数据结构(三):线性表-顺序表,链表
一、 线性表概述
线性表是最简单的一种的数据结构,由若干相同特征的数据元素组成的有限序列
- 在线性表中,若A在B元素前面,称A为B的前驱元素,B称为A的后继元素
- 没有前驱元素的的结点称为线性表的头结点,没有后继元素的结点称为线性表的尾结点
- 线性表按照存储元素的结构,可以分为顺序表和链表
二、 顺序表
2.1基本实现
顺序表是在计算机内存中以数组形式存在的线性表结构,即内存中用一组地址连续的存储单元,依次存储线性表中的元素,使得线性表中的相邻的数据元素存储在相邻的物理内存地址中。
|
public class OrderList<T> {
// 泛型顺序表声明 private T[] eles;
// 顺序表长度 private int N;
/** * 线性表构造方法 * * @param size */ public OrderList(int size) { eles = (T[]) new Object[size]; N = 0; }
/** * 清空顺序表 */ public void clear() { N = 0; }
/** * 是否为空表 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; }
/** * 线性表长度 * * @return */ public int length() { return N; }
/** * 获取i位置的元素 * * @param i * @return * @throws Exception */ public T get(int i) throws Exception { if (i < 0 || i > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); } return eles[i]; }
/** * 向i位置插入元素t * * @param i * @param t * @throws Exception */ public void insert(int index, T t) throws Exception { if (N == eles.length) { throw new Exception("当前表已满"); }
if (index < 0 || index > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); }
for (int i = index; i < N - 1; i++) { eles[i + 1] = eles[i]; }
eles[index] = t;
N++; }
/** * 向线性表插入元素t * * @param t * @throws Exception */ public void insert(T t) throws Exception { if (N == eles.length) { throw new Exception("当前表已满"); }
eles[N++] = t; }
/** * 移除i位置处的元素,并返回该元素 * * @param i * @return * @throws Exception */ public T remove(int index) throws Exception { if (index < 0 || index > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); }
T data = eles[index];
for (int i = index; i < N - 1; i++) { eles[i] = eles[i + 1]; }
N--;
return data; }
/** * 返回线性表中首次出现元素的序号 * * @param t * @return * @throws Exception */ public int indexOf(T t) throws Exception { if (t == null) { throw new Exception("查找的元素不合法"); }
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { if(t.equals(eles[i])) { return i; } }
return -1; }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { OrderList list = new OrderList(5); list.insert(3); list.insert(2); list.insert(2); list.insert(1); list.insert(4, 5); System.out.println(list.get(2)); System.out.println(list.indexOf(2)); System.out.println(list.get(3)); System.out.println(list.length()); System.out.println(list.isEmpty()); System.out.println(list.remove(2)); System.out.println(list.length()); list.clear(); System.out.println(list.length()); } } |
2.3 遍历
Iterable接口是java 集合框架的顶级接口,实现此接口使集合对象可以通过迭代器遍历自身元素。
|
public class OrderList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
@Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); }
public class MyIterator implements Iterator<T>{
private int cur;
public MyIterator() { this.cur = 0; }
@Override public boolean hasNext() {
return cur < N; }
@Override public T next() { return eles[cur++]; } } |
2.4 容量变化
在使用顺序表的过程中,往往会在声明时初始化一个线性表的容量,那么当往线性表中添加的元素数量大于初始化容量时怎么办?
添加元素
当往顺序表中添加一个新元素时,我们发现此时顺序表中的元素已满,此时我们会创建一个2倍于原顺序表的数组,并将原数组的元素迁移过来,达到数组扩容的效果。

移除元素
当往顺序表中移除一个元素时,发现此时数据元素不足数据容量的1/4,此时我们会创建一个原数据容量1/2的数组,并将原数组的元素迁移过来,达到数组缩容的效果,不会导致空间的浪费
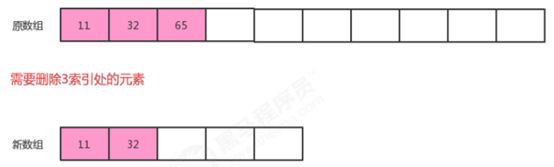
|
package com.data.struct.common.list.order;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class OrderList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
// 泛型顺序表声明 private T[] eles;
// 顺序表长度 private int N;
/** * 线性表构造方法 * * @param size */ public OrderList(int size) { eles = (T[]) new Object[size]; N = 0; }
/** * 清空顺序表 */ public void clear() { N = 0; }
/** * 是否为空表 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; }
/** * 线性表长度 * * @return */ public int length() { return N; }
/** * 获取i位置的元素 * * @param i * @return * @throws Exception */ public T get(int i) throws Exception { if (i < 0 || i > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); } return eles[i]; }
/** * 向i位置插入元素t * * @param i * @param t * @throws Exception */ public void insert(int index, T t) throws Exception { if (N == eles.length) { resize(eles.length * 2); }
if (index < 0 || index > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); }
for (int i = index; i < N - 1; i++) { eles[i + 1] = eles[i]; }
eles[index] = t;
N++; }
/** * 向线性表插入元素t * * @param t * @throws Exception */ public void insert(T t) throws Exception { if (N == eles.length) { resize(eles.length * 2); }
eles[N++] = t; }
/** * 移除i位置处的元素,并返回该元素 * * @param i * @return * @throws Exception */ public T remove(int index) throws Exception { if (index < 0 || index > N ) { throw new Exception("元素索引越界"); }
T data = eles[index];
for (int i = index; i < N - 1; i++) { eles[i] = eles[i + 1]; }
N--;
if(N>0 && N>eles.length/4) { resize(eles.length/2); }
return data; }
/** * 返回线性表中首次出现元素的序号 * * @param t * @return * @throws Exception */ public int indexOf(T t) throws Exception { if (t == null) { throw new Exception("查找的元素不合法"); }
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { if(t.equals(eles[i])) { return i; } }
return -1; }
@Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); }
public class MyIterator implements Iterator<T>{
private int cur;
public MyIterator() { this.cur = 0; }
@Override public boolean hasNext() {
return cur < N; }
@Override public T next() { return eles[cur++]; } }
/** * 改变数组大小 * @param newSize */ private void resize(int newSize) { //中间变量 T[] temp = eles;
eles = (T[]) new Object[newSize];
for(int i=0;i<eles.length;i++) { eles[i] = temp[i]; } }
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { OrderList<Integer> list = new OrderList<Integer>(5); list.insert(3); list.insert(2); list.insert(2); list.insert(1); list.insert(4, 5); System.out.println(list.get(2)); System.out.println(list.indexOf(2)); System.out.println(list.get(3)); System.out.println(list.length()); System.out.println(list.isEmpty()); System.out.println(list.remove(2)); System.out.println(list.length()); // list.clear(); // System.out.println(list.length()); for(Integer t : list) { System.out.println(t); } } } |
三、 链表
上述实现的顺序表查询效率很高,时间复杂度为O(1),但每次增删都伴随着大量的元素移动,增删的时间复杂度为O(n),另一种线性表的结构-链表,可以很好的解决顺序表增删带来的时间损耗问题。
链表是一种物理逻辑上非顺序,非连续的线性存储结构,数据元素存储的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针指向内存地址的链接顺序决定的,链表由一系列的结点组成,结点可以在运行时动态的增删。
链表:
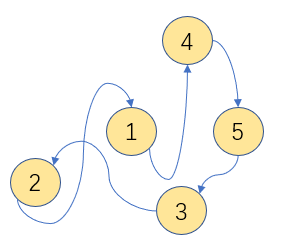
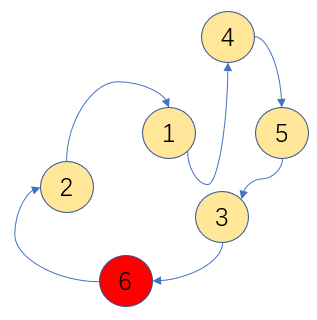
链表结点新增:
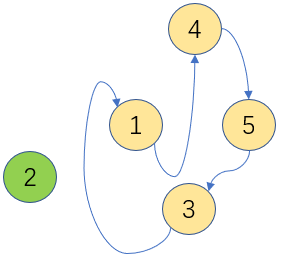
链表结点删除:
3.1 构造链表
|
public class Node<T> {
//结点元素 public T item;
//指向下一个结点 public Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; }
public static void main(String[] args) { Node node1 = new Node(1, null); Node node2 = new Node(2, null); Node node3 = new Node(3, null); Node node4 = new Node(4, null); Node node5 = new Node(5, null); node1.next = node2; node2.next = node3; node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5; } } |
3.2 单向链表
单向链表是链表的一种,由多个结点组成,每个结点包含一个数据域和一个指针域,数据域存放结点的值,指针域用来指向后继结点。
其中,头结点的的数据域为空,尾结点的指针域为空。

|
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
// 声明头结点 public Node head;
// 链表长度 public int N;
public LinkList() { head = new Node<T>(null, null); N = 0; }
/** * 置空线性表 */ public void clear() { head.item = null; head.next = null; N = 0; }
/** * 线性表是否为空 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return N == 0; }
/** * 链表长度 * * @return */ public int length() { return N; }
/** * 往链表具体位置插入元素 * * @param index * @param t */ public void insert(int i, T t) {
if (i < 0 || i > N) { System.out.println("插入位置不合法..."); }
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) { pre = pre.next; }
Node currNode = pre.next;
// 创建新结点,该结点的next指向当前结点 Node newNode = new Node<T>(t, currNode);
pre.next = newNode;
N++; }
/** * 往链表尾结点插入元素 * * @param t */ public void insert(T t) { Node n = head; while (n.next != null) { n = n.next; }
// 构建新的尾结点 Node lastNode = new Node<T>(t, null); n.next = lastNode;
N++; }
/** * 获取具体位置处数据域的值 * * @param index * @return */ public T get(int i) { if (i < 0 || i >= N) { throw new RuntimeException("位置不合法!"); } Node n = head.next; for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) { n = n.next; } return (T) n.item; }
/** * 移除链表元素 * * @param t */ public T remove(int i) { if (i < 0 || i > N) { System.out.println("移除位置非法"); }
Node pre = head;
for (int index = 0; index < i; index++) { pre = pre.next; }
Node currNode = pre.next; pre.next = currNode.next;
N--;
return (T) currNode.item; }
/** * 返回链表中首次出现该元素的位置 * * @param t * @return */ public int indexof(T t) {
Node node = head;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) { node = node.next; if(t.equals(node.item)) { return i; } }
return -1; }
@Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return new MyIterator(); }
public class MyIterator implements Iterator<T> {
Node node;
public MyIterator() { node = head; }
@Override public boolean hasNext() { return head.next != null; }
@Override public T next() { return (T) node.next.item; } }
public static void main(String[] args) { LinkList list = new LinkList<>(); list.insert(1); list.insert(2); list.insert(3); list.insert(4); System.out.println(list.get(3)); } } |
3.3 双向链表
双向链表也是线性表的一种,它由多个结点组成,每个结点由一个数据域和两个指针域组成,其中数据域用于存放结点的数据元素,一个指针域用来指向该结点的前驱结点
一个指针域用来指向该结点的后继结点,头结点的数据域,指向前驱结点的指针域为null,指向后继结点的指针域指向链表的第一个元素,尾结点指向后继结点的指针域为null。

双向链表的构造:
|
public class TWNode<T> {
// 结点元素 public T item;
// 指向前驱的指针域 public TWNode pre;
// 指向后继的指针域 public TWNode next;
public TWNode(T item,TWNode pre, TWNode next) { this.item = item; this.pre = pre; this.next = next; }
public static void main(String[] args) { TWNode twn1 = new TWNode(1, null, null); TWNode twn2 = new TWNode(2, null, null); TWNode twn3 = new TWNode(3, null, null);
twn1.next = twn2;
twn2.pre = twn1; twn2.next = twn3;
twn3.pre = twn2; } } |
双向链表实现代码:
|
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TwoWayList<T> implements Iterable<T> {
//声明头结点 public TWNode head;
//声明尾结点 public TWNode last;
//链表长度 public int N;
public TwoWayList() { last = null; head = new TWNode(null, null, null); N=0; }
/** * 置空线性表 */ public void clear() { last = null; head.next = last; head.pre = null; head.item = null; N=0; }
/** * 线性表是否为空 * * @return */ public boolean isEmpty() { return N==0; }
/** * 链表长度 * * @return */ public int length() { return N; }
/** * 往链表具体位置插入元素 * * @param index * @param t */ public void insert(int i, T t) { if(i<0 || i>N) { System.out.println("插入位置非法..."); }
TWNode pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) { pre = pre.next; }
TWNode currNode = pre.next; TWNode newNode = new TWNode<T>(t, pre, currNode); pre.next = newNode; currNode.pre = newNode;
N++; }
/** * 往链表尾结点插入元素 * * @param t */ public void insert(T t) { if(last == null) { last = new TWNode(t, head, null); head.next = last; }else { TWNode newNode = new TWNode<T>(t, last, null); last.next = newNode; last = newNode; }
N++; }
/** * 获取具体位置处数据域的值 * * @param index * @return */ public T get(int i) { if(i<0 || i>N) { System.out.println("检索位置非法..."); }
TWNode pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) { pre = pre.next; }
return (T) pre.next.item; }
/** * 移除链表元素 * * @param t */ public T remove(int i) { if(isEmpty()) { return null; }
if(i<0 || i>N) { System.out.println("检索位置非法..."); }
TWNode pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++) { pre = pre.next; }
//i位置处的结点 TWNode currNode = pre.next;
//i位置的下一个结点 TWNode currNext = currNode.next;
pre.next = currNext; currNext.pre = pre;
N--;
if(isEmpty()) { last = null; }
return (T) currNode.item; }
/** * 返回链表中首次出现该元素的位置 * * @param t * @return */ public int indexof(T t) { TWNode pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<N;index++) { pre = pre.next; if(t.equals(pre.item)) { return index; } }
return -1; }
/** * 获取双向链表第一个元素 * @return */ public T getFirst() { if(isEmpty()) { return null; }
return (T) head.next.item; }
/** * 获取双向链表第二个元素 * @return */ public T getLast() { if(isEmpty()) { return null; }
return (T) last.item; }
@Override public Iterator<T> iterator() { return null; }
public class MyIterator implements Iterator<T> {
TWNode node;
public MyIterator() { node = head; }
@Override public boolean hasNext() { return node.next != null; }
@Override public T next() { return (T) node.next.item; } }
} |
3.4 循环链表
循环链表,顾名思义,及链表要成环,在单向链表中,尾结点的指针域为null,不指向任何结点,当链表要成环时,让尾结点的指针域指向头结点即可。
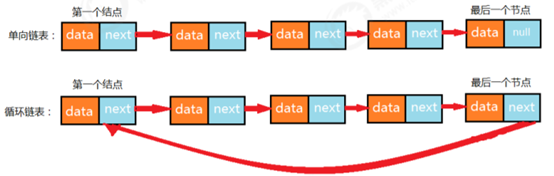
循环链表的构造:
|
public class Node<T> {
//结点元素 public T item;
//指向下一个结点 public Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next) { this.item = item; this.next = next; }
public static void main(String[] args) { Node node1 = new Node(1, null); Node node2 = new Node(2, null); Node node3 = new Node(3, null); Node node4 = new Node(4, null); Node node5 = new Node(5, null); node1.next = node2; node2.next = node3; node3.next = node4; node4.next = node5; node5.next = node1; } } |
3.5 线性表时间复杂度
链表和顺序表的时间复杂度比较:
- get(i)
链表的元素查询,都需要从链表头部开始,往后遍历,直到找到目标元素位置,时间复杂度为O(N),顺序表的元素查询,由于数组元素索引的存在,直接获取索引处元素的值即可,时间复杂度为O(1)
- insert(int i,T t)
链表的插入,每次都需要找到i位置前面处的元素,进行结点的新增和链表的连接操作,时间复杂度为O(N),顺序表的插入,每次都需要找到i位置,并将原i处和其后面的元素向后移动,时间复杂度为O(N)
- remove(int i)
链表的删除,每次都需要找到i位置处的元素,进行链表删除的连接操作,时间复杂度为O(N),顺序表的插入,每次都需要找到i位置,并将原i处后面的元素向前移动,时间复杂度为O(N)
优缺点:
- 相比顺序表,链表的查询效率较低
- 相比顺序表,链表的插入和删除的时间复杂度虽然一样,但由于链表地址空间不连续,不需要事先开辟一段连续地址的空间,也不涉及元素的交换和空间扩容等操作,所以在插入和删除方面,链表是更有优势的
- 涉及增删较多的场景,数据结构用链表,涉及查询较多的场景,则用顺序表最合适。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY