WebGPU 01之Hello Triangle
1. 引言
WebGPU是什么?
WebGPU与WebGL的对比?
2. 快速体验
参考:Orillusion | 专业WebGPU社区 | WebGPU小白入门(一): 零基础创建第一个WebGPU项目
# Clone the repo
git clone https://github.com/Orillusion/orillusion-webgpu-samples.git
# Go inside the folder
cd orillusion-webgpu-samples
# Start installing dependencies
npm install #or yarn add
# Run project at localhost:3000
npm run dev #or yarn run dev
在Chrome 浏览器(版本100+) 中打开localhost:3000,即可看到运行结果:

注意:
-
目前(2022年7月)WebGPU未正式发布,接口代码变更较快
-
WebGPU未正式发布,各个浏览器支持程度不同,本文使用Chrome版本号为:105.0.5153.0(正式版本)canary (64 位),下载地址:开发者专用的 Chrome Canary 版功能 - Google Chrome
部署别人写的代码终究是少了点感觉,接下来将编写一个入手案例
3. Hello Triangle
3.1 环境准备
浏览器:Chrome Canary版,版本号为:105.0.5153.0(正式版本)canary (64 位)
将Chrome开启WebGPU功能:
在地址栏输入 chrome://flags/ 搜索 WebGPU,将WebGPU的功能打开

3.2 基础代码
创建一个HTML文件,设置基础代码,另外,WebGPU是借助HTML中的canvas元素实现的,所以创建一个canvas元素
index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Basic Triangle</title>
<style>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
background: #000;
color: #fff;
display: flex;
text-align: center;
flex-direction: column;
justify-content: center;
}
canvas {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<canvas></canvas>
<script src="./index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
3.3 主要代码
同一目录下创建一个index.js文件,代码内容如下,流程讲解在下一节
index.js:
// initialize webgpu device & config canvas context
async function initWebGPU(canvas) {
if(!navigator.gpu)
throw new Error('Not Support WebGPU')
const adapter = await navigator.gpu.requestAdapter({
powerPreference: 'high-performance'
// powerPreference: 'low-power'
})
if (!adapter)
throw new Error('No Adapter Found')
const device = await adapter.requestDevice()
const context = canvas.getContext('webgpu')
const format = navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat ? navigator.gpu.getPreferredCanvasFormat() : context.getPreferredFormat(adapter)
const devicePixelRatio = window.devicePixelRatio || 1
canvas.width = canvas.clientWidth * devicePixelRatio
canvas.height = canvas.clientHeight * devicePixelRatio
const size = {width: canvas.width, height: canvas.height}
context.configure({
// json specific format when key and value are the same
device, format,
// prevent chrome warning
alphaMode: 'opaque'
})
return {device, context, format, size}
}
// create a simple pipiline
async function initPipeline(device, format){
const descriptor = {
layout: 'auto',
vertex: {
module: device.createShaderModule({
code: `@vertex
fn main(@builtin(vertex_index) VertexIndex : u32) -> @builtin(position) vec4<f32> {
var pos = array<vec2<f32>, 3>(
vec2<f32>(0.0, 0.5),
vec2<f32>(-0.5, -0.5),
vec2<f32>(0.5, -0.5)
);
return vec4<f32>(pos[VertexIndex], 0.0, 1.0);
}`
}),
entryPoint: 'main'
},
primitive: {
topology: 'triangle-list' // try point-list, line-list, line-strip, triangle-strip?
},
fragment: {
module: device.createShaderModule({
code: `@fragment
fn main() -> @location(0) vec4<f32> {
return vec4<f32>(1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
}`
}),
entryPoint: 'main',
targets: [
{
format: format
}
]
}
}
return await device.createRenderPipelineAsync(descriptor)
}
// create & submit device commands
function draw(device, context, pipeline) {
const commandEncoder = device.createCommandEncoder()
const view = context.getCurrentTexture().createView()
const renderPassDescriptor = {
colorAttachments: [
{
view: view,
clearValue: { r: 0, g: 0, b: 0, a: 1.0 },
loadOp: 'clear', // clear/load
storeOp: 'store' // store/discard
}
]
}
const passEncoder = commandEncoder.beginRenderPass(renderPassDescriptor)
passEncoder.setPipeline(pipeline)
// 3 vertex form a triangle
passEncoder.draw(3)
passEncoder.end()
// webgpu run in a separate process, all the commands will be executed after submit
device.queue.submit([commandEncoder.finish()])
}
async function run(){
const canvas = document.querySelector('canvas')
if (!canvas)
throw new Error('No Canvas')
const {device, context, format} = await initWebGPU(canvas)
const pipeline = await initPipeline(device, format)
// start draw
draw(device, context, pipeline)
// re-configure context on resize
window.addEventListener('resize', ()=>{
canvas.width = canvas.clientWidth * devicePixelRatio
canvas.height = canvas.clientHeight * devicePixelRatio
// don't need to recall context.configure() after v104
draw(device, context, pipeline)
})
}
run()
运行代码(笔者这里使用VS Code和Live Server插件),使用Chrome打开,顺利的话即可看到三角形:

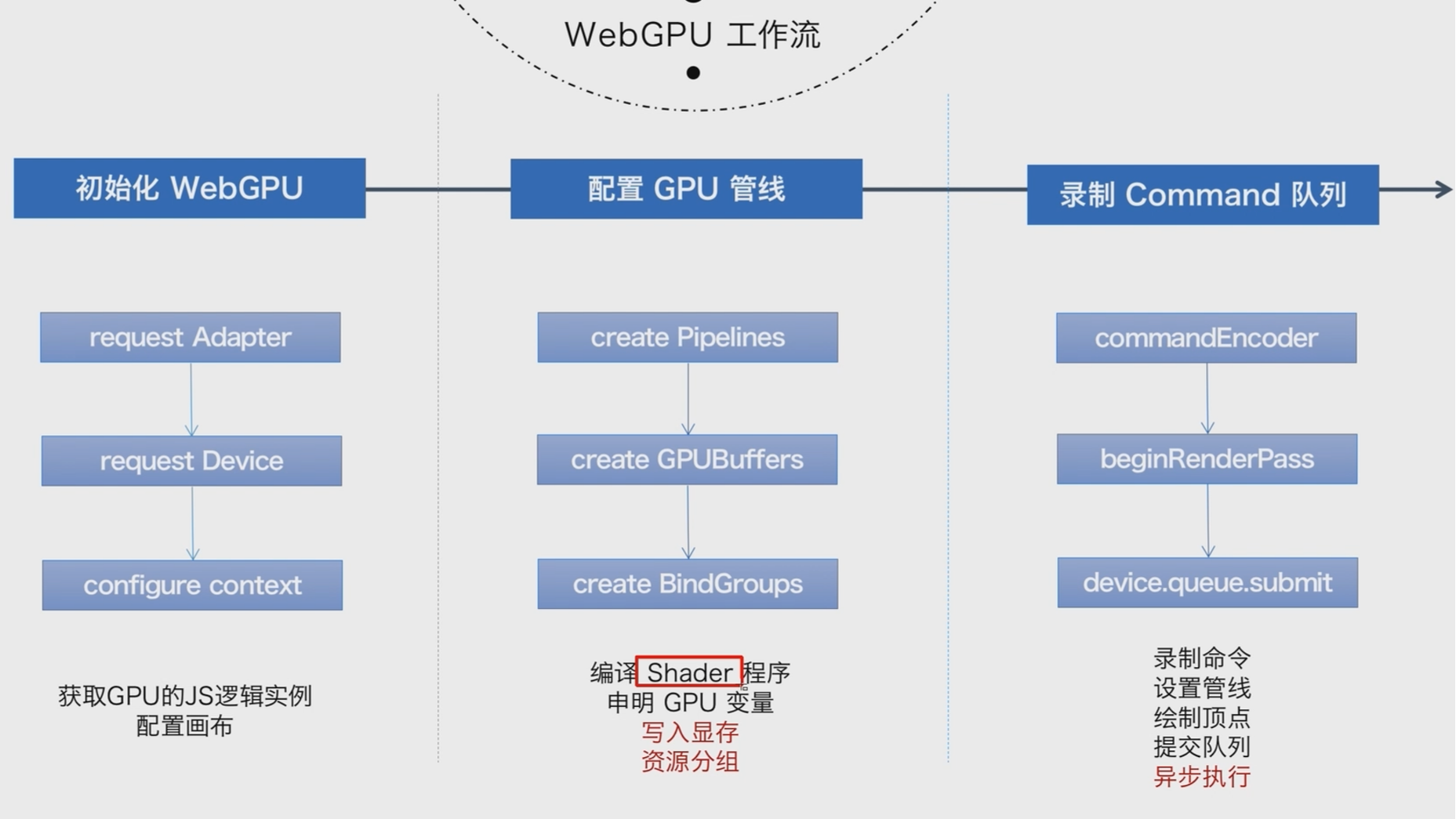
4. 运行流程

5. 参考资料
[1]WebGPU 到底是什么? - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
[2]WebGPU学习系列目录 - Wonder-YYC - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
[3]WebGPU性能测试分析 - Wonder-YYC - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
[4]WebGL 与 WebGPU 比对 前奏 - 四季留歌 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
[7]Orillusion | 专业WebGPU社区 | WebGPU小白入门(一): 零基础创建第一个WebGPU项目


 基于JavaScript的WebGPU入门小案例
基于JavaScript的WebGPU入门小案例

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号