Redis服务端事件处理流程分析
一、事件处理#
1.1 什么是事件#
Redis 为什么运行得比较快?
原因之一就是它的服务端处理程序用了事件驱动的处理方式。
那什么叫事件处理?就是把处理程序当成一个一个的事件处理。比如我前面文章:服务端高性能网络IO编程模型简析(https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16586900.html)中高性能 IO 模型中,就提到过这个事件处理。
服务端网络开发中,IO 的处理过程,可以把一个完整 IO 处理过程分解为一个一个小的任务,可以把这个小的任务叫做事件,处理每个小任务也叫作事件处理。比如把 IO 处理过程分为 读事件、计算事件、写事件等各种小的任务进行处理。就是分而治之的思想。
而在 Redis 服务端处理程序中,它把处理程序抽象为了 2 大类的事件进行处理:文件事件 file event 和 时间事件 time event。
- 文件事件:
Redis 把对网络套接字操作的过程抽象为了各种文件事件。客户端与服务端通信产生的处理程序抽象为相应的文件事件,Redis 服务端通过监听并处理这些文件事件来完成各种网络操作。
- 时间事件
Redis 服务器中的一些操作需要在给定的时间点执行,而时间事件就是 Redis 服务器对这类定时操作的抽象。
- 网络处理模型
Redis 中的网络模型处理模式-Reactor 单线程分发模式,可以参考 服务端高性能网络IO编程模型简析(https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16586900.html)5.4.1 小结的单线程模式。
(单 Reactor 单线程模式 (来自《Scalable IO in Java》作者:Doug Lea))
基于 redis 3.0 分析
1.2 文件事件#
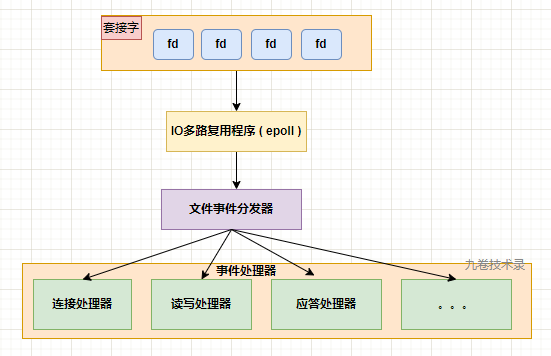
1.2.1 套接字处理介绍#
在上一小节,我们了解 redis 是单线的分发模式,及是 dispatch 分发模式。那 Redis 是怎么实现的呢?它用到了 epoll,IO 多路复用程序,epoll 能同时监听多个套接字变化,并根据套接字不同的动作变化来执行注册的事件处理器。
一个套接字整个过程可以分为应答-accept、读取-read、写入-write、关闭-close 等操作,而这些操作可以看作是一个一个事件,在 redis 中,可以当成文件事件,发生相应的事件时,文件处理器就会调用前面已经注册好的相应的文件事件处理器(实际就是函数)来处理。
epoll 怎么监听多个套接字事件的变化?
看下面的这些文章,就可以了解其中的详情:
- epoll的本质二:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/64138532 作者:罗陪羽
- epoll的本质三:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/64746509
在 redis 中,对 epoll 进行了封装叫 ae_epoll.c 。
而事件的处理类型、处理函数接口可以在 ae.h 文件中找到。
1.2.2 文件事件处理器#
Redis 为文件事件的处理编写了多个事件处理器,用于不同的套接字变化的事件处理。
- 连接应答处理器
networking.c/acceptTcpHandler 函数,这个处理器用于对连接服务器监听套接字的客户端进行应答,是对系统的 accept 函数的封装。
- 命令请求处理器-从客户端读取数据
networking.c/readQueryFromClient 函数,这个处理器负责从套接字中读入客户端发送的命令请求内容,是对系统 read 函数的封装。
- 命令回复处理器
networking.c/sendReplyToClient 函数,这个处理器将服务器执行后的命令回复通过套接字返回给客户端,是对系统 write 函数的封装。
1.3 时间事件#
时间事件分为2类:
- 定时事件:让一段程序在指定的时间之后执行一次。
- 周期性事件:让一段程序每隔一段时间执行一次。
时间事件的结构,ae.h/aeTimeEvent:
/* Time event structure */
typedef struct aeTimeEvent {
long long id; /* time event identifier. */
long when_sec; /* seconds */
long when_ms; /* milliseconds */
aeTimeProc *timeProc;
aeEventFinalizerProc *finalizerProc;
void *clientData;
struct aeTimeEvent *next;
} aeTimeEvent;
在 Redis 正常模式下,只有一个 serverCron 时间事件,函数在 redis.c/serverCron,这个时间事件函数干了很多事情。
- 更新服务器各类统计信息,比如时间、内存占用、数据占用情况等
- 清理数据库中的过期键值
- 关闭和清理连接失败的客户端
- 尝试进行 AOF 和 RDB 的持久化操作
- 。。。。。。
Redis 以周期性的事件方式来运行 ServerCron 函数。默认平均每隔 100 毫秒运行一次,从 Redis2.8 开始,可以在 redis.conf 中修改 hz 选项来调整 serverCron 每秒执行的次数。
2 Redis 事件驱动框架#
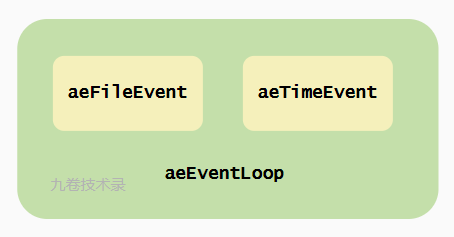
核心数据结构 aeEventLoop#
不管是文件事件还是时间事件都封装在结构体 ae.h/aeEventLoop 中,它们关系图如下:
- struct aeEventLoop 结构体和它的主要结构体
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.h#L87
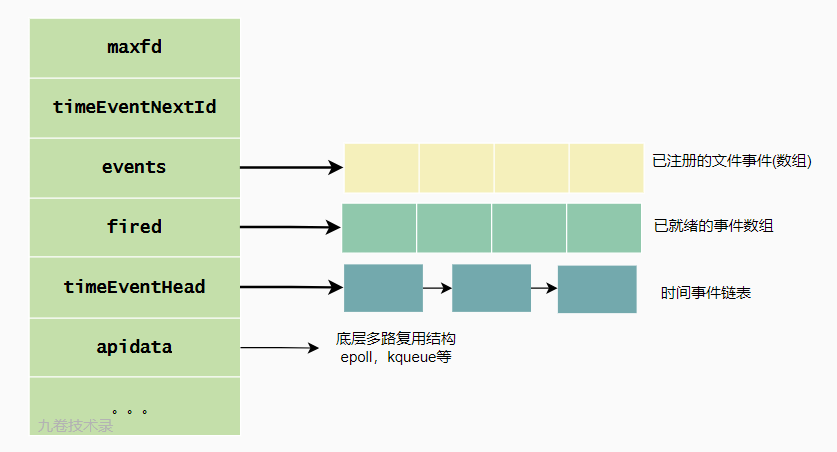
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered 当前注册的最大文件描述符*/
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked 当前已经追踪的最大文件描述符数*/
long long timeEventNextId; // 生成时间事件的唯一标识 ID
time_t lastTime; /* Used to detect system clock skew 记录最后一次执行时间事件的时间*/
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events 存储已经注册的文件事件,它是一个数组,用 fd 做索引来访问相应事件(对应处理函数)*/
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events 已经就绪的事件数组*/
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; // 时间事件链表头节点,因为可能有多个时间事件,组成一个链表
int stop; // 标识事件循环是否结束
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data 底层不同结构多路复用的私有数据,可以是epoll, select 或 kqueue*/
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep; // 进程阻塞之前会调用的函数,事件函数运行前调用的函数,相当于事件函数运行前的钩子函数
} aeEventLoop;
/* File event structure 文件事件结构体*/
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE) */
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;
// 定义 epoll 中所发生的事件对应的处理函数(函数指针)
typedef void aeFileProc(struct aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, void *clientData, int mask);
/* A fired event 已经就绪的文件事件结构体*/
typedef struct aeFiredEvent {
int fd;
int mask;
} aeFiredEvent;
初始化 aeEventLoop 结构体的函数 ae.c/aeCreateEventLoop(),而这个函数里有一个很重要函数 ae_epoll.c/aeApiCreate() 函数,创建 epoll 对象,是对 epoll_create 函数的封装。
其实 redis 还对 epoll 的操作做了其它封装,都在 ae_epoll.c 文件里:
-
aeApiCreate 函数创建 epoll 对象,是对 epoll_create 的封装
-
aeApiAddEvent 函数用于添加事件,是对 epoll_ctl 的封装
-
aeApiDelEvent 函数用于删除事件,是对 epoll_ctl 的封装
-
aeApiPoll 是对 epoll_wait 的封装
初始化:aeCreateEventLoop 函数:#
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.c#L63
// 初始化事件处理器
aeEventLoop *aeCreateEventLoop(int setsize) {
aeEventLoop *eventLoop;
int i;
if ((eventLoop = zmalloc(sizeof(*eventLoop))) == NULL) goto err;
eventLoop->events = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFileEvent)*setsize);
eventLoop->fired = zmalloc(sizeof(aeFiredEvent)*setsize);
if (eventLoop->events == NULL || eventLoop->fired == NULL) goto err;
// 初始化结构体 aeEventLoop
eventLoop->setsize = setsize;
eventLoop->lastTime = time(NULL);
eventLoop->timeEventHead = NULL;
eventLoop->timeEventNextId = 0;
eventLoop->stop = 0;
eventLoop->maxfd = -1;
eventLoop->beforesleep = NULL;
// 调用 aeApiCreate 创建 epoll 对象
if (aeApiCreate(eventLoop) == -1) goto err;
/* Events with mask == AE_NONE are not set. So let's initialize the
* vector with it. */
// 初始化监听事件
for (i = 0; i < setsize; i++)
eventLoop->events[i].mask = AE_NONE;
return eventLoop;
err:
if (eventLoop) {
// 释放内存
zfree(eventLoop->events);
zfree(eventLoop->fired);
zfree(eventLoop);
}
return NULL;
}
事件添加:aeApiAddEvent 函数#
ae_epoll.c/aeApiAddEvent 函数作用上面介绍了,是对 epoll_ctl 函数的封装,添加一个 epoll 事件。它是在哪里被调用的呢?在 ae.c/aeCreateFileEvent 函数中调用的。
执行 ae.c/aeCreateFileEvent 函数创建对应的文件事件,然后把这个事件存储在 aeEventLoop 结构体的 events 字段中。
- aeCreateFileEvent 函数代码:
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.c#L135
// 根据 mask 的值监听 fd 文件的状态变化,当 fd 可用时,执行 proc 函数
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask,
aeFileProc *proc, void *clientData)
{
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; // 取出注册的文件事件,fd 作为索引
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1) // 这里调用 aeApiAddEvent 函数,把事件添加到eventLoop中
return AE_ERR;
// 根据文件处理类型(可读 或 可写),设置对应事件处理器 proc
fe->mask |= mask;
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
// 私有数据
fe->clientData = clientData;
// 如果fd大于最大的maxfd,那么就把当前fd更新最大fd数据maxfd
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd;
return AE_OK;
}
- ae_epoll.c/aeApiAddEvent 函数代码:
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae_epoll.c#L73
static int aeApiAddEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd, int mask) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
struct epoll_event ee;
/* If the fd was already monitored for some event, we need a MOD
* operation. Otherwise we need an ADD operation. */
int op = eventLoop->events[fd].mask == AE_NONE ?
EPOLL_CTL_ADD : EPOLL_CTL_MOD;
ee.events = 0;
mask |= eventLoop->events[fd].mask; /* Merge old events */
if (mask & AE_READABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLIN; // 可读事件,EPOLLIN -> AE_READABLE
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) ee.events |= EPOLLOUT; // 可写事件,EPOLLOUT -> AE_WRITABLE
ee.data.u64 = 0; /* avoid valgrind warning */
ee.data.fd = fd;
if (epoll_ctl(state->epfd,op,fd,&ee) == -1) return -1;
return 0;
}
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae_epoll.c
// 作为 eventLoop 结构的apidata存储
typedef struct aeApiState {
int epfd; // epoll事件的文件描述符fd
struct epoll_event *events; // 事件列表,epoll_wait 返回的事件列表
} aeApiState;
- epoll_ctl 函数说明:
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event)
- epfd:函数 epoll_create 返回的 epoll 文件描述符fd。
- op:要执行的操作。有几个操作的标识,EPOLL_CTL_ADD 表示添加事件;EPOLL_CTL_MOD 表示修改网络连接事件;EPOLL_CTL_DEL 表示删除事件。
- fd:网络连接的 socket 文件描述符。
- event:事件列表,用结构体 epoll_event 表示。
epoll_event 结构体代码:
struct epoll_event { __uint32_t events; epoll_data_t data; }; typedef union epoll_data { void *ptr; int fd; __uint32_t u32; __uint64_t u64; } epoll_data_t;evnets 表示要监听的事件类型,常用的 EPOLLIN 表示文件描述符可读事件,EPOLLOUT 表示文件描述符可写事件。
data 表示与文件描述符相关联的数据。
其他 epoll 函数详细解释请参考这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/archive/2013/08/17/3263780.html
事件调度循环:aeMain 函数#
在事件驱动程序中,一般都有事件循环(while),循环等待事件发生并处理,这个循环处理函数是 ae.c/aeMain():
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.c#L450
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) {
eventLoop->stop = 0;
while (!eventLoop->stop) {
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop); // 事件处理前要做的事情
aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS); // 开始处理事件
}
}
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.c#L352
// ae.c/aeProcessEvents() 函数,所有事件处理都封装在这个函数里,又进行了一个封装
#define AE_ALL_EVENTS (AE_FILE_EVENTS|AE_TIME_EVENTS)
二、redis 启动初始化#
2.1 main() 入口函数#
redis.c 文件中的 redis.c/main() 函数,这个函数里代码虽然很长,但是最重要的就两个函数-redis 服务器启动初始化(initServer)和事件处理循环函数(aeMain),
- redis.c/initServer() , redis 启动初始化
- ae.c/aeMain(server.el) ,运行事件处理循环,一直到 Redis 服务器停止为止
2.2 initServer() redis 服务器初始化#
initServer() 函数:redis 服务器启动初始化。
initServer() 函数代码很长,截取几个重要的地方来分析下:
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/redis.c#L1766
void initServer(void) {
int j;
... ...
// 创建事件循环结构,上面有讲到过这个函数
server.el = aeCreateEventLoop(server.maxclients+REDIS_EVENTLOOP_FDSET_INCR);
server.db = zmalloc(sizeof(redisDb)*server.dbnum);
/* Open the TCP listening socket for the user commands. */
// 监听端口
if (server.port != 0 &&
listenToPort(server.port,server.ipfd,&server.ipfd_count) == REDIS_ERR)
exit(1);
... ...
/* Create the serverCron() time event, that's our main way to process
* background operations. */
// 创建时间事件,运行 serverCron 函数
if(aeCreateTimeEvent(server.el, 1, serverCron, NULL, NULL) == AE_ERR) {
redisPanic("Can't create the serverCron time event.");
exit(1);
}
/* Create an event handler for accepting new connections in TCP and Unix
* domain sockets. */
// 创建文件事件,并注册相应的事件处理函数
for (j = 0; j < server.ipfd_count; j++) {
if (aeCreateFileEvent(server.el, server.ipfd[j], AE_READABLE,
acceptTcpHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) // acceptTcpHandler 接收连接时间处理函数
{
redisPanic(
"Unrecoverable error creating server.ipfd file event.");
}
}
if (server.sofd > 0 && aeCreateFileEvent(server.el,server.sofd,AE_READABLE,
acceptUnixHandler,NULL) == AE_ERR) redisPanic("Unrecoverable error creating server.sofd file event."); // acceptUnixHandler 本地unix处理器
... ...
}
结合上一节,Redis 服务端网络初始化过程,很重要的其实就是对 epoll IO多路复用的一个封装处理,封装抽象成了一个一个的事件处理。
等待客户端连接,创建 epoll 对象,注册相应事件,等待事件发生。
刚好对应于 epoll 的 3 个函数:
- epoll_create:创建 epoll 对象。
- epoll_ctl:事件注册。EPOLL_CTL_ADD,注册新的fd到epfd中;EPOLL_CTL_MOD,修改已经注册的fd的监听事件;EPOLL_CTL_DEL,从epfd中删除一个fd。【int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event)】。
- epoll_wait:等待事件发生,进行处理。
initServer 小结#
initServer() 初始化服务器
->初始化事件循环(aeCreateEventLoop,epoll的封装) -> 监听端口(listenToPort) -> 用aeCreateFileEvent()把事件注册到处理器中acceptTcpHandler
这一切准备完毕后,等待事件处理,也就是用户请求处理。
与 tcp/ip 网络编程的 socket 套接字编程处理过程差不多,见前面的文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16586900.html 第二小节。
三、事件循环处理 aeMain 函数#
就是前面讲到的 ae.c/aeMain(server.el) 函数,里面有个重要的函数 ae.c/aeProcessEvents(),处理所有已经到达的时间事件和所有已经就绪的文件事件。
aeProcessEvents 函数:
/* Process every pending time event, then every pending file event
* (that may be registered by time event callbacks just processed).
* Without special flags the function sleeps until some file event
* fires, or when the next time event occurs (if any).
*
* If flags is 0, the function does nothing and returns.
* if flags has AE_ALL_EVENTS set, all the kind of events are processed.
* if flags has AE_FILE_EVENTS set, file events are processed.
* if flags has AE_TIME_EVENTS set, time events are processed.
* if flags has AE_DONT_WAIT set the function returns ASAP until all
* the events that's possible to process without to wait are processed.
*
* The function returns the number of events processed. */
// https://github.com/redis/redis/blob/3.0/src/ae.c#L352
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
/* Note that we want call select() even if there are no
* file events to process as long as we want to process time
* events, in order to sleep until the next time event is ready
* to fire. */
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
aeTimeEvent *shortest = NULL;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
// 查询最近时间事件
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
shortest = aeSearchNearestTimer(eventLoop);
if (shortest) {// 如果找到了,就与当前时间计算差值
long now_sec, now_ms;
/* Calculate the time missing for the nearest
* timer to fire. */
// 计算距离当前时间最近的时间事件还要多久到达
// 将计算的时间距离保存在 tv 结构中
aeGetTime(&now_sec, &now_ms);
tvp = &tv;
tvp->tv_sec = shortest->when_sec - now_sec;
if (shortest->when_ms < now_ms) {
tvp->tv_usec = ((shortest->when_ms+1000) - now_ms)*1000;
tvp->tv_sec --;
} else {
tvp->tv_usec = (shortest->when_ms - now_ms)*1000;
}
if (tvp->tv_sec < 0) tvp->tv_sec = 0;
if (tvp->tv_usec < 0) tvp->tv_usec = 0;
} else {
/* If we have to check for events but need to return
* ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout
* to zero */
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) { // 设置文件事件不阻塞
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* Otherwise we can block */
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */ // 一直等待,文件事件阻塞直到有文件事件到达
}
}
// 处理文件事件,阻塞时间由第二个参数决定
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp);
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd]; // 从已经就绪的文件事件数组中取出事件
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int rfired = 0;
/* note the fe->mask & mask & ... code: maybe an already processed
* event removed an element that fired and we still didn't
* processed, so we check if the event is still valid. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {// 可读事件
rfired = 1;
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {// 可写事件
if (!rfired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc)
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) // 执行时间事件
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
四、参考:#
- 《Redis设计与实现》作者:黄健宏
- https://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/archive/2013/08/17/3263780.html epoll相关函数
- https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/12884938.html Redis的整个主体流程分析
作者:九卷 (公众号:九卷技术录)
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16723573.html
版权:本文采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 by nc nd 4.0 国际」知识共享许可协议进行许可。
【升认知赚好钱】






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!