C++之封装
希望暴露public
希望隐藏private
对象实例化有两种方式,从栈实例化,从堆(new出来的)实例化。
以谁做什么作为核心。
public 放前面,private放后面(属性可以定义为private格式)。
只读属性,只有get方法,没有set方法。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**
* 定义类:Student
* 数据成员:m_strName
* 数据成员的封装函数:setName()、getName()
*/
class Student
{
public:
// 定义数据成员封装函数setName()
void setName(string name) {
m_strName = name;
}
// 定义数据成员封装函数getName()
string getName() {
return m_strName;
}
//定义Student类私有数据成员m_strName
private:
string m_strName;
};
int main()
{
// 使用new关键字,实例化对象
Student *str = new Student;
// 设置对象的数据成员
str->setName("cpp");
// 使用cout打印对象str的数据成员
cout << str->getName() << endl;
// 将对象str的内存释放,并将其置空
delete str;
str = NULL;
return 0;
}
栈区,存储变量。
new分配的内存,是堆区。
全局区,存储全局变量和静态变量。
常量区,存储常量。
代码区,存储代码。
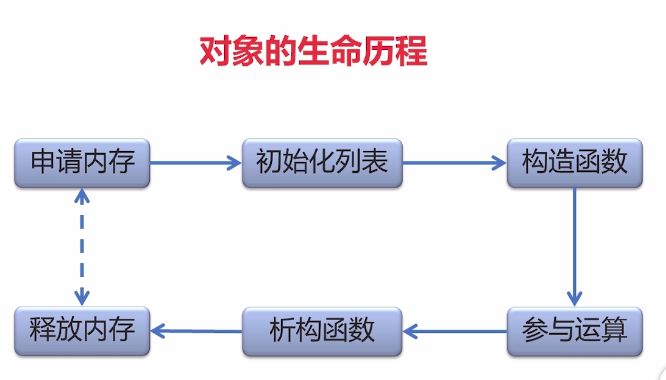
对象需要初始化,有的只有一次,有的需要初始化多次。
构造函数,会在对象实例化时被调用。
读书,视频,先看思想,读其骨架。细节次之。
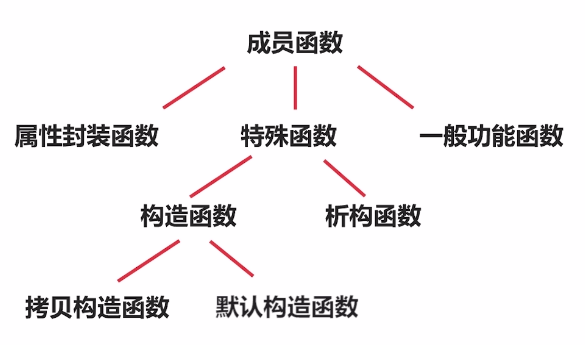
都有默认值的构造函数,称为默认构造函数。
一个类可以没有默认构造函数,有别的构造函数也可以实例化对象。
可以全屏观看,看到关键点可以暂停,记录一下。因为屏幕太小,看着眼疼。或者全屏观看的时候,把文本置顶。
C++中,构造函数与类名相同,析构函数前面加一个波浪线。析构函数,可以进行资源释放。
tips:class 声明类,要小写的c。构造函数,析构函数前面,不需要任何修饰。class结尾还需要分号;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**
* 定义类:Student
* 数据成员:m_strName
* 无参构造函数:Student()
* 有参构造函数:Student(string _name)
* 拷贝构造函数:Student(const Student& stu)
* 析构函数:~Student()
* 数据成员函数:setName(string _name)、getName()
*/
class Student
{
public:
Student() {
m_strName = "jack";
cout<<"Student()"<<endl;
}
Student(string _name) {
m_strName = _name;
cout<<"Student(string _name)"<<endl;
}
Student(const Student& stu) {
cout<<"Student(const Student& stu)"<<endl;
}
~Student() {
cout<<"~Student()"<<endl;
}
void setName(string _name) {
m_strName = _name;
}
string getName() {
return m_strName;
}
private:
string m_strName;
};
int main(void)
{
// 通过new方式实例化对象*stu
Student *stu = new Student("小李");
// 更改对象的数据成员为“慕课网”
stu->setName("慕课网");
// 打印对象的数据成员
cout<<stu->getName()<<endl;
delete stu;
stu = NULL;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/**
* 定义类:Student
* 数据成员:m_strName
* 无参构造函数:Student()
* 有参构造函数:Student(string _name)
* 拷贝构造函数:Student(const Student& stu)
* 析构函数:~Student()
* 数据成员函数:setName(string _name)、getName()
*/
class Student
{
public:
Student() {
m_strName = "jack";
cout<<"Student()"<<endl;
}
Student(string _name) {
m_strName = _name;
cout<<"Student(string _name)"<<endl;
}
Student(const Student &stu) {
cout<<"Student(const Student &stu)"<<endl;
}
~Student() {
cout<<"~Student()"<<endl;
}
void setName(string _name) {
m_strName = _name;
}
string getName() {
return m_strName;
}
private:
string m_strName;
};
int main(void)
{
// 通过new方式实例化对象*stu
Student stu;
Student stu2 = stu;
// 更改对象的数据成员为“慕课网”
stu.setName("慕课网");
// 打印对象的数据成员
cout<<stu.getName()<<endl;
return 0;
}
Student()
Student(const Student &stu)
慕课网
~Student()
~Student()



