BFS算法练习 HDU 1732
去年三星邮件里的一些题。

/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/26 19:34
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Node {
Node parent;
/**
* 决策:本次乘船安排
* 下标0是野人数,1是传教士数
*/
int[] decision = new int[2];
/**
* 船到岸后的状态:
* 下标0,1分别是野人在左岸,右岸的人数
* 下标2,3分别是传教士在左岸,右岸的人数
*/
int[] state = new int[4];
/**
* 阶段:船往返的次数
*/
int level = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int[] decision, int[] state, int level) {
this.parent = parent;
this.decision = decision;
this.state = state;
this.level = level;
}
public Node(int n) {
state[0] = n;
state[2] = n;
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Stack;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/26 19:34
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Demo01 {
/**
* 野人或传教士人数
*/
private static int n = 10;
/**
* 船载客数
*/
private static int m = 4;
private static Node optimalV = new Node(null,null,null,Integer.MAX_VALUE);
private static void bfs(){
LinkedList<Node> liveNode = new LinkedList<>();
liveNode.offer(new Node(n));
while (!liveNode.isEmpty()){
Node parent = liveNode.poll();
int[] state = parent.state;
/*因为追求最少航次,所以每次尽量满载*/
//本次全部运野人
//船上野人数
int c1 = Math.min(state[0], m);
//
if (c1>0&&state[1]+c1<=state[3]||state[1]==0&&state[3]==0){
int[] d1 = {c1,0};
int[] s1 = {state[0]-c1,state[1]+c1,state[2],state[3]};
Node n1 = new Node(parent,d1,s1,parent.level+1);
if (s1[0]==0&&s1[2]==0){
if (n1.level< optimalV.level){
optimalV = n1;
}
}else {
liveNode.offer(n1);
}
}
//本次全部运传教士
//船上教士数
int c2 = Math.min(state[2], m);
//
if (c2>0&&state[2]-c2>=state[0]||state[2]-c2==0&&c2>0){
int[] d2 = {0,c2};
int[] s2 = {state[0],state[1],state[2]-c2,state[3]+c2};
Node n2 = new Node(parent,d2,s2,parent.level+1);
if (s2[0]==0&&s2[2]==0){
if (n2.level< optimalV.level){
optimalV = n2;
}
}else {
liveNode.offer(n2);
}
}
//其他运载方案,i是传教士人数,j是野人数
for (int i = 1; i < c2 ; i++) {
int m1 = Math.min(i,m-i);
for (int j = 1; j <= m1; j++) {
int a1 = state[0]-j;
int a2 = state[1]+j;
int a3 = state[2]-i;
int a4 = state[3]+i;
//
if (a1<=a3&&a2<=a4){
int[] di = {j,i};
int[] si = {a1,a2,a3,a4};
Node ni = new Node(parent,di,si,parent.level+1);
if (si[0]==0&&si[2]==0){
if (ni.level< optimalV.level){
optimalV = ni;
}
}else {
liveNode.offer(ni);
}
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
bfs();
System.out.println("最少航次:"+optimalV.level);
Stack<Node> s = new Stack<>();
while (optimalV.parent!=null){
s.push(optimalV);
optimalV = optimalV.parent;
}
int s1 = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < s1; i++) {
Node n1 = s.pop();
System.out.println("第"+n1.level+"次乘船安排:");
System.out.println("[野人"+n1.decision[0]+" | 传教士"+n1.decision[1]+"]");
System.out.println("乘船后左岸: [野人"+n1.state[0]+" | 传教士"+n1.state[2]+"] 右岸: [野人"+n1.state[1]+" | 传教士"+n1.state[3]+"]");
}
}
}
N*M的矩阵,有坦克A和B,终点C和D坦克A需要走到C,坦克B需要走到D。每经过一秒,坦克可以选择周围的8个方向任意移动一步,也可以选择原地不动。
但是两个坦克不能相邻(周围8个方向),也不能去有墙的地方。问,最少需要多少秒,才能使两个坦克都达到目的地?
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/27 11:41
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Node {
Node parent;
/**
* 决策,1-8分别表示8个方向,0表示不动
*/
int[] decision = new int[2];
/**
* 状态:[0,1],[2,3]分别是A,B在地图数组中的位置下标
*/
int[] state = new int[4];
/**
* 阶段:第几秒
*/
int level = 0;
/**
* 标记当前路径走过的点
*/
int[][]mark;
/**
* 优先级
*/
int priority = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int[] decision, int[] state, int level, int[][] mark, int priority) {
this.parent = parent;
this.decision = decision;
this.state = state;
this.level = level;
this.mark = mark;
this.priority = priority;
}
public Node() {
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/27 11:41
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Demo01 {
private static int n = 6;
private static int m = 6;
/**
* 地图
*/
private static int[][] map = new int[n][m];
/**
* 方向
*/
private static int[] dirX = {0,0,1,1,1,0,-1,-1,-1};
private static int[] dirY = {0,1,1,0,-1,-1,-1,0,1};
private static int[] outset = new int[4];
private static int[] end = new int[4];
private static Node optimalV = new Node();
private static void bfs(){
optimalV.level = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
PriorityQueue<Node> liveNode = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.priority));
Node top = new Node();
top.state = Arrays.copyOf(outset,4);
top.mark = new int[n][m];
top.mark[top.state[0]][top.state[1]] = 1;
top.mark[top.state[2]][top.state[3]] = 1;
liveNode.offer(top);
while (!liveNode.isEmpty()){
Node parent = liveNode.poll();
int[] state = Arrays.copyOf(parent.state,4);
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) {
int[] childDecision = {i,j};
int[] childState = {state[0]+dirX[i],state[1]+dirY[i],
state[2]+dirX[j],state[3]+dirY[j]};
int b = check(childDecision,childState,parent.mark);
if (b!=0){
int[][] mark = copyArr(parent.mark);
mark[childState[0]][childState[1]]=1;
mark[childState[2]][childState[3]]=1;
int priority = priority(childState);
Node child = new Node(parent,childDecision,childState, parent.level+1,mark,priority);
if (b==1&&child.level<optimalV.level){
optimalV = child;
return;
}
if (b==2){
liveNode.offer(child);
}
}
}
}
}
}
private static int[][] copyArr(int[][] mark){
int[][] temp = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
temp[i][j] = mark[i][j];
}
}
return temp;
}
private static int check(int[] d,int[] s,int[][] mark){
//不越界
boolean b1 = s[0]>=0&&s[1]>=0&&s[2]>=0&&s[3]>=0 && s[0]<n&&s[1]<m&&s[2]<n&&s[3]<m;
if (b1){
//到达终点
boolean b2 = s[0]==end[0]&&s[1]==end[1]&&s[2]==end[2]&&s[3]==end[3];
if (b2){
return 1;
}
//不相邻
boolean b3 = Math.abs(s[0]-s[2])>1||Math.abs(s[1]-s[3])>1;
//不重复
boolean bl1 = mark[s[0]][s[1]]==0;
boolean bl2 = mark[s[2]][s[3]]==0;
boolean bl3 = d[0]==0;
boolean bl4 = d[1]==0;
boolean b4 = bl1 && bl2 && !bl3 && !bl4 || bl3 && bl2 || bl4 && bl1;
if (b3&&b4){
return 2;
}
}
return 0;
}
private static int priority(int[] state){
int dist = Math.abs(state[0]-end[0])+Math.abs(state[1]-end[1])+Math.abs(state[2]-end[2])+Math.abs(state[3]-end[3]);
return dist;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
outset = new int[] {0,0,0,m-1};
end = new int[] {n-1,0,n-2,m-1};
bfs();
System.out.println("最少要"+optimalV.level+"秒俩坦克到达目的地");
}
}
SAM-ROUTE是一种用于自动驾驶车辆的寻路算法。SAM-ROUTE提供了一种功能,每当向地图添加新建筑信息时,该功能会自动更新最佳路线。
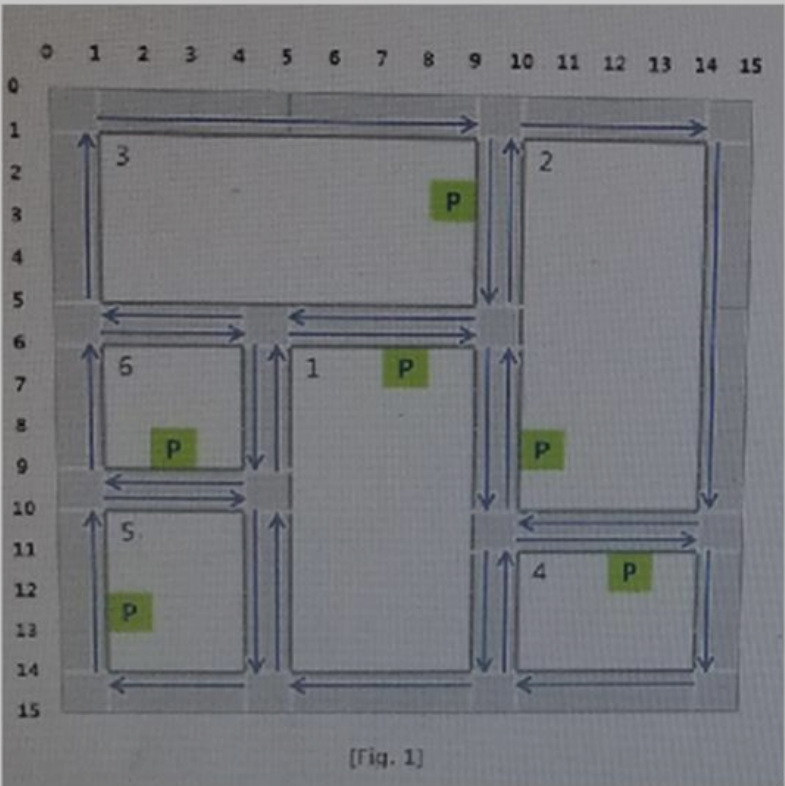
图1给出了N*N地图上各建筑物的信息。基于此信息,您需要实现一种逻辑,以计算建筑物之间的最短距离。
每栋建筑周围都有一条宽度为1的道路。道路规则如下:
1、汽车只能以建筑为中心顺时针行驶。
2、从一个地方开车到另一个地方时,起点和终点总是两栋楼的停车场。
3、与每个建筑的顶点对角相邻的点始终成为交点。在十字路口,汽车可以直行或右转、左转和掉头。
4、汽车在1条件下还能进出停车场。
建筑物的信息包括建筑物的位置、建筑物的宽度和高度以及停车场的位置。
设计一个函数查找从起点建筑的停车场到终点建筑的停车场的最短路径,并返回相应的移动距离。
只有当预先调用两次附加建筑函数时,才调用该函数。
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 0:14
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Node {
Node parent;
/**
* 决策:0,1,2,3表示上下左右四种方向
*/
int dir = 0;
/**
* 状态:决策后的位置
*/
int[] position = new int[2];
/**
* 阶段:当前路径行驶的距离
*/
int dist = 0;
/**
* 标记
*/
int[][] mark;
/**
* 优先级,当前位置到终点的距离越小优先级越高
*/
int priority = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int dir, int[] position, int dist, int[][] mark, int priority) {
this.parent = parent;
this.dir = dir;
this.position = position;
this.dist = dist;
this.mark = mark;
this.priority = priority;
}
public Node() {
}
}
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 13:33
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Building {
int[] position = new int[2];
int width = 0;
int length = 0;
/**
* 0,1是停车场坐标,3是停车场位于建筑的方向
*/
int[] park = new int[3];
public Building(int[] position, int width, int length, int[] park) {
this.position = position;
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
this.park = park;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 0:14
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Deom01 {
private static int n = 15;
private static int[][] map = new int[n][n];
/**
* 建筑数量
*/
private static int buildingNum = 0;
private static ArrayList<Building> buildings = new ArrayList();
/**
* 添加建筑
*/
private static int addBuilding(int[] position,int width,int length,int[] p){
//检查是否越界
if (position[0]<1||position[1]<1||position[0]+width>n-1||position[1]+length>n-1){
return 1;
}
int conf = 0;
//检查是否和其他建筑冲突
if (buildingNum>0){
for (int i = 0; i < buildingNum; i++) {
Building bi = buildings.get(i);
boolean b1 = position[0]+width<bi.position[0]||position[1]+length<bi.position[1];
boolean b2 = bi.position[0]+bi.width<position[0]||bi.position[1]+bi.length<position[1];
if (!(b1||b2)){
conf = 1;
}
}
}
if (conf==1){
return 2;
}
//确定停车场位置
int[] park = new int[3];
//上下左右四条边
if (p[0]==0){
