分支限界法基础练习笔记
分支限界法的本质也是穷举。同样地,把一个多阶段决策问题的每个决策和状态组织成一棵解空间树,然后遍历解空间树得到最优值和最优解。分支限界法的搜索方式是先搜索完一层的节点再搜索下一层。比如下面这棵子集树,搜索顺序是A→B→C→D→E→F→G→……→O.
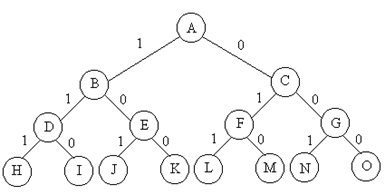
同一层的结点之间并没有什么联系,要按广度优先的顺序搜索结点,就要设一个队列使结点按顺序排列。因为广度优先搜索时每搜索一个活结点都会一次性产生其所有子节点,所以队列只需要记录活结点。又因为父结点和子结点之间可能包含其他活结点,所以每次产生子节点都从队尾入队。
综上可得分支限界法的搜索方式:首先设队列Q; 活结点A入队,Q=[A]; 循环(第一次){ 取出队头元素A,扩张得到子节点B,C按顺序入队。} Q=[B,C]; 循环(第二次){ 取出队头元素B,扩张得到子节点D,E按顺序入队。} Q=[C,D,E]; 循环(第三次){ 取出队头元素C,扩张得到子节点F,G按顺序入队。} Q=[D,E,F,G]; 循环(第四次){ 取出队头元素D,扩张得到叶子节点H,I,叶子节点不必入队,直接比较最优值。} Q=[E,F,G]; 循环到Q=[]结束。搜索过程中同样可以用约束函数和限界函数剪枝。
上述方法还有缺陷,既不能判断当前结点在第几层,也不能判断当前结点的父结点是哪个,所以无法判断叶子结点,也无法根据最优值结点构造最优解。可以设一个结点类,包含结点的父结点,决策,状态,以及所在层数。根节点层数为0,每个子节点的层数都是父结点的层数+1, 当层数为n时就能判断当前结点为叶子结点了。找到最优值结点时可以根据结点对象的决策和层数得到最优解的一个分量,追溯父结点直到根节点就能构造出最优解。以上就是队列式分支限界法。
队列式分支限界法寻找最优值和最优解比回溯法还麻烦,搜索量没有变,还要花费存储空间。根据动态规划中以空间换时间的经验,队列式分支限界法显然还能优化一下。队列的作用是安排搜索顺序,可以尝试在排序上下功夫,而且结点对象包含了结点的所有信息,无论怎么排序都不影响其他操作。
限界函数是用来判断一个结点的潜力的,对于最大化问题,当一个结点的上界函数值不大于当前最优值,则可以判断该节点的子结点树中不存在最优值,对该结点的子树剪枝。换个思路,当一个结点的上界函数值比其他已知的结点的上界函数值大时,这个结点的子树中存在最优值的可能性也更大,应该优先搜索该结点。所以可以给结点类增加一个变量:优先级,优先级的值等于该结点的上界函数值,使用优先队列按优先级对活结点实时排序,这样每次取出的头结点都是最有可能获得最优值的,以便尽快地找出一个最优值结点。因为优先级大于等于状态值,当一个叶子结点的状态值大于或等于当前队列头结点的优先级时,说明队列中的活结点都无法获得更优的子节点了,所以剩下的活结点也不必搜索了,这个叶子结点就是一个最优值结点。
【例1】装载问题:有一批共 n 个集装箱要装上 2 艘载重量分别为 c1 和 c2 的轮船,其中集装箱 i 的重量为 wi,且所有货物总重量<=c1+c2。要求确定是否有一个合理的装载方案可将这个集装箱装上这 2 艘轮船。如果有,找出一种装载方案。
首先将第一艘轮船尽可能装满,然后将剩余的集装箱装在第二艘轮船上。只需要找到尽可能把第一个轮船装满的方案就可获得最优值和最优解,相当于只考虑重量的0-1背包问题。为了简化设n=3。设1表示当前集装箱装入1船,0表示不装。解空间:{(1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0), (0, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), (0, 0, 1), (0, 0, 0)}。解空间结构为子集树。
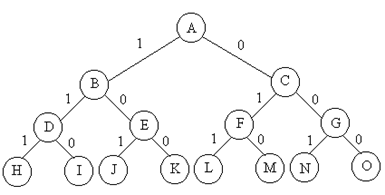
队列式分支限界法:

1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.Arrays;
3 import java.util.Collections;
4 import java.util.LinkedList;
5 import java.util.Random;
6
7 public class Demo5 {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 //集装箱数量
10 int n = 20;
11 //第一艘船的载重量
12 int c1 = 30;
13 //第二艘船的载重量
14 int c2 = 30;
15 //各个集装箱的重量
16 int[] w = new int[n+1];
17 //所有集装箱总重量
18 int tW = 0;
19 Random r = new Random();
20 int num = 1;
21 while (num<=n){
22 int wi = r.nextInt((c1+c2)*2/n)+1;
23 if ((tW+wi+(n-num)) <= (c1+c2)){
24 w[num] = wi;
25 tW+=wi;
26 num++;
27 }
28 }
29 System.out.println("第一艘船载重量是:"+c1+" ; "+"第二艘船载重量是:"+c2+" ;");
30 System.out.println("各个集装箱的重量为:");
31 int[] w1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(w,1,n+1);
