shell初级-----结构化命令
if-then语句
bash shell的if语句会执行if后面的那个命令,如果该命令的退出码状态为0会执行then部分的命令,如果是其他值不会执行。
格式如下:
1 2 3 4 | if commandthen commandsfi |
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashif pwdthen echo "ok"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh /ljyok |
在then部分可以使用多条命令。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashtestuser=ljyif grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo "ok"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh ljy:x:1000:1000::/home/ljy:/bin/bashok |
if-then-else
格式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 | if commandthen commandselse commandsfi |
用法很简单,看一个例子就行
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashtestuser=ljyif grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo "$testuser exit on system!"else echo "$testuser does ont on system!"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh ljy:x:1000:1000::/home/ljy:/bin/bashljy exit on system!#此时我定义一个不存在的变量[root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashtestuser=ljy1if grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo "$testuser exit on system!"else echo "$testuser does ont on system!"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh ljy1 does ont on system! |
嵌套if
语法很简单看一个例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashtestuser=zhangsanif grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo "$testuser exit on system!"else echo "$testuser does ont on system!" if ls -d /home/$testuser then echo "but $testuser have a directory!" fifi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh zhangsan does ont on system!/home/zhangsanbut zhangsan have a directory! |
也可以用else部分的另外一种形式elif
格式如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | if commandthen commandselif command2then more commandsfi |
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashtestuser=zhangsanif grep $testuser /etc/passwdthen echo "$testuser exit on system!"elif ls -d /home/$testuserthen echo "but $testuser have a directory!"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh /home/zhangsanbut zhangsan have a directory! |
test命令
如果test命令中列出的条件成立,test命令就会退出并返回特推出状态码0
test 命令可以判断3类条件:
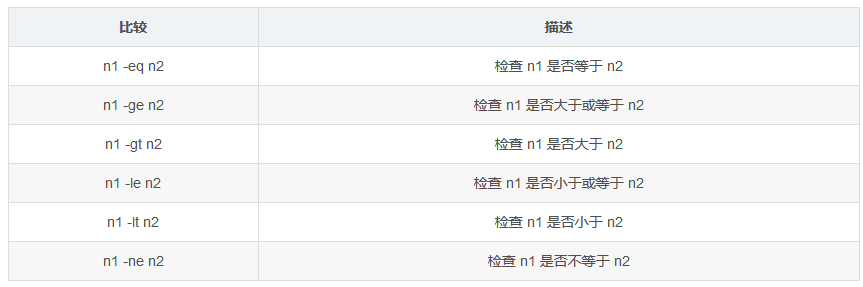
1. 数值比较
2. 字符串比较
3. 文件比较
1、数值比较
注意:test 命令中不能使用浮点数。
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1=10value2=11#if [ $value1 -gt 5 ] #左括号右侧和右括号左侧各加一个空格,否则会报错。then echo "$value1 is bigger than 5"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh 10 is bigger than 5 |
2、字符串比较
条件测试还允许比较字符串值

字符串比较的三大注意事项:
1. 比较的变量最好加上双引号。
2. 大于小于符号必须转义(使用\>),否则 shell 会把它们当做重定向符号而把字符串值当做文件名。
3. 大于小于顺序和 sort 命令所采用的不同。(test默认大写字母小于小写字母)
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1=basketballvalue2=football#if [ $value1 \> $value2 ]then echo "$value1 is greater than $value2"else echo "$value1 is less than $value2"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh basketball is less than football |
-n和-z可以检查一个变量是否含有数据。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1=basketballvalue2=' '#if [ -n $value1 ]then echo "'$value1' is not empty"else echo "'$value1' is empty"fi#if [ -z $value2]then echo "'$value2' is empty"else echo "'$value2' is not empty"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh 'basketball' is not empty' ' is empty |
