IO流之文件流类操作
IO流原理和分类
流的分类
按操作数据单位:字节流,字符流
按数据流流向:输入流,输出流
按流的角色:节点流,处理流/包装流
IO流共涉及40多个类,
字节流:InputStream,OutStream
字符流:Reader,Writer
这4个类都是抽象类,不能直接创建,要用他的子类创建相应对象IO流里面的类都是这4个派生出来的;
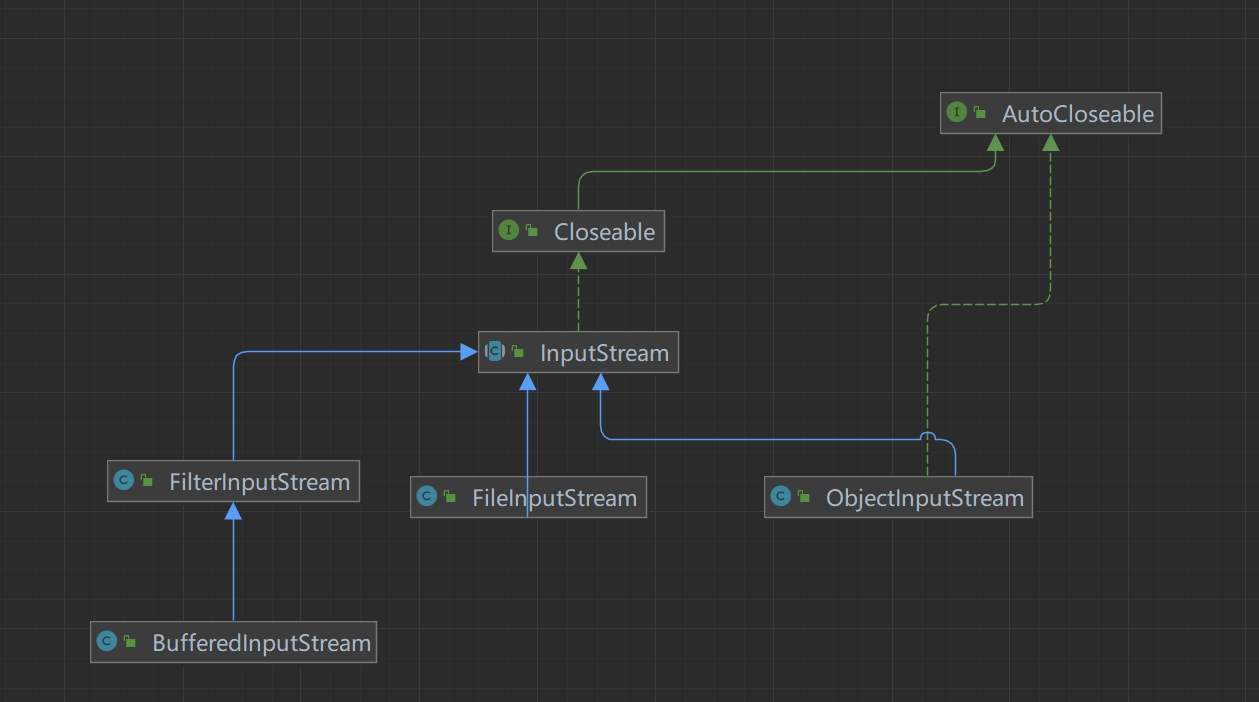
InputStream字节输入流
这个类是所有类字节输入流的超类
常用子类:
文件输入流:FileInputStream
缓冲字节输入流: BufferedInputStream
对象字节输入流:ObjectInputStream
关系图
FileInputStream
package com.wang;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
public class fileinputstream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void Fileread()
{
int readdata=0;
String filepath="d:/helloworld.txt";
File file = new File(filepath);
FileInputStream input=null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(file);
while((readdata=input.read())!=-1)
{
System.out.print((char)readdata);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
finally {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
@Test
public void Fileread02()
{
int readdata=0;
String filepath="d:/helloworld.txt";
File file = new File(filepath);
byte[] zip=new byte[8];
FileInputStream input=null;
try {
input = new FileInputStream(file);
while((readdata=input.read(zip))!=-1)
{
System.out.print(new String(zip,0,readdata));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
finally {
try {
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
FileOutStream
Java程序向文件输出数据有三种方式,在传送数据时,如果该文件不存在,那么该文件会被创建并且写入其中数据,如果存在直接写入数据,如果在new FileoutStream的时候,只读入了文件而没有写true,则会覆盖掉之前的文件数据。
例如下:
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file,true);
这样写直接将数据存在文件末尾,如果不加就会覆盖之前的数据;
第一种方式,读入单个字节
@Test
public void fileoutputstream()
{
String path="d:/helloname.txt";
File file = new File(path);
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
try {
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file);
// String hello="hello,world";
fileOutputStream.write('a');
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
第二种方式,将字符串通过getbytes变为单个字符输出,这样可以输出整个字符串
String hello="hello,world";
fileOutputStream.write(hello.getBytes());
第三种方式,可以将字符串中的第几个字节到第几个字节输出
String hello="hello,world";
fileOutputStream.write(hello.getBytes(),0,3);
在这里加true后,字符会挨个从文件末尾往后输出
将文件拷贝
@Test
public void copy()
{
String path="d:/对象1.jpg";
String path2="d:/对象2.jpg";
File file = new File(path);
File file2 = new File(path2);
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
int readlen=0;
try {
byte[] bt=new byte[1024];
fileInputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(file2);
while((readlen=fileInputStream.read(bt))!=-1)
{
fileOutputStream.write(bt,0,readlen);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
if(fileInputStream!=null)
fileInputStream.close();
if(fileOutputStream!=null);
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
字符流读取文件(Filereader)
单个字符度文件
@Test
public void readerstory()
{
String path="d:/hello.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data=0;
try {
fileReader =new FileReader(path);
while ((data= fileReader.read())!=-1)
{
System.out.print((char)data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(fileReader!=null)
{
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
字符数组读文件
@Test
public void readerstory2()
{
String path="d:/hello.txt";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data=0;
char[] bt=new char[8];
try {
fileReader =new FileReader(path);
while ((data= fileReader.read(bt))!=-1)
{
System.out.print(new String(bt,0,data));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(fileReader!=null)
{
try {
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
@Test
public void writer()
{
String path="d:/hello.txt";
FileWriter fileWriter = null;
char[] chars={'a','b','c'};
try {
fileWriter=new FileWriter(path);
//输出单个字符
fileWriter.write('好');
//输出字符数组
fileWriter.write(chars);
//输出字符串
fileWriter.write("你好世界");
//可以输出指定字符串
fileWriter.write("我是大王",0,2);
//指定字符数组
fileWriter.write("我很厉害".toCharArray(),0,2);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(fileWriter!=null)
{
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号