park[0] = position[0]+Math.min(width,p[1])-1;
park[1] = position[1];
}
if (p[0]==1){
park[0] = position[0]+Math.min(width,p[1])-1;
park[1] = position[1]+length-1;
}
if (p[0]==2){
park[0] = position[0];
park[1] = position[1]+Math.min(length,p[1])-1;
}
if (p[0]==3){
park[0] = position[0]+width-1;
park[1] = position[1]+Math.min(length,p[1])-1;
}
park[2] = p[0];
Building bi = new Building(position,width,length,park);
buildings.add(bi);
buildingNum++;
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < length; j++) {
map[position[0]+i][position[1]+j] = buildingNum;
}
}
map[park[0]][park[1]] = -buildingNum;
return 0;
}
private static int[] dirX = {0,0,-1,1,1,1,-1,-1};
private static int[] dirY = {-1,1,0,0,-1,1,1,-1};
private static Node optimalV = new Node();
private static void getDistance(int starting,int finishing){
//最优值设为无穷大
optimalV.dist = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[] topPosition = new int[2];
topPosition[0] = buildings.get(starting-1).park[0]+dirX[buildings.get(starting-1).park[2]];
topPosition[1] = buildings.get(starting-1).park[1]+dirY[buildings.get(starting-1).park[2]];
Node top = new Node();
top.position = Arrays.copyOf(topPosition,2);
top.dist=1;
top.mark = new int[n][n];
top.mark[topPosition[0]][topPosition[1]] = 1;
PriorityQueue<Node> liveNode = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.priority));
liveNode.offer(top);
//转换下标,找到当前方向的左边
int[] left = {3,2,0,1};
int[] ending = Arrays.copyOfRange(buildings.get(finishing-1).park,0,2);
int[] reset = {1,0,3,2};
//BFS
while (!liveNode.isEmpty()){
Node parent = liveNode.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
/*判断该方向是否可行:往前一步是道路0,
当前方向右边或右上方是建筑物(符合顺时针方向)*/
int a = parent.position[0]+dirX[i];
int b = parent.position[1]+dirY[i];
int c = parent.position[0]+dirX[left[i]];
int d = parent.position[1]+dirY[left[i]];
int e = a+dirX[left[i]];
int f = b+dirY[left[i]];
boolean b1 = a>=0&&b>=0&&a<n&&b<n&&map[a][b]==0;
boolean b2 = c>=0&&d>=0&&c<n&&d<n&&map[c][d]!=0;
boolean b3 = e>=0&&f>=0&&e<n&&f<n&&map[e][f]!=0;
boolean b4 = reset[i]!=parent.dir;
if (b1&&(b2||b3)&&b4){
int[] cPos = {a,b};
int[][] mark = copyArr(parent.mark);
mark[a][b] = 1;
int priority = Math.abs(a-ending[0])+Math.abs(b-ending[1]);
Node child = new Node(parent,i,cPos,parent.dist+1,mark,priority);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
if (a+dirX[j]==ending[0]&&b+dirY[j]==ending[1]){
optimalV = child;
optimalV.dist+=1;
return;
}
}
liveNode.offer(child);
}
}
}
}
private static int[][] copyArr(int[][] mark){
int[][] temp = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
temp[i][j] = mark[i][j];
}
}
return temp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
addBuilding(new int[]{5,6},4,8,new int[]{0,3});
addBuilding(new int[]{10,1},4,9,new int[]{2,8});
addBuilding(new int[]{1,1},8,4,new int[]{3,2});
addBuilding(new int[]{10,11},4,3,new int[]{0,3});
addBuilding(new int[]{1,10},3,4,new int[]{2,3});
addBuilding(new int[]{1,6},3,3,new int[]{1,2});
int s = 4;
int f = 5;
getDistance(s,f);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (map[j][i]<0){
System.out.print(map[j][i]+" ");
}else {
System.out.print(" "+map[j][i]+" ");
}
if (j==n-1){
System.out.println();
}
}
}
System.out.println("从城市"+s+"到城市"+f+"的最短距离为:"+optimalV.dist);
}
}
坦克大战:
你的坦克不能穿过河流或墙壁,但它可以通过射击摧毁砖墙。当你击中砖墙时,砖墙会变成空的空间,但是,如果你的子弹击中了钢墙,墙就不会受到损坏。
在每个回合中,您可以选择移动到相邻(4个方向,而不是8个方向)的空白区域,或者在四个方向中的一个方向上不移动射击。
射击将朝那个方向继续,直到它超出地图或撞到墙上。如果射击击中砖墙,墙将消失(即在本回合中)。那么,根据地图的描述,你的坦克和目标的位置,你至少要转多少圈才能到达那里?
输入由几个测试用例组成。输入文件的第一行包含一个整数t(1≤ T≤ 100),测试用例的数量。然后,t测试用例在下面几行中给出。每个测试用例的第一行包含两个整数M和N(2<=M,N<=300)。以下M行中的每一行都包含N个大写字母,每个字母都是“Y”(你)、“T”(目标)、“S”(钢墙)、“B”(砖墙)、“R”中的一个(河流)和“E”(空白)。“Y”和“T”只出现一次。
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 22:29
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Node {
Node parent;
/**
* 决策:0-3表示向上右下左四个方向移动,4-7表示向四个方向射击。
*/
int dir = 0;
/**
* 状态:决策后的位置
*/
int[] position = new int[2];
/**
* 阶段:回合数
*/
int turns = 0;
/**
* 标记
*/
char[][] mark;
/**
* 优先级
*/
int priority = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int dir, int[] position, int dist, char[][] mark, int priority) {
this.parent = parent;
this.dir = dir;
this.position = position;
this.turns = dist;
this.mark = mark;
this.priority = priority;
}
public Node() {
}
}
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 22:29
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Demo01 {
private static int n = 8;
private static int m = 6;
private static char[][] map = {
{'E','B','B','B','E','B'},
{'E','S','B','E','R','E'},
{'B','E','R','E','B','E'},
{'S','E','E','E','B','R'},
{'B','T','B','B','E','B'},
{'B','E','B','E','Y','E'},
{'B','B','B','B','S','E'},
{'B','E','E','B','B','R'}
};
/**
* 起点的坐标
*/
private static int[] starting = new int[2];
/**
* 终点的坐标
*/
private static int[] ending = new int[2];
/**
* 最优值结点
*/
private static Node optimalV = new Node();
/**
* 方向
*/
private static int[] dirX = {-1,0,1,0};
private static int[] dirY = {0,1,0,-1};
/**
*
*/
private static void bfs(){
/*先把最少回合设置成最大*/
optimalV.turns = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
/*头结点*/
Node top = new Node();
top.position = Arrays.copyOf(starting,2);
top.mark = copyArr(map);
PriorityQueue<Node> liveNode = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.priority));
liveNode.offer(top);
while (!liveNode.isEmpty()){
Node parent = liveNode.poll();
/*往四个方向移动的子节点*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int a = parent.position[0] + dirX[i];
int b = parent.position[1] + dirY[i];
boolean bl1 = a>=0&&b>=0&&a<n&&b<m;
boolean bl2 = parent.mark[a][b] == 'E'||parent.mark[a][b] == 'T';
/*如果往i方向移动一步为空或者终点就选择移动*/
if (bl1&&bl2) {
int[] p1 = {a,b};
int t1 = parent.turns +1;
char[][] mark1 = copyArr(parent.mark);
int pri1 = getPriority(p1,ending,t1);
Node child1 = new Node(parent,i,p1,t1,mark1,pri1);
if (mark1[a][b]=='T'){
optimalV=child1;
return;
}else {
child1.mark[a][b]='Y';
liveNode.offer(child1);
}
}
//如果往i方向是可击毁的墙就原地发射炮弹
if (bl1&&parent.mark[a][b] == 'B'){
int dir = i+4;
int[] p2 = Arrays.copyOf(parent.position,2);
int t2 = parent.turns +1;
char[][]mark2 = copyArr(parent.mark);
mark2[a][b] = 'E';
int pri2 = getPriority(p2,ending,t2);
Node child2 = new Node(parent,dir,p2,t2,mark2,pri2);
liveNode.offer(child2);
}
}
}
}
private static int getPriority(int[] p,int[] end,int t){
//两队距离加回合数,给射击墙的动作加权
return Math.abs(p[0]-end[0])+Math.abs(p[1]-end[1])+t;
}
private static char[][] copyArr(char[][] arr){
int a = arr.length;
int b = arr[0].length;
char[][] temp = new char[a][b];
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b; j++) {
temp[i][j] = arr[i][j];
}
}
return temp;
}
private static void getStartAndEnd(){
int b = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < map.length; i++) {
if (b==2){
return;
}
for (int j = 0; j < map[0].length; j++) {
if (map[i][j]=='Y'){
starting[0] = i;
starting[1] = j;
b++;
}
if (map[i][j]=='T'){
ending[0] = i;
ending[1] = j;
b++;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
getStartAndEnd();
bfs();
System.out.println("最少回合数:"+optimalV.turns);
int si = optimalV.turns+1;
for (int i = 0; i < si; i++) {
System.out.println("决策:"+optimalV.dir);
System.out.println("状态:"+Arrays.toString(optimalV.position));
optimalV=optimalV.parent;
}
}
}
HDU 1732 Push Box
Push Box是一款经典的益智游戏。这个游戏在一个格子里玩,有五种类型的方块,玩家、盒子、洞、空地和墙。在每一步中,如果目标位置为空,玩家可以向上、向下、向左或向右移动。此外,如果目标位置的一个盒子,并且该方向的下一个位置是空的,玩家可以移动到目标位置,然后将盒子推到下一个地方。记住,玩家和盒子都不能移出网格,或者你可以假设整个网格周围有一堵墙。这个游戏的目的是把每个盒子都推到一个洞里。现在,你的问题是找到用最短步骤实现目标的策略,假设只有三个框。
输入:输入由几个测试用例组成。每个测试用例以包含两个数字n,m(1<n,m)的线开始≤ 8) 、网格的行和列。接下来是n行,每行包含精确的m个字符,表示其中的块类型。(表示空位,X表示玩家,表示盒子,#表示墙,@表示洞)。每个案例都包含一个X、三个和三个@。输入以EOF结束。
输出:您必须在一行中为每个案例打印最短策略的长度。(如果没有此类策略,则为-1)
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 19:17
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Node {
Node parent;
/**
* 决策:0,1,2,3表示上下左右四种方向
*/
int dir = 0;
/**
* 状态:决策后的位置
*/
int[][] position = new int[4][2];
/**
* 阶段:当前走过的步数;
*/
int dist = 0;
/**
* 进洞箱子数量
*/
int intoNum = 0;
// int[][] mark;
/**
* 优先级
*/
int priority = 0;
public Node(Node parent, int dir, int[][] position, int dist, int intoNum, int priority) {
this.parent = parent;
this.dir = dir;
this.position = position;
this.dist = dist;
this.intoNum = intoNum;
this.priority = priority;
}
public Node() {
}
}
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* @Author jinjun99
