Three.js中实现碰撞检测
1. 引言
碰撞检测是三维场景中常见的需求,Three.js是常用的前端三维JavaScript库,本文就如何在Three.js中进行碰撞检测进行记述
主要使用到的方法有:
- 射线法Raycaster
- 包围盒bounding box
- 物理引擎Cannon.js
2. Raycaster
Raycaster用于进行raycasting(光线投射), 光线投射用于进行鼠标拾取(在三维空间中计算出鼠标移过了什么物体)
在某些情况下也能用于初略的碰撞检测
示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> html, body, canvas { height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <canvas id="canvas"></canvas> <script type="importmap"> { "imports": { "three": "https://unpkg.com/three/build/three.module.js", "three/addons/": "https://unpkg.com/three/examples/jsm/" } } </script> <script type="module"> import * as THREE from 'three'; import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'; import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js' const scene = new THREE.Scene(); const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(); const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff }); const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); scene.add(cube); // 创建性能监视器 let stats = new Stats(); // 将监视器添加到页面中 document.body.appendChild(stats.domElement) const canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas'); const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, canvas.clientWidth / canvas.clientHeight, 0.1, 100000); camera.position.set(0, 0, 10); // 添加环境光 const ambient = new THREE.AmbientLight("#FFFFFF"); ambient.intensity = 5; scene.add(ambient); // 添加平行光 const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight("#FFFFFF"); directionalLight.position.set(0, 0, 0); directionalLight.intensity = 16; scene.add(directionalLight); // 添加Box const box = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }); const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(box, boxMaterial); boxMesh.position.set(6, 0, 0); scene.add(boxMesh); const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas: document.querySelector('#canvas'), antialias: true }); renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight, false) const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement); function animate() { // 更新帧数 stats.update() boxMesh.position.x -= 0.01; cube.material.color.set(0x0000ff); raycaster.set(boxMesh.position, new THREE.Vector3(-1, 0, 0).normalize()); const intersection = raycaster.intersectObject(cube); if (intersection.length > 0) { if (intersection[0].distance < 0.5) { intersection[0].object.material.color.set(0xff0000); } } raycaster.set(boxMesh.position, new THREE.Vector3(1, 0, 0).normalize()); const intersection2 = raycaster.intersectObject(cube); if (intersection2.length > 0) { if (intersection2[0].distance < 0.5) { intersection2[0].object.material.color.set(0xff0000); } } requestAnimationFrame(animate); renderer.render(scene, camera); } animate(); </script> </body> </html>

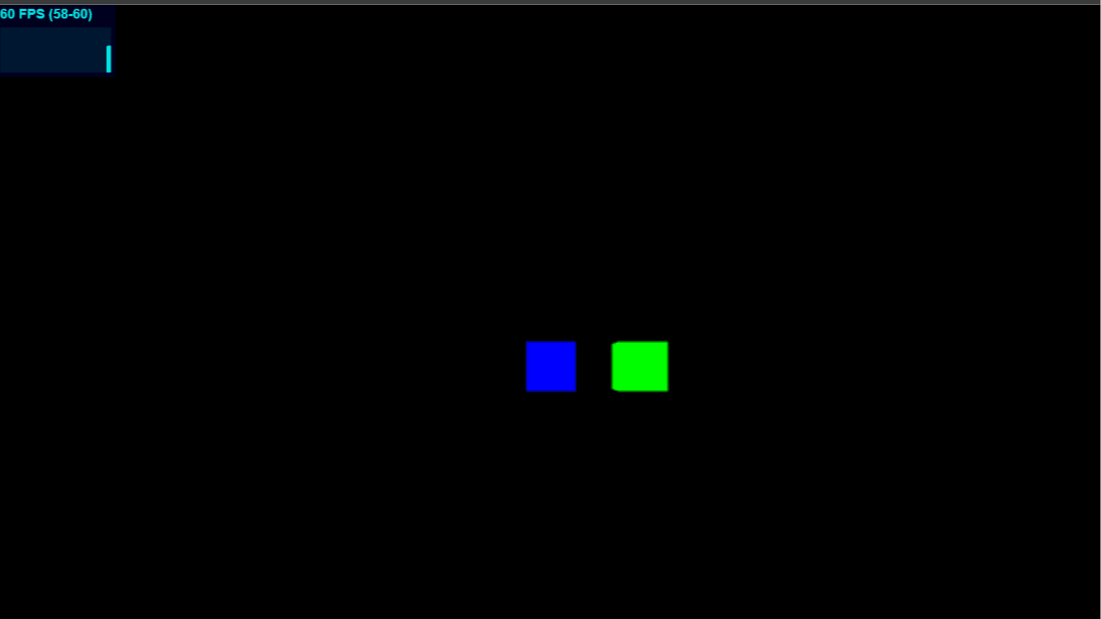
可以看到,两个立方体在刚接触时和要分开时检测出了碰撞,但是在两个立方体接近重合时却没检测出碰撞
这是因为Raycaster使用的是一根射线来检测,射线需要起点和方向,上述例子中将起点设为绿色立方体的中心,当绿色立方体中心在蓝色立方体内时,就检测不出碰撞了
另外,射线是需要方向的,上述示例中设置为检测左右两个方向,然而方向是难以穷举的,太多的Raycaster也严重损耗性能
所以说,Raycaster在某些情况下也能用于初略的碰撞检测,然而问题是显著的
3. bounding box
bounding box,在Three.js中为Box3类,表示三维空间中的一个轴对齐包围盒(axis-aligned bounding box,AABB)
利用bounding box,可以用来检测物体是否相交(即,碰撞)
示例如下(和Raycaster部分的代码相比只修改了animate函数):
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> html, body, canvas { height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <canvas id="canvas"></canvas> <script type="importmap"> { "imports": { "three": "https://unpkg.com/three/build/three.module.js", "three/addons/": "https://unpkg.com/three/examples/jsm/" } } </script> <script type="module"> import * as THREE from 'three'; import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'; import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js' const scene = new THREE.Scene(); const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster(); const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff }); const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material); scene.add(cube); // 创建性能监视器 let stats = new Stats(); // 将监视器添加到页面中 document.body.appendChild(stats.domElement) const canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas'); const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, canvas.clientWidth / canvas.clientHeight, 0.1, 100000); camera.position.set(0, 0, 10); // 添加环境光 const ambient = new THREE.AmbientLight("#FFFFFF"); ambient.intensity = 5; scene.add(ambient); // 添加平行光 const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight("#FFFFFF"); directionalLight.position.set(0, 0, 0); directionalLight.intensity = 16; scene.add(directionalLight); // 添加Box const box = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const boxMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }); const boxMesh = new THREE.Mesh(box, boxMaterial); boxMesh.position.set(6, 0, 0); scene.add(boxMesh); const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas: document.querySelector('#canvas'), antialias: true }); renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight, false) const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement); function animate() { // 更新帧数 stats.update() boxMesh.position.x -= 0.02; const cubeBox = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(cube); const boxMeshBox = new THREE.Box3().setFromObject(boxMesh); cubeBox.intersectsBox(boxMeshBox) ? cube.material.color.set(0xff0000) : cube.material.color.set(0x0000ff); requestAnimationFrame(animate); renderer.render(scene, camera); } animate(); </script> </body> </html>

可以看到,在Three.js中使用bounding box来检测碰撞效果还可以,当然,AABB这种bounding box是将物体用一个立方体或长方体包围起来,如果物体的形状很不规则,那么使用bounding box来检测碰撞可能是不够精细的,比如下面这个例子:

示例中绿色立方体还没撞到蓝色锥体,但是bounding box已经检测出碰撞
所以,利用bounding box来检测物体是否相交是大体可行的
4. Cannon.js
Cannon.js是一个3d物理引擎,它能实现常见的碰撞检测,各种体形,接触,摩擦和约束功能
这里笔者想借助物理引擎来实现碰撞检测,当然,其他的物理引擎(如,Ammo.js,Oimo.js等)也是可以的
使用Cannon.js进行两个Cube的碰撞检测示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>Document</title> <style> html, body, canvas { height: 100%; width: 100%; margin: 0; } </style> </head> <body> <canvas id="canvas"></canvas> <script type="importmap"> { "imports": { "three": "https://unpkg.com/three/build/three.module.js", "three/addons/": "https://unpkg.com/three/examples/jsm/" } } </script> <script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/cannon.js/0.6.2/cannon.js"></script> <script type="module"> import * as THREE from 'three'; import { OrbitControls } from 'three/addons/controls/OrbitControls.js'; import Stats from 'three/addons/libs/stats.module.js' const scene = new THREE.Scene(); const world = new CANNON.World() // 创建性能监视器 let stats = new Stats(); // 将监视器添加到页面中 document.body.appendChild(stats.domElement) const canvas = document.querySelector('#canvas'); const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(75, canvas.clientWidth / canvas.clientHeight, 0.1, 100000); camera.position.set(0, 0, 10); // 添加环境光 const ambient = new THREE.AmbientLight("#FFFFFF"); ambient.intensity = 5; scene.add(ambient); // 添加平行光 const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight("#FFFFFF"); directionalLight.position.set(0, 0, 0); directionalLight.intensity = 16; scene.add(directionalLight); // 创建第一个Cube的Three.js模型 const cubeGeometry1 = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const cubeMaterial1 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x0000ff }); const cube1 = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry1, cubeMaterial1); scene.add(cube1); // 创建第一个Cube的Cannon.js刚体 const cubeShape1 = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)); const cubeBody1 = new CANNON.Body({ mass: 1, shape: cubeShape1 }); cubeBody1.position.set(1, 0, 0); world.addBody(cubeBody1); // 创建第二个Cube的Three.js模型 const cubeGeometry2 = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1); const cubeMaterial2 = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({ color: 0x00ff00 }); const cube2 = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry2, cubeMaterial2); scene.add(cube2); // 创建第二个Cube的Cannon.js刚体 const cubeShape2 = new CANNON.Box(new CANNON.Vec3(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)); const cubeBody2 = new CANNON.Body({ mass: 1, shape: cubeShape2 }); cubeBody2.position.set(-1, 0, 0); world.addBody(cubeBody2); // 监听碰撞事件 cubeBody2.addEventListener("collide", function (e) { cube2.material.color.set(0xff0000); }); const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ canvas: document.querySelector('#canvas'), antialias: true }); renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight, false) const controls = new OrbitControls(camera, renderer.domElement); function animate() { // 更新帧数 stats.update() world.step(1 / 60); cubeBody1.position.x -= 0.02; // 更新Three.js模型的位置 cube1.position.copy(cubeBody1.position); cube1.quaternion.copy(cubeBody1.quaternion); cube2.position.copy(cubeBody2.position); cube2.quaternion.copy(cubeBody2.quaternion); requestAnimationFrame(animate); renderer.render(scene, camera); } animate(); </script> </body> </html>

至于精确性呢,使用Cannon.js也是不错的,示例如下:

看上去,使用Cannon.js的效果是相当不错的,在追求效果的情况下使用物理引擎是不错的选择,当然,增加的编码成本、计算开销也是不少
5. 参考资料
[1] Raycaster – three.js docs (three3d.cn)
[2] Box3 – three.js docs (threejs.org)
[3] schteppe/cannon.js: A lightweight 3D physics engine written in JavaScript. (github.com)
[4] Three.js - 物体碰撞检测(二十六) - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
[5] Three.js 进阶之旅:物理效果-碰撞和声音 💥 - 掘金 (juejin.cn)
[6] pmndrs/cannon-es: 💣 A lightweight 3D physics engine written in JavaScript. (github.com)



 本文就如何在Three.js中进行碰撞检测进行记述
本文就如何在Three.js中进行碰撞检测进行记述



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」