-n判断长度是否非0,-z判断长度是否为0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | 在变量可能为0的情况下,比较两个字符串是否相等可以这样: if [ "$test"x = "test"x ]; then这里的关键有几点:1 使用单个等号2 注意到等号两边各有一个空格:这是unix shell的要求3 注意到"$test"x最后的x,这是特意安排的,因为当$test为空的时候,上面的表达式就变成了x = testx,显然是不相等的。而如果没有这个x,表达式就会报错:[: =: unary operator expected |
3、文件比较
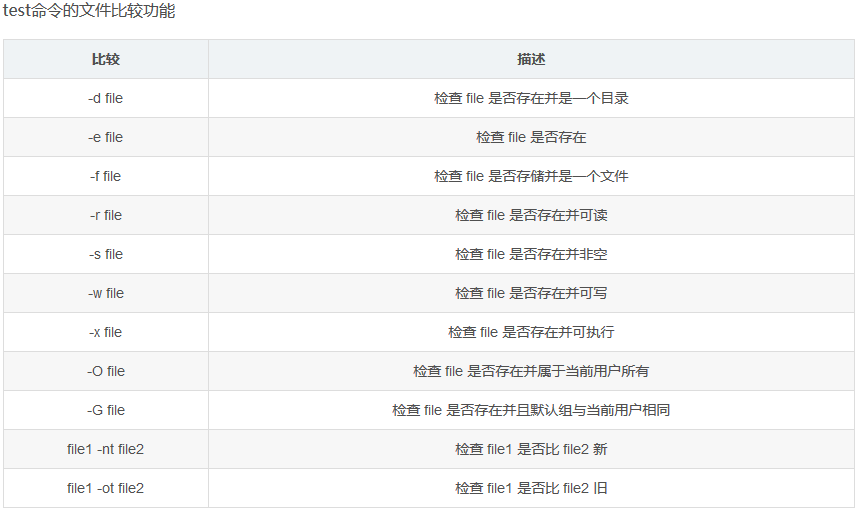
-d检测目录是否存在。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1=/home/ljyif [ -d $value1 ]then echo "$value1 is exited"else echo "$value1 is not exited"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh /home/ljy is exited |
-e允许脚本代码在使用文件或者目录前先检测是否存在。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1='lisi'if [ -e /home/$value1 ]then echo "$value1 is exited"else echo "$value1 is not exited"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh lisi is exited |
-f确定对象是否为文件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh #!/bin/bashvalue1='zhangsan'if [ -e /home/$value1 ] #判断变量是否存在then echo "$value1 is exited" if [ -f /home/$value1 ] #判断是否为文件 then echo "$value1 is a file" else echo "$value1 is a directory" fielse echo "$value1 is not exited"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh zhangsan is exitedzhangsan is a directory |
-r测试文件是否可读。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | [ljy@node1 ljy]$ more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashpwfile=/home/lisi#if [ -r $pwfile ]then tail $pwfileelse echo "this file unable to read!"fi[ljy@node1 ljy]$ sh ceshi2.sh this file unable to read! |
-s检测文件是否为非空,尤其是在不想删除非空文件的时候。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashpwfile=/home/lisi#if [ -s $pwfile ]then echo "this file is not empty"else echo "$pwfile is empty" echo "Deleting empty file..." rm $pwfilefi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh /home/lisi is emptyDeleting empty file... |
-w判断对文件是否可写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashpwfile=/home/lisi#if [ -w $pwfile ]then echo "this file can be write!" date +%H%M >> $pwfileelse echo "$pwfile can not be write"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh this file can be write! |
-x判断文件是否有执行权限。
当然这是针对的非root用户。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashpwfile=/home/test.sh#if [ -x $pwfile ]then echo "this file can be run!" sh $pwfileelse echo "$pwfile can not be run!"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh this file can be run! |
复合条件测试
if-then 语句允许使用布尔逻辑来组合测试:
- 与:[ condition1 ] && [ condition2 ] 或者 [ condition1 -a condition2 ]
- 或:[ condition1 ] || [ condition2 ] 或者 [ condition1 -o condition2 ]
- 非:[ !condition ]
实例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashpwfile=/home/test.sh#if [ -d $pwdfile ] && [ -x $pwfile ] then echo "this file can be run!" sh $pwfileelse echo "$pwfile can not be run!"fi[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh this file can be run! |
case命令
为单个变量寻找特定的值,可以用 case 命令,而不是写那么多的 elif 语句检查。case 命令会检查单个变量列表格式的多个值:
1 2 3 4 5 | case variable inpattern1 | pattern2) commands1 ;; pattern3) commands2 ;; *) default commands ;; esac |
case 命令会将指定的变量同不同模式进行比较。
如果变量和模式是匹配的,那么 shell 会执行为该模式指定的命令。
也可以通过竖线操作符来分割模式,在一行列出多个模式。星号会捕获所有跟所有列出的模式都不匹配的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh #!/bin/bashcase $USER inroot | barbara) echo "Welcome $USER" echo 'Enjoy your visit' ;; testing) echo "Special testing acount" ;; jessica) echo "Don't forget to log off" ;; *) echo "Sorry, you aren't allowed here" ;; esac[root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh Welcome rootEnjoy your visit |



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY