数据结构已学知识总结
思维导图
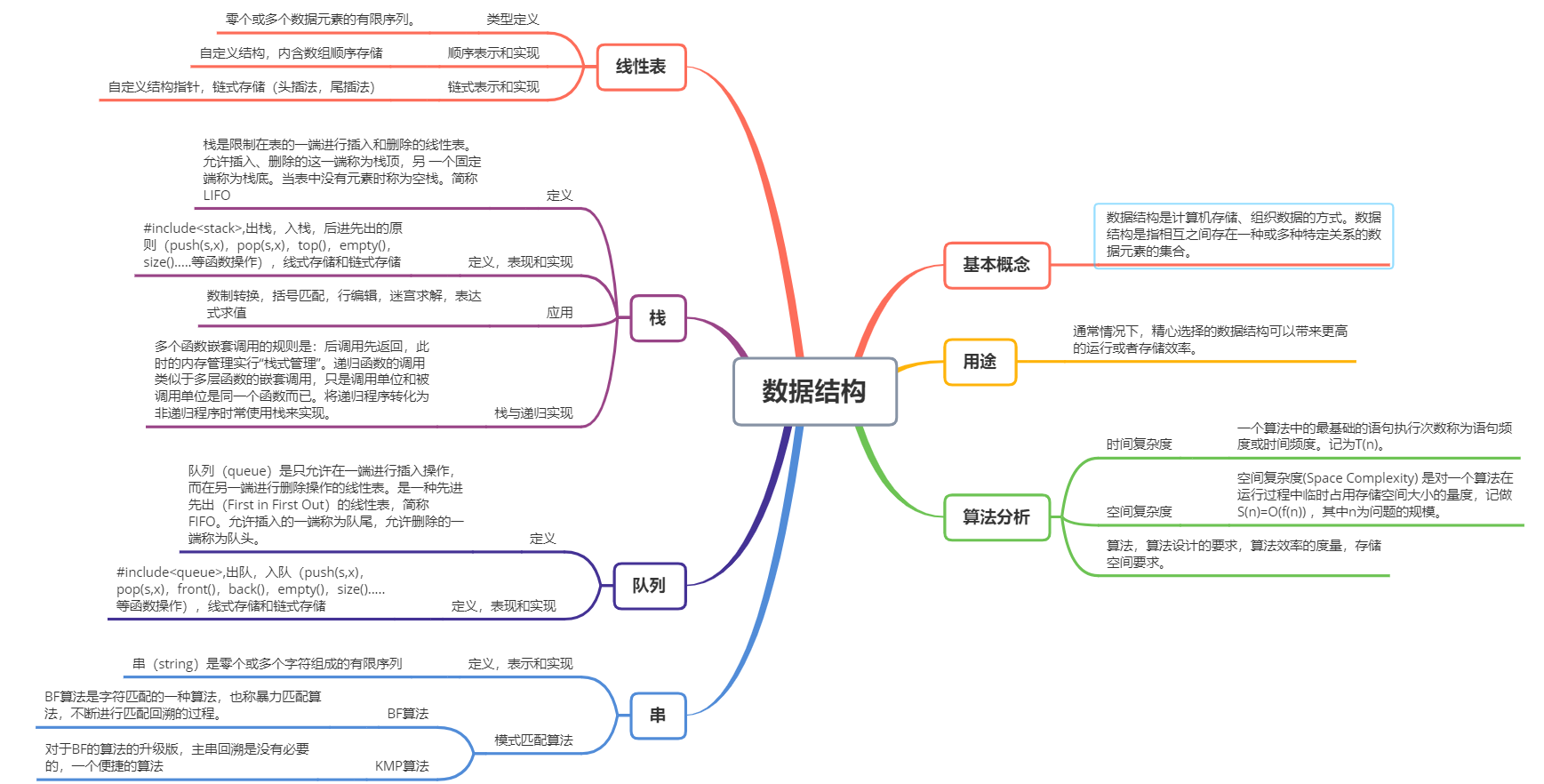
重要概念
1.线性表
(1)顺序存储
struct LNode{
ElementType Data[MAXSIZE];
Position Last;
};
typedef PtrToLNode List;
//List L;
//初始化
List MakeEmpty(){
List L;
L = (List)malloc(sizeof (struct LNode));
L->Last = -1;
return L;
}
//查找
//#define ERROR -1
Position Find(List L,ElementType X){
Position i = 0;
while(i<=L->Last&&L->Data[i]!=X){
i++;
}
if(i>L->Last) printf("您查找的数不存在\n");
else printf("您查找数的存储下标为:%d",i);
}
//插入
bool Insert(List L ,ElementType X,int i){
Position j;
//表空间已满,不能插入
if(L -> Last == MAXSIZE-1){
printf("表满");
return false;
}
//检查插入位序的合法性:是否在1~n+1.
if(i<1||i>L->Last+2){
printf("位序不合法");
return false;
}
for(j=L->Last;j>=i-1;j--){
L->Data[j+1] = L-> Data[j];
}
L->Data[i-1] = X;
L->Last++;
return true;
}
//删除
bool Delete(List L,int i){
Position j;
if(i<1||i>L->Last+1){
printf("位序%d不存在元素\n",i);
}
else{
for(j=i;j<=L->Last;j++){
L->Data[j] = L->Data[j+1];
}
L->Last--;
printf("删除成功\n");
}
}
//求表长
int Length(List L){
return L->Last+1;
}
(2)链式存储
void DestroyList(LinkList &L)
{
LinkList p = L;
while (L)
{
p = L;
L = L->next;
delete p;
}
}
void CreateListF(LinkList& L, int n)//头插法建链表,L表示带头结点链表,n表示数据元素个数
{
int i;
LinkList p;
L = new LNode;
L->next = NULL;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p = new LNode;
cin >> p->data;
p->next = L->next;
L->next = p;
}
}
void CreateListR(LinkList& L, int n)//尾插法建链表,L表示带头结点链表,n表示数据元素个数
{
int i;
LinkList head, p;
L = new LNode;
head = L;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
p = new LNode;
cin >> p->data;
head->next = p;
head = p;
}
head->next = NULL;
}
2.栈和队列
1、stack
用数据结构c++中自带的
定义stack对象的示例代码如下:
stack
stack的基本操作有:
1.入栈,如例:s1.push(x);
2.出栈,如例:s1.pop();注意,出栈操作只是删除栈顶元素,并不返回该元素。**
3.访问栈顶,如例:s1.top()
4.判断栈空,如例:s1.empty(),当栈空时,返回true。
5.访问栈中的元素个数,如例:s1.size()
2、queue
用数据结构c++中自带的
queue
queue的基本操作有:
1.入队,如例:q1.push(x); 将x接到队列的末端。
2.出队,如例:q1.pop(); 弹出队列的第一个元素,注意,并不会返回被弹出元素的值。
3.访问队首元素,如例:q1.front(),即最早被压入队列的元素。
4.访问队尾元素,如例:q1.back(),即最后被压入队列的元素。
5.判断队列空,如例:q1.empty(),当队列空时,返回true。
6.访问队列中的元素个数,如例:q1.size()
3.串
(1)BF算法
BF(Brute Force)算法是普通的模式匹配算法,BF算法的思想就是将目标串S的第一个字符与模式串T的第一个字符进行匹配,若相等,则继续比较S的第二个字符和 T的第二个字符;若不相等,则比较S的第二个字符和T的第一个字符,依次比较下去,直到得出最后的匹配结果。
int BF(char S[],char T[],int pos)
{//c从第pos位开始搜索匹配
int i=pos,j=0;
while(S[i+j]!='\0'&&T[j]!='\0')
{
if(S[i+j]==T[j])
j++;
else
{
i++;
j=0;
}
}
if(T[j]=='\0')
return i+1;
else
return -1;
}
(2)KMP算法
//建立模式串的next数组
void GetNext(char* p, int next[])
{
int pLen = strlen(p);
next[0] = -1;
int k = -1;
int j = 0;
while (j < pLen - 1)
{
if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k])
{
++k;
++j;
next[j] = k;
}
else
{
k = next[k];
}
}
}
//进行主串和模式串匹配
void getNext(const char* pattern,int next[])
{
next[0]= -1;
int k=-1,j=0;
while(pattern[j] != '\0')
{
if(k!= -1 && pattern[k]!= pattern[j] )
k=next[k];
++j;++k;
if(pattern[k]== pattern[j])
next[j]=next[k];
else
next[j]=k;
}
}
疑难问题及解决方案
1.队列
银行业务队列简单模拟

由题目可以来理清思路,建立AB两个队列,分别将编号以偶数和非偶数存储在AB两个队列,然后将按照输出要求,先输出两个A队列的编号,在输出B队列的一个编号,判断两个队列是否为空,当A或B队列为空,就退出,将A或B中剩下的队列全部输出。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAXSIZE 1000
#define OVERFLOW -2
#define OK 1
#define ERROR -1
using namespace std;
//定义队列,有头位置和尾位置记录
typedef struct
{
int* base;
int front;
int rear;
} SqQueue;
//新建一个队列
int InitQueue(SqQueue& Q)
{
Q.base = new int[MAXSIZE];
if (!Q.base)
return OVERFLOW;
Q.front = Q.rear = 0;
return OK;
}
//出队列的一个元素,存储在e中。
int DeQueue(SqQueue& Q, int& e)
{
if (Q.front == Q.rear)
return ERROR;
e = Q.base[Q.front];
Q.front = (Q.front + 1) % MAXSIZE;
return OK;
}
//将数组中编号遍历输出。
void Print(int* arr, int n)
{
cout << arr[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cout << " " << arr[i];
}
int main()
{
SqQueue A, B;
//新建AB两个队列存储编号
InitQueue(A);
InitQueue(B);
int N, data, tmp, i = 0;
cin >> N;
int result[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cin >> data;
if (data % 2 != 0)//判断不为偶数存储在A队列
{
if ((A.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == A.front)
return ERROR;
A.base[A.rear] = data;
A.rear = (A.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
else//判断为偶数存储在B队列
{
if ((B.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE == B.front)
return ERROR;
B.base[B.rear] = data;
B.rear = (B.rear + 1) % MAXSIZE;
}
}
//当AB两个队列都不为空,将两个A队列头元素,一个B队列头元素,存储在result数组中。
while ((A.front != A.rear) && (B.front != B.rear)
{
DeQueue(A, tmp);
result[i++] = tmp;
DeQueue(A, tmp);
result[i++] = tmp;
DeQueue(B, tmp);
result[i++] = tmp;
}
//如果A队列不为空,将A队列元素存储在result数组中
while (A.front != A.rear)
{
DeQueue(A, tmp);
result[i++] = tmp;
}
//如果B队列不为空,将B队列元素存储在result数组中
while (B.front != B.rear)
{
DeQueue(B, tmp);
result[i++] = tmp;
}
//输出result数组
Print(result, N);
return 0;
}
2.实现KMP算法

由所学知识来看这个题目,要用到KMP算法,由我们理解的KMP算法的精髓部分,我们还需要将他们总结起来,能够实现具体功能,才能说是做好了,所以自己写出整体代码,是什么重要的。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
#include <string.h>
void GetNext(char* p, int next[]);//由模式串算出next数组所含值。
int KmpSearch(char* s, char* p);//在主串中找到模式串。
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
char s[100],t[100];
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> s;
cin >> t;
int k = KmpSearch(s, t);
if (k != -1) {
cout << k << endl;
}
else {
cout << "not find!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
void GetNext(char* p, int next[])
{
int pLen = strlen(p);
next[0] = -1;
int k = -1;
int j = 0;
while (j < pLen - 1)
{
if (k == -1 || p[j] == p[k])
{
++k;
++j;
next[j] = k;
}
else
{
k = next[k];
}
}
}
int KmpSearch(char* s, char* p)
{
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
int sLen = strlen(s);
int pLen = strlen(p);
int next[1000];
GetNext(p, next);
while (i < sLen && j < pLen)
{
if (j == -1 || s[i] == p[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}
else
{
j = next[j];
}
}
if (j == pLen)
return i - j;
else
return -1;
}