32 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(w1));
33 //分支界限法开始时间
34 long s = System.nanoTime();
35 //分支界限法遍历解空间树
36 Node optimalN = branchAndBound(n,c1,w);
37 //分支界限法结束时间
38 long e = System.nanoTime();
39 //最终装入第一艘船的集装箱重量(最优值)
40 int optimalV1 = optimalN.nodeW;
41 //最终装入第二艘船的集装箱重量
42 int optimalV2 = tW - optimalV1;
43 //最终装入第一艘船的集装箱的代号(最优解集)
44 ArrayList<Integer> optimalS1 = new ArrayList<>();
45 //最终装入第二艘船的集装箱的代号
46 ArrayList<Integer> optimalS2 = new ArrayList<>();
47 for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
48 if (optimalN.layer == i) {
49 if (optimalN.isLeft) {
50 optimalS1.add(i);
51 } else {
52 optimalS2.add(i);
53 }
54 optimalN = optimalN.parent;
55 }else {
56 optimalS2.add(i);
57 }
58 }
59 Collections.sort(optimalS1);
60 Collections.sort(optimalS2);
61 System.out.println("装入第一艘船的集装箱重量是:" + optimalV1);
62 System.out.println("装入第一艘船的集装箱编号是:" + optimalS1);
63 System.out.println("装入第二艘船的集装箱重量是:" + optimalV2);
64 System.out.println("装入第二艘船的集装箱编号是:" + optimalS2);
65 System.out.println("遍历解空间树用时:"+(e - s)+"纳秒");
66 }
67 //结点类
68 public static class Node {
69 //本结点的父结点
70 Node parent;
71 //本结点的载重量(第一艘船当前载重量)
72 int nodeW;
73 //层数对应集装箱编号
74 int layer;
75 //判断是否是左子结点,(记录决策)
76 boolean isLeft;
77 public Node(Node parent, int nodeW, int layer, boolean isLeft) {
78 this.parent = parent;
79 this.nodeW = nodeW;
80 this.layer = layer;
81 this.isLeft = isLeft;
82 }
83
84 public Node() {
85 }
86 }
87 private static Node branchAndBound(int n, int c1, int[] w) {/* i记录层数,每层表示对第i个集装箱的选择(已确定的,第一结点还没选记为0)*/
88 //记录活结点的队列
89 LinkedList<Node> activeNode = new LinkedList<>();
90 //第一个活结点入队
91 activeNode.offer(new Node(null,0,0,false));
92 //记录最优值节点
93 Node optimalN = new Node();
94 //每次循环搜索完一个结点的所有子结点。
95 while (true){
96 Node cNode = activeNode.poll();
97 assert cNode != null;
98 //获取当前遍历的结点的载重量
99 int cW = cNode.nodeW;
100 int cLayer = cNode.layer + 1;
101 int leftW = cW + w[cLayer];
102 int rW = 0;
103 for (int i = cLayer+1; i <= n; i++) {
104 rW += w[i];
105 }
106 //如果集装箱i能装入第一艘船就装船,创建一个新的左儿子结点
107 if (leftW <= c1 ){
108 Node leftSonNode = new Node(cNode,leftW,cLayer,true);
109 //如果当前结点的载重量大于最优值的就更最优值结点
110 if (leftW > optimalN.nodeW) {
111 optimalN = leftSonNode;
112 }
113 /*非叶子结点,主要是在创建子结点时帮助获取父结点数据,叶子结点没有子节点了就不需要放入活结点队列了。*/
114 if (cLayer < n) {
115 //左儿子结点入队
116 activeNode.offer(leftSonNode);
117 }
118 }
119 if (cLayer < n && cW + rW > optimalN.nodeW) {
