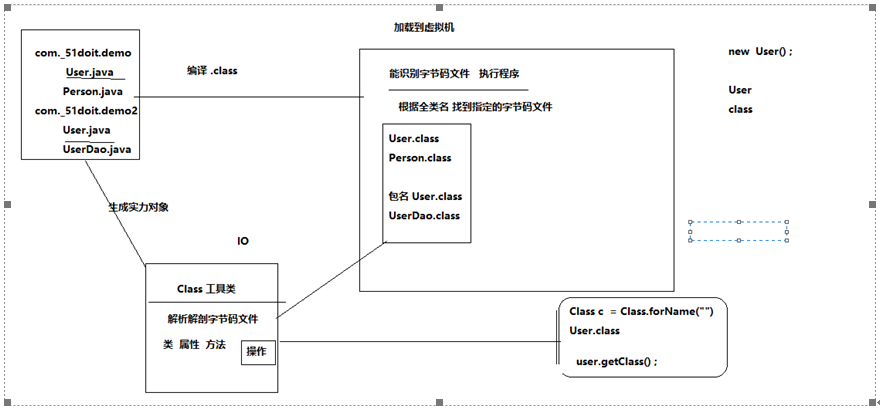
Class类是一个解析.class文件的工具类,类似于IO类可以读取内容。Class类解析了字节码文件就能知道里面的所有内容了,就可以依此为基础创建对应字节码的java对象了
2.2 读取项目配置文件的三种方式
(1). 使用本项目的类获取类加载器
Properties p = new Properties(); p.load(ReadProperties.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("bean.properties"));
(2). 获取配置文件的输入流
Properties p = new Properties(); p.load(new FileInputStream(new File("conf/bean.properties")));
(3). 使用ResourceBundle类
ResourceBundle b = ResourceBundle.getBundle("bean"); String name = b.getString("className");
3. 日志流量案例
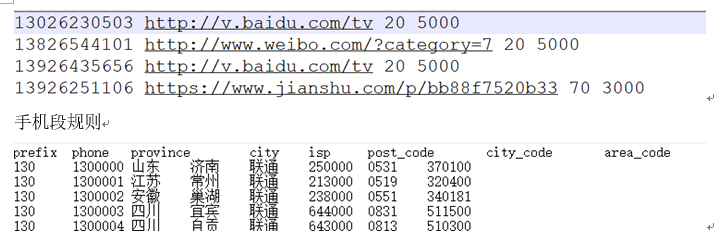
在给的http.log日志文件中,是电信运营商记录用户上网访问某些网站行为的日志记录数据,一条数据中有多个字段用空格分隔。例如:"18611132889 http://v.baidu.com/tv 20 5000"是一条上网行为,第一个字段代表手机号码,第二个字段代表请求网站的URL,第三个字段代表请求发送的数据即上行流量(20字节),第四个字段代表服务器响应给用户的流量即下行流量(5000字节)。
部分数据截图:
需求:
(1)计算出用户上网流量总流量(上行+下行)最高的网站Top3

public class Test1 { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { //域名 key:站点 value:总流量 Map<String , Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/http.log")); String line = null ; while((line = br.readLine())!=null){ //System.out.println(line); String[] split = line.split("\\s"); if(split.length>=4){ String url = split[1] ; String[] split2 = url.split("\\."); if(split2.length==3){ String phone = split[0] ; String downData = split[2] ; String upData = split[3] ; String yuming = split2[1] ; Integer sum = Integer.parseInt(upData)+Integer.parseInt(downData); //判断map中是否有相同的key值 /*1 * if(map.containsKey(yuming)){ sum += map.get(yuming); map.put(yuming, sum) ; } map.put(yuming, sum) ; *2 map.get("")返回value 根据value判断 */ Integer res = map.getOrDefault(yuming, 0); sum+=res ; map.put(yuming, sum); } } } //对map数据进行排序操作 br.close(); } }
(2)根据个的手机号段归属地规则,计算出总流量最高的省份Top3
首先定义一个javabean用来存储各个字段

public class PhoneBean { private String prefix; private String phone; private String province; private String city; private String isp; public PhoneBean() { } public void set(String prefix, String phone, String province, String city, String isp) { this.prefix = prefix; this.phone = phone; this.province = province; this.city = city; this.isp = isp; } public String getPrefix() { return prefix; } public void setPrefix(String prefix) { this.prefix = prefix; } public String getPhone() { return phone; } public void setPhone(String phone) { this.phone = phone; } public String getProvince() { return province; } public void setProvince(String province) { this.province = province; } public String getCity() { return city; } public void setCity(String city) { this.city = city; } public String getIsp() { return isp; } public void setIsp(String isp) { this.isp = isp; } }
定义工具类(PhoneUtils)用来将各个字段存入javabean中

public class PhoneUtils { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { getPhoneList(); } /** * 将数据号段数据封装在map中 * 以手机的前七位作为key * 对应的一行数据的javaBean作为value * @return * @throws FileNotFoundException * @throws IOException */ private static Map<String,PhoneBean> getPhoneMap() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { Map<String,PhoneBean> map = new HashMap<>() ; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/手机号段规则.txt")); String line = null; br.readLine();// 去除头信息 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); String[] split = line.split("\\s"); String prefix = split[0]; String phone = split[1]; String province = split[2]; String city = split[3]; String isp = split[4]; PhoneBean bean = new PhoneBean(); // 将每行数据封装在javabean bean.set(prefix, phone, province, city, isp); // 将数据放在map中 map.put(phone, bean) ; } br.close(); return map; } /** * 将数据号段数据封装在list中 * @return * @throws FileNotFoundException * @throws IOException */ private static List<PhoneBean> getPhoneList() throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { List<PhoneBean> list = new ArrayList<>(); BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/手机号段规则.txt")); String line = null; br.readLine();// 去除头信息 while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); String[] split = line.split("\\s"); String prefix = split[0]; String phone = split[1]; String province = split[2]; String city = split[3]; String isp = split[4]; PhoneBean bean = new PhoneBean(); // 将每行数据封装在javabean bean.set(prefix, phone, province, city, isp); // 将数据放在list中 list.add(bean); } br.close(); return list; } }
获取总流量最高的省份Top3

public class Test2 { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Map<String, PhoneBean> map = PhoneUtils.getPhoneMap();//10万 //存储运算结果的map 省key 流量value Map<String , Integer> pMap = new HashMap<>() ; BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/http.log")); String line ; while((line = br.readLine())!=null){ //System.out.println(line); String[] split = line.split("\\s"); String tel = split[0]; //流量数据 String upData = split[2]; String downData = split[3]; //根据手机号的前七位获取对应的手机数据 PhoneBean bean = map.get(tel.substring(0, 7)); //手机号对应的省份 String province = bean.getProvince(); Integer sum = pMap.getOrDefault(province, 0); sum+=Integer.parseInt(upData)+Integer.parseInt(downData) ; pMap.put(province, sum); } Set<String> ksys = pMap.keySet(); for (String string : ksys) { System.out.println(string+":"+pMap.get(string)); } //map排序 br.close(); } }
此处的代码每次访问都要加载(但实际加载一次就行了),数据量若特别大的话,就耗费时间,解决办法是,使用静态代码块(随类的加载而加载一次)
Map<String, PhoneBean> map = PhoneUtils.getPhoneMap();//10万
换成静态代码块,如下
static Map<String, PhoneBean> static{ map = PhoneUtils.getPhoneMap(); }
(3)根据给的手机号段运营商规则,计算出总流量最高的运营商Top3

public class Test3 { @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[] args) { try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/data/http.log"));){ Map<String, PhoneBean> map = PhoneUtils.getPhoneMap(); Map<String , Integer> iMap = new HashMap<>(); String line ; while((line = br.readLine())!=null){ String[] split = line.split("\\s"); String tel = split[0] ; String up = split[2] ; String down = split[3] ; PhoneBean bean = map.get(tel.substring(0, 7)); String isp = bean.getIsp(); Integer sum = iMap.getOrDefault(isp, 0); sum+=Integer.parseInt(up)+Integer.parseInt(down); iMap.put(isp, sum) ; } //map排序 }catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } }




