Go微服务框架go-kratos实战学习02:proto 代码生成和项目代码编写步骤
在上一篇 kratos quickstart 文章(https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16322725.html)中,我们直接用 kratos new 命令生成了一个项目。
这一篇来看看 kratos API 的定义和使用。
一、kratos 中 API 简介#
1.1 简介#
API 全称是 Application Programming Interface,应用程序接口。
在 kratos 中,API 指的是 REST API 和 RPC API ,REST API 是用户访问应用程序时的入口,
RPC API 作为应用程序内部相互访问的接口定义。
那怎么定义 API?使用的是 protocol-buffers 这种与编程语言无关的接口自定义语言(IDL),它可以根据定义的 pb 来生成你
所需的编程语言程序。
gRPC 是 Go 语言编写的一个开源的 RPC 框架,它使用的 IDL 就是 protocol-buffers。
protocol-buffers 语法学习可以参考文档:
-
proto3 语法, https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3
- 中译版 (时间有点早2017-03)
-
proto2 语法,https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto
二、kratos 中 API 定义和使用#
下面一步一步实现 api 文件(proto 文件)生成,然后根据 proto 文件生成对应的 pb.http, pb.grpc 代码。
然后生成 service 代码,使用 service 代码。然后编写 biz 代码等等步骤。
来理清 kratos 里代码编写的步骤。毕竟 internal 文件夹里各种 go 文件业务逻辑顺序还是要有些繁琐。
2.1 快速生成 proto 文件#
在上一篇文章的项目基础上生成一个新的 API(proto 文件)。
先安装 kratos cli :
go install github.com/go-kratos/kratos/cmd/kratos/v2@latest
kratos cli 工具使用文档:https://go-kratos.dev/docs/getting-started/usage
进入项目 quickstart 目录,运行命令:
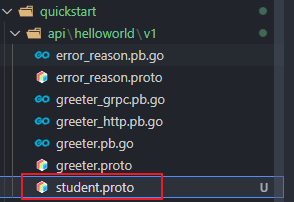
kratos proto add api/helloworld/v1/student.proto
在 api/helloworld/v1 目录先就会出现一个 student.proto 的文件,
里面的代码:
syntax = "proto3";
package api.helloworld.v1;
option go_package = "quickstart/api/helloworld/v1;v1";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "api.helloworld.v1";
service Student {
rpc CreateStudent (CreateStudentRequest) returns (CreateStudentReply);
rpc UpdateStudent (UpdateStudentRequest) returns (UpdateStudentReply);
rpc DeleteStudent (DeleteStudentRequest) returns (DeleteStudentReply);
rpc GetStudent (GetStudentRequest) returns (GetStudentReply);
rpc ListStudent (ListStudentRequest) returns (ListStudentReply);
}
message CreateStudentRequest {}
message CreateStudentReply {}
message UpdateStudentRequest {}
message UpdateStudentReply {}
message DeleteStudentRequest {}
message DeleteStudentReply {}
message GetStudentRequest {}
message GetStudentReply {}
message ListStudentRequest {}
message ListStudentReply {}
生成了一个 student.proto 的模板,定义了一些基本操作,Create、Update、Delete、Get、List。
2.2 给 proto 添加内容#
学习 greeter.proto 里的用法,给 student.proto 添加一个简单的 HTTP 转换。
添加一个 hello 的 http 转换接口
第一步:引入 import "google/api/annotations.proto";
第二步:在 service Student 里添加代码:
在服务里定义一个 Hello 的操作,然后在里面用 option (google.api.http) 语法,如下:
rpc Hello (HelloReq) returns (HelloResp) {
option (google.api.http) = {
get: "/hello/{name}"
};
}
定义 HelloReq 和 HelloResp:
请求的字段和返回的字段
message HelloReq {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloResp {
string message = 1;
}
上面就是把 HTTP REST 转换为 gRPC :
| HTTP | gRPC |
|---|---|
| GET /hello/tom | Hello(name: "tom") |
还可以给这个接口添加额外的接口,用 additional_bindings:
rpc Hello (HelloReq) returns (HelloResp) {
option (google.api.http) = {
// 定义 GET 接口,把 name 参数映射到 HelloReq
get: "/hello/{name}",
// 添加额外的接口
additional_bindings {
// 定义了一个 POST 接口,并且把 body 映射到了 HelloReq
post: "/hello/{id}/sayhello/{sayname}",
body: "*",
}
};
}
// 这里的 HelloReq 和 HelloResp
message HelloReq {
string name = 1;
string id = 2;
string sayname = 3;
}
message HelloResp {
string message = 1;
string text = 2;
}
HTTP 转换问 gRPC:
| HTTP | gRPC |
|---|---|
| GET /hello/tom | Hello(name: "tom") |
| POST /hello/123/sayhello/tom | Hello(id: "123", sayname:"tom" text:"world!") |
2.3 生成 proto 对应代码#
通过 make 命令生成:
make api
或者通过 kratos cli 生成:
kratos proto client api/helloworld/v1/student.proto
这里通过 kratos proto client api/helloworld/v1/student.proto 来生成 proto 对应的代码:
api/helloworld/v1/student.pb.go
api/helloworld/v1/student_grpc.pb.go// 注意 http 代码只会在 proto 文件中声明了 http 时才会生成
api/helloworld/v1/student_http.pb.go
2.4 生成 Service 代码#
通过 proto 文件,直接生成对应的 Service 代码。使用 -t 指定生成目录:
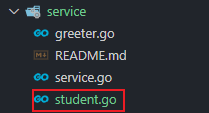
kratos proto server api/helloworld/v1/student.proto -t internal/service
internal/service/student.go:
package service
import (
"context"
pb "quickstart/api/helloworld/v1"
)
type StudentService struct {
pb.UnimplementedStudentServer
}
func NewStudentService() *StudentService {
return &StudentService{}
}
func (s *StudentService) Createstudent(ctx context.Context, req *pb.CreateStudentRequest) (*pb.CreateStudentReply, error) {
return &pb.CreateStudentReply{}, nil
}
func (s *StudentService) Updatestudent(ctx context.Context, req *pb.UpdateStudentRequest) (*pb.UpdateStudentReply, error) {
return &pb.UpdateStudentReply{}, nil
}
func (s *StudentService) Deletestudent(ctx context.Context, req *pb.DeleteStudentRequest) (*pb.DeleteStudentReply, error) {
return &pb.DeleteStudentReply{}, nil
}
func (s *StudentService) Getstudent(ctx context.Context, req *pb.GetStudentRequest) (*pb.GetStudentReply, error) {
return &pb.GetStudentReply{}, nil
}
func (s *StudentService) Liststudent(ctx context.Context, req *pb.ListStudentRequest) (*pb.ListStudentReply, error) {
return &pb.ListStudentReply{}, nil
}
func (s *StudentService) Hello(ctx context.Context, req *pb.HelloReq) (*pb.HelloResp, error) {
return &pb.HelloResp{}, nil
}
看上面的代码,里面的内容是空的,需要你自己编写相应的代码逻辑。
通过上一篇文章我们知道,service 实现了 api 定义的服务,其实就是 student.proto 里定义的服务。它要把数据传输对象(比如 http request data) 传入到 internal/biz 里进行处理,它一般不会涉及业务逻辑代码。业务逻辑的组装会在 biz 里实现。
有了 service/student.go ,怎么使用?
2.5 向 wire 中注入 Service 代码#
在 kratos 中,组织代码是用 wire 依赖注入的方式。
在 internal/service/service.go 文件里加上 NewStudentService:
var ProviderSet = wire.NewSet(NewStudentService)
假如我们要通过 http 来访问,那又要怎么做?对,还需要在服务端加 student 服务代码。
2.6 向server添加代码#
向 internal/server/http.go,internal/server/grpc.go 添加服务代码:
在 http.go 中:
// 在函数参数中添加 student *service.StudentService
func NewHTTPServer(c *conf.Server, student *service.StudentService, logger log.Logger) *http.Server {
... ...
srv := http.NewServer(opts...)
// v1.RegisterGreeterHTTPServer(srv, greeter)
v1.RegisterStudentHTTPServer(srv, student) // 在 httpserver 上注册 student
return srv
}
在 grpc.go 中:
// 在函数参数中添加 student *service.StudentService
func NewGRPCServer(c *conf.Server, student *service.StudentService, logger log.Logger) *grpc.Server {
... ...
// v1.RegisterGreeterServer(srv, greeter)
v1.RegisterStudentServer(srv, student) // 在 grpcserver 上注册 student
return srv
}
那需不需要在向 wire 注册后才能使用呢?不需要,在 internal/server/server.go 中已经有了:
var ProviderSet = wire.NewSet(NewHTTPServer, NewGRPCServer)
接下来,接受了参数,是不是要对参数进行相应处理。
顺序是:service -> biz -> data
2.7 业务逻辑 biz#
先简单分析下 internal/biz/greeter.go 里的代码。
// 定义了一个 Greeter struct,主要内容就是定义 Greeter 的字段
type Greeter struct {
Hello string
}
// 对 Greeter 定义操作接口 GreeterRepo
type GreeterRepo interface {
Save(context.Context, *Greeter) (*Greeter, error)
Update(context.Context, *Greeter) (*Greeter, error)
FindByID(context.Context, int64) (*Greeter, error)
ListByHello(context.Context, string) ([]*Greeter, error)
ListAll(context.Context) ([]*Greeter, error)
}
// 操作加上日志
type GreeterUsecase struct {
repo GreeterRepo
log *log.Helper
}
// 初始化 GreeterUsercase
func NewGreeterUsecase(repo GreeterRepo, logger log.Logger) *GreeterUsecase
// 对 Greeter 的真正操作,用到的方法都是上面 GreeterRepo 定义的
func (uc *GreeterUsecase) CreateGreeter(ctx context.Context, g *Greeter) (*Greeter, error) {
uc.log.WithContext(ctx).Infof("CreateGreeter: %v", g.Hello)
return uc.repo.Save(ctx, g)
}
基本步骤:1.定义 struct,里面包含字段 2.定义操作 struct 的 interface 3.给操作加上日志 4.定义真正执行操作函数
这里只定义了操作的接口 GreeterRepo interface,里面定义了常规的操作。
而操作接口里定义的操作需要到 data 里实现。
照葫芦画瓢,在 internal/biz/ 文件夹下新建文件 student.go:
1.定义 struct Student:
type Student struct {
ID string
Name string
Sayname string
}
2.定义对 struct student 的操作接口:
type StudentRepo interface {
Save(context.Context, *Student) (*Student, error)
Get(context.Context, *Student) (*Student, error)
}
3.对 student 的操作加上日志:
type StudentUsercase struct {
repo StudentRepo
log *log.Helper
}
4.初始化 StudentUsercase
func NewStudentUsercase(repo StudentRepo, logger log.Logger) *StudentUsercase {
return &StudentUsercase{repo: repo, log: log.NewHelper(logger)}
}
5.编写 CreateStudent 方法,也就是一些业务逻辑编写
func (uc *StudentUsercase) CreateStudent(ctx context.Context, stu *Student) (*Student, error) {
uc.log.WithContext(ctx).Infof("CreateStudent: %v", stu.ID)
return uc.repo.Save(ctx, stu)
}
biz 里就是完成业务逻辑组装,数据的处理。
6.向 wire 注入 student
internal/biz/biz.go:
var ProviderSet = wire.NewSet(NewGreeterUsecase, NewStudentUsercase)
上面对 struct student 定义了操作的接口,那具体实现在哪里实现?就是在 internal/data 里实现。
2.8 持久化操作#
可以仿照 2.7 小结,先看看 internal/data/greeter.go 怎么编写代码的。
greeter.go 里的具体代码就留给读者自己研究了。
下面开始编写 internal/data/student.go 代码。
1.定义持久化的 struct
type studentRepo struct {
data *Data // 这里 *Data 是连接数据库客户端
log *log.Helper
}
2.初始化 studentRepo struct
func NewStudentRepo(data *Data, logger log.Logger) biz.StudentRepo {
return &studentRepo{
data: data,
log: log.NewHelper(logger),
}
}
3.实现接口定义的操作
在 biz/student.go 里的 StudentRepo 接口,定义了 2 个操作 Save、Get,在这里实现,
func (repo *studentRepo) Save(ctx context.Context, stu *biz.Student) (*biz.Student, error) {
return stu, nil
}
func (repo *studentRepo) Get(ctx context.Context, stu *biz.Student) (*biz.Student, error) {
return stu, nil
}
上面是一个实现的模板代码。
2.9 配置文件#
配置文件是放在 internal/conf 文件夹中,这里放置了配置文件结构的定义文件,使用 .proto 进行配置定义,
然后通过在根目录执行 make config 命令,就可以将对应的 .pb.go 文件生成到同一目录下使用。
在初始状态下,这个 conf.proto 所定义的结构,就是 configs/config.yaml 的接口,请保持两者一致。
每次修改配置文件后,记得使用
make config命令重新生成 go 文件。
2.10 重新生成 wire_gen.go 文件#
进入到 cmd/quickstart 目录,然后直接用 wire 命令重新生成 wire_gen.go 文件。
// cmd/quickstart
wire
wire 的用法可以看这篇文章:Go 依赖注入工具 wire 使用
这篇文章已经写的有点长了,接下来的一篇文章结合 gorm 进行一些简单的增加修改列表等简单的操作。
虽然 kratos 以前用的是 Ent 操作数据库,但是我感觉还是 gorm 使用的人多。
下一篇:Go微服务框架go-kratos学习03:使用 gorm 实现增删改查操作
也可以到我的公众号讨论本文 : 九卷技术录-go-kratos实战学习02
三、参考#
- https://go-kratos.dev/docs/getting-started/usage kratos cli 工具使用
- https://go-kratos.dev/docs/component/api kratos api 定义
- https://cloud.google.com/endpoints/docs/grpc/transcoding http/json 转码为 gRPC
- https://go-kratos.dev/docs/guide/api-protobuf/ Protobuf 规范
- https://go-kratos.dev/docs/component/config 配置
- https://developers.google.com/protocol-buffers/docs/proto3 proto3 文档
- https://colobu.com/2017/03/16/Protobuf3-language-guide/ Protobuf3 语法指南(中译)
作者:九卷 (公众号:九卷技术录)
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/jiujuan/p/16331967.html
版权:本文采用「署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 by nc nd 4.0 国际」知识共享许可协议进行许可。
【升认知赚好钱】





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· Docker 太简单,K8s 太复杂?w7panel 让容器管理更轻松!