120 /*先计算右子树根节点的上界,如果其上界值>当前的最优值,右子树中就可能
121 存在第一艘船的装载最优解,则创建一个新的右儿子结点。*/
122 Node rightSonNode = new Node(cNode, cW,cLayer,false);
123 //右儿子结点入队
124 activeNode.offer(rightSonNode);
125 }
126 if (activeNode.isEmpty()){
127 return optimalN;
128 }
129 }
130 }
131 }
优先队列式分支限界法:

1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.Arrays;
3 import java.util.Collections;
4 import java.util.PriorityQueue;
5 import java.util.Random;
6
7 public class Demo6 {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 //集装箱数量
10 int n = 10;
11 //第一艘船的载重量
12 int c1 = 30;
13 //第二艘船的载重量
14 int c2 = 30;
15 //各个集装箱的重量
16 int[] w = new int[n+1];
17 //所有集装箱总重量
18 int tW = 0;
19 //最终装入第一艘船的集装箱重量(最优值)
20 Random r = new Random();
21 int num = 1;
22 while (num<=n){
23 int wi = r.nextInt((c1+c2)*2/n)+1;
24 if ((tW+wi+(n-num)) <= (c1+c2)){
25 w[num] = wi;
26 tW+=wi;
27 num++;
28 }
29 }
30 System.out.println("第一艘船载重量是:"+c1+" ; "+"第二艘船载重量是:"+c2+" ;");
31 System.out.println("各个集装箱的重量为:");
32 int[] w1 = Arrays.copyOfRange(w,1,n+1);
33 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(w1));
34 //分支界限法开始时间
35 long s = System.nanoTime();
36 //分支界限法遍历解空间树
37 Node optimalN = branchAndBound(n,c1,w,tW);
38 //分支界限法结束时间
39 long e = System.nanoTime();
40 int optimalV1 = optimalN.nodeW;
41 //最终装入第二艘船的集装箱重量
42 int optimalV2 = tW - optimalV1;
43 //最终装入第一艘船的集装箱的代号(最优解集)
44 ArrayList<Integer> optimalS1 = new ArrayList<>();
45 //最终装入第二艘船的集装箱的代号
46 ArrayList<Integer> optimalS2 = new ArrayList<>();
47 for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
48 if (optimalN.layer == i) {
49 if (optimalN.isLeft) {
50 optimalS1.add(i);
51 } else {
52 optimalS2.add(i);
53 }
54 optimalN = optimalN.parent;
55 }else {
56 optimalS2.add(i);
57 }
58 }
59 Collections.sort(optimalS1);
60 Collections.sort(optimalS2);
61 System.out.println("装入第一艘船的集装箱重量是:" + optimalV1);
62 System.out.println("装入第一艘船的集装箱编号是:" + optimalS1);
63 System.out.println("装入第二艘船的集装箱重量是:" + optimalV2);
64 System.out.println("装入第二艘船的集装箱编号是:" + optimalS2);
65 System.out.println("遍历解空间树用时:"+(e - s)+"纳秒");
66 }//结点类
67 public static class Node{
68 //本结点的父结点
69 Node parent;
70 //本结点的载重量(记录状态)
71 int nodeW;
72 //层数对应集装箱编号
73 int layer;
74 //当前结点的优先级(上界函数值)
75 int priority;
76 //是否是左儿子结点,(记录决策)
77 boolean isLeft;
78
79 public Node(Node parent, int nodeW, int layer, int priority, boolean isLeft) {
80 this.parent = parent;
81 this.nodeW = nodeW;
82 this.layer = layer;
83 this.priority = priority;
84 this.isLeft = isLeft;
85 }
86 }
87
88 public static Node branchAndBound (int n, int c1, int[] w, int tW) { /* i记录层数,每层表示对第i个集装箱的选择(已确定的,第一结点还没选记为0),
89 j记录活结点的个数减一,为了获取活结点队列的最后一个元素,方便标记每一层的最后一个结点。*/
90 //记录活结点的队列
91 PriorityQueue<Node> activeNode = new PriorityQueue<>((node1, node2) -> node2.priority - node1.priority);
92 //根结点入队
93 activeNode.offer(new Node(null,0,0,tW,false));
94 //每次循环搜索完一个结点的所有子结点。
95 while (true){
96 //取出队头活结点
97 Node cNode = activeNode.poll();
98 assert cNode != null;
99 //获取当前活结点的载重量
100 int cW = cNode.nodeW;
101 //子结点层数=父结点层数+1
102 int cLayer = cNode.layer + 1;
103 //左子结点的重量
104 int leftW = cW + w[cLayer];
105 //剩余集装箱总重量
106 int rW = cNode.priority-leftW;
107 //如果当前集装箱cLayer能装入第一艘船就装船,创建一个新的左儿子结点
108 if (leftW <= c1 ){
109 Node leftN = new Node(cNode,leftW,cLayer,leftW+rW,true);
110 if (cLayer<n){
111 //非叶子节点入队
112 activeNode.offer(leftN);
113 //右子节点的状态等于父节点,优先级小于父节点,所以不必参与最优值判断
114 activeNode.offer(new Node(cNode,cW,cLayer,cW+rW,false));
115 }else {//如果是叶子节点则对比当前活节点队列的最大优先级
116 assert activeNode.peek() != null;
117 if (leftW>=activeNode.peek().priority){
118 //返回最优值节点
119 return leftN;
120 }
121 }
122 }
123 }
124 }
125 }
【例2】0-1背包:物品20件,背包容量50,物品重量1-20随机赋值,物品价值1-50随机赋值。
为了简化设n=3。设1表示当前物品装入背包,0表示不装。解空间:{(1, 1, 1), (1, 1, 0), (0, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1), (1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 1), (0, 0, 1), (0, 0, 0)}。解空间结构为子集树。
解空间树:
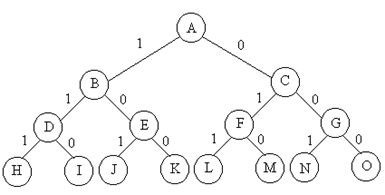
优先队列式分支限界法:

1 import java.util.ArrayList;
2 import java.util.Arrays;
3 import java.util.Collections;
4 import java.util.PriorityQueue;
5 import java.util.Random;
6
7 public class Demo12 {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 //物品数量
10 int n = 10;
11 //背包容量
12 int c = 50;
13 //各个物品重量和价值。忽略下标0元素,goods[i][0]表示物品i的重量,goods[i][1]表示物品i的价值
14 int[][] goods = new int[n+1][2];
15 //所有物品的总价值
16 int tV = 0;
17 Random r = new Random();
18 //随机赋值
19 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
20 goods[i][0] = r.nextInt(20)+1;
21 goods[i][1] = r.nextInt(50)+1;
22 tV += goods[i][1];
23 }
24 System.out.println("背包容量为:" + c);
25 System.out.println("所有物品的重量和价值为:" );
26 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
27 if (i%5 == 0){
28 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(goods[i]));
29 }else {
30 System.out.print(Arrays.toString(goods[i])+" ");
31 }
32 }
33 long s = System.nanoTime();
34 Node optimalN = branchAndBound(n,c,goods,tV);
35 long e = System.nanoTime();
36 //(最优值)
37 int optimalV = optimalN.nodeV;
38 //(最优解)
39 ArrayList<Integer> optimalS = new ArrayList<>();
40 for (int i = n; i > 0; i--) {
41 if (optimalN.layer == i) {
42 if (optimalN.isLeft) {
43 optimalS.add(i);
44 }
45 optimalN = optimalN.parent;
46 }
47 }
48 Collections.sort(optimalS);
49 System.out.println("放入背包的物品价值为:"+optimalV);
50 System.out.println("放入背包的物品编号为:" +optimalS);
51 System.out.println("算法用时"+(e-s)+"纳秒");
52 }
53 public static class Node{
54 //父母结点
55 Node parent;
56 //当前结点的重量
57 int nodeW;
58 //当前结点的价值
59 int nodeV;
60 //当前结点的层数,对应物品编号
61 int layer;
62 //当前结点的优先级,(上界函数值)
63 int priority;
64 //是否是左儿子结点,(记录决策)
65 boolean isLeft;
66
67 public Node(Node parent, int nodeW, int nodeV, int layer, int priority, boolean isLeft) {
68 this.parent = parent;
69 this.nodeW = nodeW;
70 this.nodeV = nodeV;
71 this.layer = layer;
72 this.priority = priority;
73 this.isLeft = isLeft;
74 }
75 }
76
77 private static Node branchAndBound (int n, int c, int[][] goods,int tV) {
78 //活结点队列
79 PriorityQueue<Node> activeNode = new PriorityQueue<>((node1, node2) -> node2.priority - node1.priority);
80 //根节点入队
81 activeNode.offer(new Node(null,0,0,0,tV,false));
82 //每次循环搜索完一个结点的所有子结点。
83 while (true){
84 //取出队头活结点
85 Node cNode = activeNode.poll();
86 assert cNode != null;
87 //获取当前活结点的重量和价值
88 int cW = cNode.nodeW;
89 int cV = cNode.nodeV;
90 //子结点层数=父结点层数+1
91 int cLayer = cNode.layer + 1;
92 //左子节点的重量和价值
93 int leftW = cW + goods[cLayer][0];
94 int leftV = cV + goods[cLayer][1];
95 //剩余物品总价值
96 int rV = cNode.priority-leftV;
97 //如果当前物品cLayer能装入背包就装,创建一个新的左子节点
98 if (leftW <= c){
99 Node leftN = new Node(cNode,leftW,leftV,cLayer,leftV+rV,true);
100 if (cLayer < n) {
101 //非叶子节点入队
102 activeNode.offer(leftN);
103 //右子节点的状态等于父节点,优先级小于父节点,所以不必参与最优值判断
104 activeNode.offer(new Node(cNode,cW,cV,cLayer,cV+rV,false));
105 }else {//如果是叶子节点则对比当前活节点队列的最大优先级
106 assert activeNode.peek() != null;
107 if (leftV>=activeNode.peek().priority){
108 //返回最优值节点
109 return leftN;
110 }
111 }
112 }
113 }
114 }
115 }
【例3】旅行售货员问题:某售货员要到若干城市去推销商品,一直各城市之间的路程,他要选定一条从驻地出发,经过每个城市一遍,最后回到住地的路线,使总的路程最短。

解空间:{(1,2,3,4),(1,2,4,3),(1,3,2,4),(1,3,4,2),(1,4,2,3),(1,4,3,2)}。解空间结构为排列树。
解空间树:
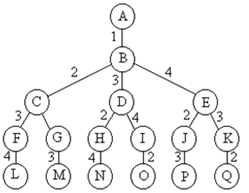
搜索到叶子节点加上返回1的路程才是最终状态值。
优先队列式分支限界法(优先级为当出发点到当前节点的距离):

1 import java.util.Arrays;
2 import java.util.Comparator;
3 import java.util.PriorityQueue;
4