* @Date Created in 2021/11/28 19:16
* @Description
* @Since version-1.0
*/
public class Demo01 {
private static int n = 6;
private static int m = 6;
private static char[][] maze = {
{'.','.','.','#','@','.'},
{'@','.','.','*','.','.'},
{'#','*','#','#','.','.'},
{'.','.','#','#','*','#'},
{'.','.','X','.','.','.'},
{'.','@','#','.','.','.'}};
private static Node optimalV = new Node();
private static int[] dirX = {0,1,0,-1};
private static int[] dirY = {-1,0,1,0};
private static void bfs(int[][]position){
Node top = new Node();
top.position=copyArr(position);
PriorityQueue<Node> liveNode = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.priority));
liveNode.offer(top);
while (!liveNode.isEmpty()){
Node parent = liveNode.poll();
//四个方向搜索
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int[][] cP = copyArr(parent.position);
int a = cP[0][0]+dirX[i];
int b = cP[0][1]+dirY[i];
boolean bl1 = a>=0&&b>=0&&a<n&&b<m;
int c = a+dirX[i];
int d = b+dirY[i];
boolean bl2 = c>=0&&d>=0&&c<n&&d<m;
boolean bl3 = true;
//先遍历'*'的位置
for (int j = 1; j < 4; j++) {
//如果该方向上往前一步是'*'
if (bl1&&cP[j][0]==a&&cP[j][1]==b){
//则跳过'.'的情况
bl3 = false;
//如果往前一步不是'#'(即是'.'或'@')
if (bl2&&maze[c][d]!='#'){
//人和箱子往前一步
cP[0][0] = a;
cP[0][1] = b;
cP[j][0] = c;
cP[j][1] = d;
//子结点
int di = parent.dist+1;
int in = parent.intoNum;
if (maze[c][d]=='@'){
in++;
}
int pri = getPriority(di,in);
Node child = new Node(parent,i,cP,di,in,pri);
if (in==3){
optimalV=child;
return;
}
liveNode.offer(child);
break;
}
}
}
if (bl1&&bl3){
cP[0][0] = a;
cP[0][1] = b;
int di = parent.dist+1;
int in = parent.intoNum;
int pri = getPriority(di,in);
liveNode.offer(new Node(parent,i,cP,di,in,pri));
}
}
}
}
private static int getPriority(int dist,int intoNum){
if (intoNum==0){
return dist;
}else {
return dist /intoNum;
}
}
private static int[][] copyArr(int[][] arr){
int n = arr.length;
int m = arr[0].length;
int[][] a1 = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
a1[i][j]=arr[i][j];
}
}
return a1;
}
private static int[][] hide(int num){
int[][] temp = new int[num+1][2];
int c = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (maze[i][j]=='*'){
temp[c][0]=i;
temp[c][1]=j;
maze[i][j]='.';
c++;
}
if (maze[i][j]=='X'){
temp[0][0]=i;
temp[0][1]=j;
maze[i][j]='.';
}
}
}
return temp;
}
private static void recover(int[][] p){
maze[p[0][0]][p[0][1]] = 'X';
maze[p[1][0]][p[1][1]] = '*';
maze[p[2][0]][p[2][1]] = '*';
maze[p[3][0]][p[3][1]] = '*';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] starPosition = hide(3);
bfs(starPosition);
recover(starPosition);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
System.out.print(maze[i][j]+" ");
if (j==m-1){
System.out.println();
}
}
}
System.out.println("最短距离:"+optimalV.dist);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号