BFS+记忆化+DFS,为c个目标点找一个最优中心点。
题目大意:在一个8×8的地图中,0是建筑物,1是道路,红、绿、蓝色格子表示3个目标点的位置,黄色格子表示一个中心点,这些点都只会出现在道路中,要找一个最优的中心点,使得从中心点出发到三个目标点的总路程最短,并且最长的子路径也要最短。就是总路程最短的中心点可能有多个,都会有一条子路径是最长的,要求从里面挑出最短的,输出这条最短的最长子路径长度。不能走对角线方向。
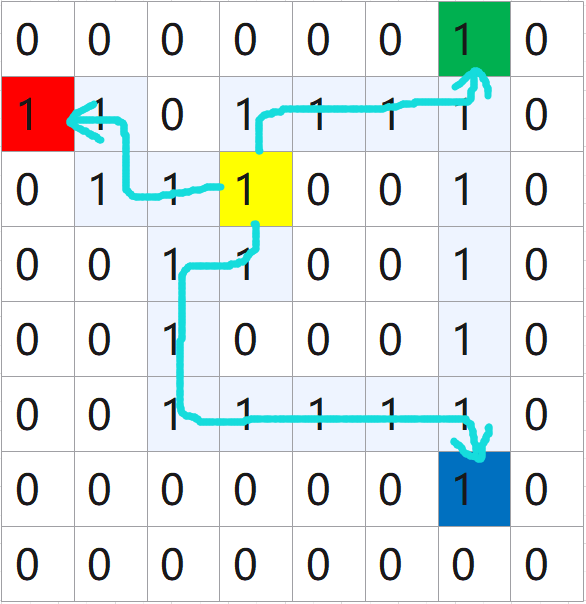
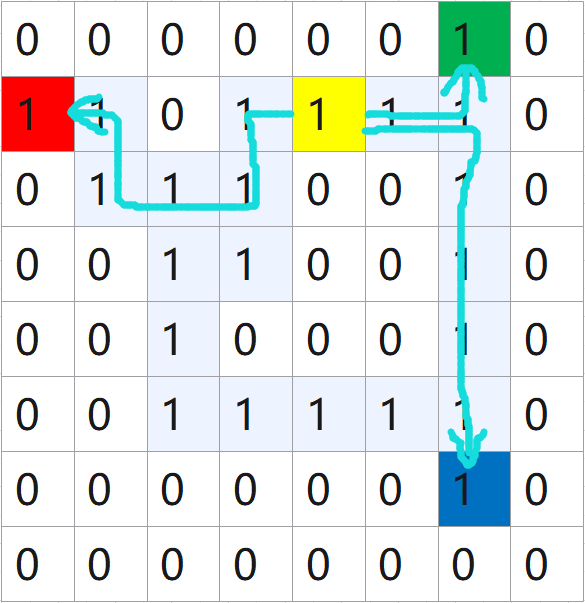
输入:第一行一个整数t表示t个case;第二行两个整数n, c ;n是地图边长,c是目标点个数,然后接c行,每行两个整数表示第i个目标的坐标(y , x),后面再接n行地图数据。因为按照外层循环i为地图数组的x下标,内层循环j为y下标的顺序读取地图数组,得到的是转置的矩阵,目标i的坐标要对应上都进去的数组就要把y放前面,虽然可以人为改变一下读地图的顺序,但是原题示例用的坐标也是反的,就这样吧。
输出:"#"+t+最短的最长子路径长度。
示例输入:
2
5 2
4 3
3 4
1 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 1
0 1 1 1 0
8 3
0 6
1 0
6 6
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
示例输出:
#1 1
#2 8
这是南京某外企的机试题,我没想到今年会比去年难这么多,复习的时候为了省时间就可以避开了困难题。没复习到BFS+记忆化数组,BFS类题目我只复习到使用标记数组记录每个状态是否访问过,然后去重。当时看到这题就想着最短路径BFS,但是没有确定起点一时不知道如何下手,想过求一个目标到另一个目标的最短路径,再继续搜下一个目标,路程连续加起来。也想过DFS+记忆化,但是DFS求最短路径本来就容易超时,这题状态太多了更加对剪枝没信心。
我是跟着一些刷题指南刷的,没看到有BFS+记忆化,一直没往这方面想,回家的火车上突然想到:BFS找到中心点到目标i的最短距离时,最优值节点就是在目标i处获得的,可以追溯最优值节点的父节点,遍历路径上每个节点。从目标i的位置倒退一步(父节点)的位置到目标i的最短距离是1,每往后退一步这个值+1,记录到缓存数组。这样BFS一次就能确定一条路径上所有点到目标i的最短距离,下一次BFS碰到有缓存的就直接用。有缓存就不怕超时,可以对每个可能的点进行BFS,分别确定到c个目标的最短距离。缓存数组记录会每个点到c个目标的最短距离,总路程和最长子路程,每搜完一个点就可以把总路程和最长子路径和两个全局变量对比一次,找到符合题目要求的最优中心点。
详细的步骤看代码吧,写了很详细的注释。
import java.util.Scanner;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2022/11/5 12:30
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Main {
static int n;
static int c;
/**
* 目标i的坐标
*/
static int[][] goal;
/**
* 地图数组
*/
static int[][] map;
/**
* 方向数组
*/
static final int[][] DIR = {{-1, 0}, {0, -1}, {1, 0}, {0, 1}};
/**
* 记忆数组,负责记忆地图每个位置作为中心点时的各种数据。
* 第三维下标[0]-[c-1]是到c个目标的最短路程,[c]是最长子路程,[c+1]是总路程。
*/
static int[][][] cache;
/**
* 记录总路程最短的长度
*/
static int minSun;
/**
* 记录中心点最长的子路径最短的情况
*/
static int becomeShortest;
/**
* 记录最优中心点坐标
*/
static int[] bestCenter;
/**
* 标记路径连通的区域,如果某个"1"的点和另一个"1"的点被0分隔开无法到达,
* 则会被标记成1和2两个区域,搜索时如果起点终点不在一个区域直接淘汰这个点。
*/
static int[][] mark;
/**
* 标记区域编号
*/
static int id;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = sc.nextInt();
long s = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
n = sc.nextInt();
c = sc.nextInt();
/*初始化数据*/
initData();
/*读取c个目标*/
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
goal[j][0] = sc.nextInt();
goal[j][1] = sc.nextInt();
}
/*读取地图*/
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
map[j][k] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
/*遍历所有可能的中心点*/
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
/*在路上的位置才有可能建设中心点*/
if (map[j][k] == 1) {
int[] xy = {j, k};
findCenter(xy);
}
}
}
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("#"+(i+1)+" "+becomeShortest);
/* System.out.println("最优中心点:(" + bestCenter[0] + "," + bestCenter[1] + "),总路程:" + cache[bestCenter[0]][bestCenter[1]][c + 1]);
System.out.println("最长子路径长度:" + becomeShortest);
System.out.println("计算时间:" + (e - s) + "微秒");
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (k==n-1){
System.out.println(cache[j][k][c]);
}else {
System.out.print(cache[j][k][c]+" ");
}
}
}
System.out.println(" ");
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {
if (k==n-1){
System.out.println(cache[j][k][c+1]);
}else {
System.out.print(cache[j][k][c+1]+" ");
}
}
}*/
}
}
/**
* 数据初始化
*/
public static void initData() {
map = new int[n][n];
goal = new int[c][2];
cache = new int[n][n][c + 2];
becomeShortest = 0;
minSun = 0;
bestCenter = new int[2];
mark = new int[n][n];
id = 0;
}
/**
* 输入一个坐标作为中心点,分别搜索该中心点到c个目标点的最短路程以及总路程,记录到缓存数组cache
* 顺便记录最长子路径最短的中心点的数据。
*
* @param xy 中心点坐标
*/
public static void findCenter(int[] xy) {
/*判断该位置是不是合法的,是就可以BFS*/
if (isValidCenter(xy)) {
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {
/*查询一下当前点到某个目标的路径有没有被搜过,没有缓存就可以bfs*/
if (cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][i] == 0) {
/*bfs返回一个最优值节点*/
Node optimal = bFs(xy, goal[i], i);
if (optimal != null) {
/*追溯其路径可以缓存路径上每个位置到i目标的最短距离*/
buffer(optimal, i);
}
}
}
/*记录总路程最短的中心点中最长子路径最短的数据*/
if (minSun==0||cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c+1]<=minSun){
/*先看总路程,总路程更短全部数据更新*/
if (cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c+1]!=minSun){
becomeShortest = cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c];
minSun = cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c+1];
bestCenter = xy;
/*总路程一样时,如果最长子路径更短,则更新数据,中心点也更新*/
}else if (becomeShortest == 0 || cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c] < becomeShortest) {
becomeShortest = cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][c];
bestCenter = xy;
}
}
}
}
/**
* 判断一个中心点是否合法,
* 1,不是任何一个目标点
* 2,和所有目标点在同一个区域,保证能走到所有目标点
* @param xy
* @return
*/
public static boolean isValidCenter(int[] xy) {
/*判断该位置是不是某个目标点*/
boolean notGoal = true;
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {
if (goal[i][0] == xy[0] && goal[i][1] == xy[1]) {
notGoal = false;
break;
}
}
/*如果不是目标点暂时合法*/
boolean valid = notGoal;
if (notGoal) {
/*判断该点有没有标记,没有就用DFS进行标记*/
if (mark[xy[0]][xy[1]] == 0) {
id++;
mark[xy[0]][xy[1]] = id;
dFs(xy);
}
/*遍历所有目标点在mark数组中标记的区域编号,必须和起点相同才合法*/
for (int i = 0; i < c; i++) {
if (mark[goal[i][0]][goal[i][1]] != mark[xy[0]][xy[1]]) {
valid = false;
break;
}
}
}
return valid;
}
/**
* 从一个点开始搜索同一区域的所有点,标上编号
* @param xy
*/
public static void dFs(int[] xy) {
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int[] next = {xy[0] + DIR[i][0], xy[1] + DIR[i][1]};
/*不越界*/
if (next[0] >= 0 && next[0] < n && next[1] >= 0 && next[1] < n) {
/*该点在地图中有路且标记数组中未标号*/
if (map[next[0]][next[1]] == 1 && mark[next[0]][next[1]] == 0){
mark[next[0]][next[1]] = id;
dFs(next);
}
}
}
}
/**
* BFS+记忆化,搜索出发点到终点的距离,每走一步查询当前点的cache,
* 如果有缓存就直接取用,对当前子树剪枝。
*
* @param start 起点坐标
* @param end 终点坐标
* @param g 当前搜索的是起点到第g个目标的最短路径,记录到cache第三维的g下标处
* @return
*/
public static Node bFs(int[] start, int[] end, int g) {
/*创建根节点并入队*/
Node root = new Node();
root.xy = start;
LinkQueue list = new LinkQueue();
list.offer(root);
/*标记走过的点*/
boolean[][] visit = new boolean[n][n];
visit[start[0]][start[1]] = true;
/*记录有缓存的节点,因为四个方向都有可能有缓存,
其中minStep最小的那个是通往目标的正确路径*/
Node storage = null;
while (!list.isEmpty()) {
Node parent = list.poll();
/*搜索四个方向*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
/*向i方向走一步*/
int[] xy = {parent.xy[0] + DIR[i][0], parent.xy[1] + DIR[i][1]};
/*如果不出界并且有路继续*/
if (xy[0] >= 0 && xy[0] < n && xy[1] >= 0 && xy[1] < n ) {
/*有路并且没走过*/
if (map[xy[0]][xy[1]]==1&&!visit[xy[0]][xy[1]]){
visit[xy[0]][xy[1]] = true;
Node child = new Node(parent, xy, parent.currStep + 1);
/*找到目标g则返回最优值节点*/
if (xy[0] == end[0] && xy[1] == end[1]) {
return child;
}
/*当前位置有缓存的子节点不入队,先记录到外层,顺便选出minStep最小的*/
if (cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][g] != 0) {
child.minStep = cache[xy[0]][xy[1]][g];
if (storage == null || child.minStep < storage.minStep) {
storage = child;
}
} else {
/*没有缓存也要求当前步数比缓存的步数更小才入队*/
if (storage == null || child.currStep < storage.minStep) {
list.offer(child);
}
}
}
}
}
}
/*如果在限制内没有找到步数更少的最优值节点,说明缓存点是最优的,直接返回*/
return storage;
}
/**
* 把一个最优值节点追溯到起点的一条路上所有位置的节点都记录在cache中
*
* @param optimal
* @param g
*/
public static void buffer(Node optimal, int g) {
/*currStep是一次bfs搜索到当前节点的步数,不一定是到目标的步数,
可能中途遇到cache就结束了,用这个步数遍历当前bfs
走过的节点链路,不会遍历到存储过的节点*/
int step = optimal.currStep;
for (int i = 0; i < step; i++) {
/*获取父节点*/
Node par = optimal.parent;
/*记录父节点到目标点g的步数*/
par.minStep = optimal.minStep + 1;
/*把当前位置xy[]到目标g的距离记录到cache数组*/
if (cache[par.xy[0]][par.xy[1]][g] == 0) {
cache[par.xy[0]][par.xy[1]][g] = par.minStep;
/*顺便记录当前点所有子路径中最长的*/
if (par.minStep > cache[par.xy[0]][par.xy[1]][c]) {
cache[par.xy[0]][par.xy[1]][c] = par.minStep;
}
/*顺便距离当前点到所有目标的总路程*/
cache[par.xy[0]][par.xy[1]][c + 1] += par.minStep;
}
/*更新当前路径的下一个节点*/
optimal = optimal.parent;
}
}
/**
* bfs节点
*/
static class Node {
/**
* 父节点指针
*/
Node parent;
/**
* 当前位置坐标
*/
int[] xy;
/**
* 此次bfs搜索到当前节点的步数
*/
int currStep;
/**
* 当前节点到指定目标点的步数
*/
int minStep = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int[] xy, int currStep) {
this.parent = parent;
this.xy = xy;
this.currStep = currStep;
}
public Node() {
}
}
/**
* 队列节点
*/
static class QueueNode {
Node item;
QueueNode next;
public QueueNode(Node item) {
this.item = item;
}
}
/**
* 单向队列
*/
static class LinkQueue {
QueueNode head;
QueueNode tail;
int size;
/**
* 入队到尾部
*
* @param n
*/
public void offer(Node n) {
QueueNode qN = new QueueNode(n);
if (tail == null) {
head = tail = qN;
} else {
tail.next = qN;
tail = qN;
}
size++;
}
/**
* 头元素出队
*
* @return
*/
public Node poll() {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
Node oldH = head.item;
head = head.next;
if (head == null) {
tail = null;
}
size--;
return oldH;
}
/**
* 判断队列为空
*
* @return
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return size == 0;
}
}
}
做完以后我又感觉DFS好像也行,有空试一试。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号