PHP MySQL 存储层级结构的两种方式 邻接表和MPTT
层级结构,也叫树形结构。在关系型数据库中保存树状结构数据,常用的方法有两种:
- 邻接表(Adjacency List)
- 修改过的前序遍历算法(MPTT)
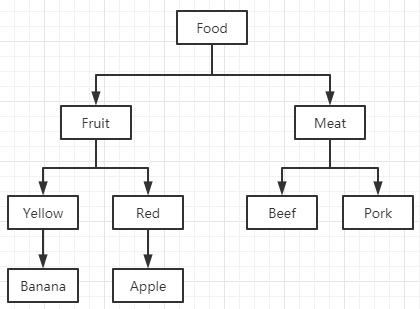
要存储的树状结构数据图如下
表名:Food
1、邻接表
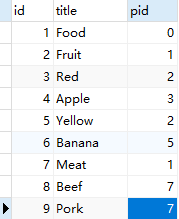
邻接表依赖于pid字段连接上下级。id为自增主键,pid为上一节点的id,例如:Apple的上一节点是Red,所以 Apple pid = Red id
1.1 打印树结构
1 class Tree 2 { 3 private $treeM; // pdo实例 4 private $tname; // 表名称 5 private $stmt; // 结果集 6 private $res; // 结果 7 public function __construct(TreeM $treeM, $tname) 8 { 9 $this->treeM = $treeM->getTreeM(); 10 $this->tname = $tname; 11 } 12 /** 13 * 打印树结构 14 * @param {Int} $root_id 父节点id,为0则显示整个树结构 15 * @param {Int} $level 当前节点所处的层级,用于缩进显示节点 16 */ 17 public function show_tree($root_id = 0, $level) 18 { 19 // 1. 获取父节点 20 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select id, title from {$this->tname} where pid={$root_id}"); 21 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetchAll(2); 22 foreach ($this->res as $row) { 23 // 2. 缩进显示 24 echo '<div style="margin-left:' . ($level * 32) . 'px">' . $row['title'] . '</div>'; 25 // 3. 递归调用当前函数,显示再下一级的子节点 26 $this->show_tree($row['id'], $level + 1); 27 } 28 } 29 }
效果图

1.2 获取节点路径
1 /** 2 * 获取节点路径 3 * @param {Int} 需要获取路径的当前节点的id 4 */ 5 public function get_path($id) 6 { 7 // 1. 获取当前节点 pid 和 title 8 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select title, pid from {$this->tname} where id={$id}"); 9 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetch(2); 10 // 此数组保存路径 11 $path = []; 12 $path[] = $this->res['title']; 13 // 如果父节点非 0,即非根节点,则进行递归调用获取父节点的路径 14 if ($this->res['pid']) { 15 // 递归调用,获取父节点的路径,并且合并到当前路径数组的其它元素前边 16 $path = array_merge($this->get_path($this->res['pid']), $path); 17 } 18 return $path; 19 }
效果图

优点
简单易懂,写入效率较高
缺点
查询起来效率低下。我们对于每个结果,期望只需要一次查询;可是当使用邻接表模型时嵌套的递归使用了多次查询,当树很大的时候,这种慢就会表现得尤为明显。
2、修改过的前序遍历算法
2.1 原理
把“树”横着放,如图所示,根节点 'Food' 左侧标记 '1',然后 'Fruit' 左侧标记2,接着按前序遍历的顺序遍历完树,依次在每个节点的左右侧标记数字
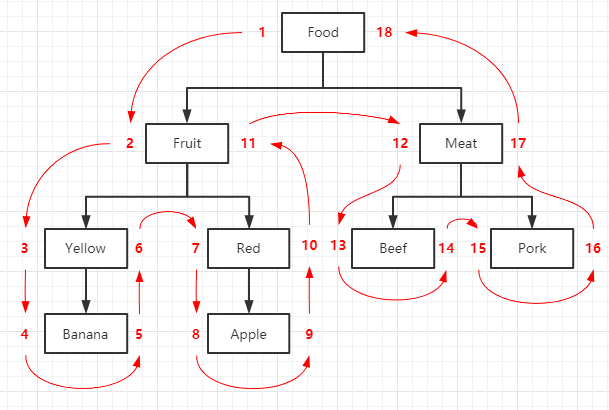
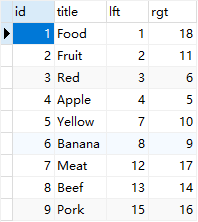
根据上图,改变数据表,增加 lft 和 rgt 两个字段用于存储左右数字(left和right是MySQL保留字,所以用简写)。
2.2 打印树结构
现在想要查看树结构只需一条SQL语句即可。比如,想要打印 'Fruit' 的子树,可以查询左数大于2并且小于11的节点
1 select * from food where lft between 2 and 11;
什么时候显示缩进?缩进多少单位?解决这个问题,需要使用堆栈,即后进先出(LIFO),每到一个节点,将其右边的数字压入堆栈中。我们知道,所有节点右边的值都比其父节点右边的值小,那么将当前节点右边的值和堆栈最上边的右边值进行比较,如果当前节点比堆栈最上边的值小,表示当前堆栈里边剩下的都是父节点了,这时可以显示缩进,堆栈的元素数量即是缩进深度。PHP 代码实现如下:
1 /** 2 * 打印树结构 3 * @param {Int} $root_id 父节点id,为0则显示整个树结构 4 */ 5 public function show_tree($root_id = 1) 6 { 7 // 1. 查询根节点的 lft 和 rgt 8 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select lft, rgt from {$this->tname} where id = {$root_id}"); 9 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetch(2); 10 11 // 堆栈, 存储节点右边的值, 用于显示缩进 12 $stack = []; 13 // 2. 获取 $root_id 节点的所有子孙节点 14 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select title, lft, rgt from {$this->tname} where lft between {$this->res['lft']} and {$this->res['rgt']} order by lft asc"); 15 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetchAll(2); 16 17 // 3. 显示节点 18 foreach ($this->res as $row) { 19 if (count($stack) > 0) { // 仅在堆栈非空的时候检测 20 // 如果当前节点右边的值比堆栈最上边的值大,则移除堆栈最上边的值,因为这个值对应的节点不是当前节点的父节点 21 while ($row['rgt'] > $stack[count($stack) - 1]) { 22 array_pop($stack); 23 } //while 循环结束之后,堆栈里边只剩下当前节点的父节点了 24 } 25 echo '<div style="margin-left:' . (count($stack) * 32) . 'px">' . $row['title'] . '</div>'; 26 // 将当前的节点压入堆栈里边, 为循环后边的节点缩进做准备 27 array_push($stack, $row['rgt']); 28 } 29 }
2.3 求节点的路径
查看某节点的路径,只需求出左数值小于其左数值,并且右数值大于其右数值的所有节点。比如,要查询Apple的路径
1 select title from food where lft < 8 and rgt >9 order by lft asc;
PHP方法实现如下:
1 /** 2 * 打印路径根节点到某节点的路径 3 * @param {Int} $node_id 需要获取路径的节点id 4 */ 5 public function get_path($node_id) 6 { 7 // 1. 获取当前节点的 lft 和 rgt 8 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select lft, rgt from {$this->tname} where id = {$node_id}"); 9 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetch(2); 10 // 2. 获取路径中的所有节点 11 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select title from {$this->tname} where lft <= {$this->res['lft']} and rgt >= {$this->res['rgt']} order by lft asc"); 12 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetchAll(2); 13 // 3. 返回结果数组 14 $path = []; 15 foreach ($this->res as $row) { 16 $path[] = $row['title']; 17 } 18 return $path; 19 }
2.4 插入节点
插入新节点之前,首先要给这个节点腾出空位来。比如我们现在要在 ‘Apple’ 的右边新增 'Orange'节点,则腾位的 SQL 语句如下:
1 update food set rgt=rgt+2 where rgt>9; 2 update food set lft=lft+2 where lft>9;
之后,插入新节点
1 insert into food value(null,'Orange',10,11);
代码:
1 /** 2 * 插入一个新节点 3 * @param {String} $title 节点名称 4 * @param {Int} $pid 父节点id 5 */ 6 public function add($title, $pid) 7 { 8 // 1. 查询父节点的 rgt 值 9 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->query("select rgt from {$this->tname} where id = {$pid}"); 10 $this->res = $this->stmt->fetch(2); 11 // 2. 通过图看出规律, 父节点的子节点中 rgt值最大的为 父节点的rgt值 - 1, 所以 12 $maxRgt = $this->res['rgt'] - 1; 13 // 3. 为新节点腾出空间 14 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->exec("update {$this->tname} set rgt=rgt+2 where rgt>{$maxRgt}"); 15 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->exec("update {$this->tname} set lft=lft+2 where lft>{$maxRgt}"); 16 // 4. 添加新节点 17 $lft = $maxRgt + 1; 18 $rgt = $lft + 1; 19 $this->stmt = $this->treeM->exec("insert into {$this->tname} value(null,'{$title}',{$lft},{$rgt})"); 20 if ($this->stmt) { 21 return $this->treeM->lastInsertId(); 22 } 23 }
优点
树的构造,路径获取方面性能比邻接表好很多,这个算法牺牲了一些写的性能来换取读的性能,在WEB应用中,读数据库的比例远大于写数据库的比例,所以MPTT更受欢迎些,更加实用
缺点
算法比较抽象,不易理解,增加节点时虽然只用了几条SQL语句,但可能会需要更新很多记录,从而造成阻塞