5 public class Demo7 {
6 public static void main(String[] args) {
7 //城市数量
8 int n = 4;
9 //出发城市
10 int starCity = 1;
11 //邻接矩阵
12 int[][] map = {{0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
13 {0, 0,30, 6, 4},
14 {0,30, 0, 5,10},
15 {0, 6, 5, 0,20},
16 {0, 4,10,20, 0}};
17
18 Node optimalN = branchAndBound(n,starCity,map);
19 System.out.println("最优值为:"+optimalN.dist);
20 int[] optimalR = new int[n+1];
21 optimalR[0] = starCity;
22 optimalR[n] = starCity;
23 System.out.print("最优解为:");
24 for (int i = n-1; i > 0; i--) {
25 optimalR[i] = optimalN.city;
26 optimalN = optimalN.parent;
27 }
28 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(optimalR));
29 }
30 public static class Node {
31 //父母节点
32 Node parent;
33 //当前节点的累计距离(状态),也当作优先级。
34 int dist;
35 //层数代表第几个城市(阶段)
36 int layer;
37 //当前所在城市编号(决策)
38 int city;
39 //走过的城市
40 boolean[] pass;
41
42 public Node(Node parent, int dist, int layer, int city, boolean[] pass) {
43 this.parent = parent;
44 this.dist = dist;
45 this.layer = layer;
46 this.city = city;
47 this.pass = pass;
48 }
49
50 public Node() {
51 }
52 }
53 private static Node branchAndBound(int n, int starCity, int[][] map){
54 //活结点队列
55 PriorityQueue<Node> activeNode = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(node -> node.dist));
56 //根节点入队
57 boolean[] pass = new boolean[n+1];
58 pass[starCity] = true;
59 activeNode.offer(new Node(null,0,1,starCity,pass));
60 //记录最优值结点,初始距离为无穷大,方便后面比较。
61 Node optimalN = new Node();
62 optimalN.dist=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
63 while (true){
64 //取出队头活节点
65 Node cNode = activeNode.poll();
66 assert cNode != null;
67 //遍历地图数据
68 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
69 //如果当前节点所在城市能直达i城并且当前节点的路径没走过i城,就对i城创建一个子节点
70 if (map[cNode.city][i]!= 0 && !cNode.pass[i] ){
71 //依据父节点更新子节点数据
72 int dist = cNode.dist+map[cNode.city][i];
73 int layer = cNode.layer+1;
74 boolean[] pass1 = Arrays.copyOf(cNode.pass,cNode.pass.length);
75 pass1[i] = true;
76 //创建子节点对象
77 Node sNode = new Node(cNode,dist,layer,i,pass1);
78 if (sNode.layer < n){
79 //非叶子节点入队
80 activeNode.offer(sNode);
81 }else {//先更新最优值节点
82 dist+=map[i][starCity];
83 if (dist < optimalN.dist){
84 sNode.dist=dist;
85 optimalN = sNode;
86 }//如果最优值节点的优先级不大于活节点队列头节点的优先级就找到一个最优值节点
87 assert activeNode.peek() != null;
88 if (optimalN.dist <= activeNode.peek().dist){
89 return optimalN;
90 }
91 }
92 }
93 }
94 }
95 }
96 /*打印结果:
97 最优值为:25
98 最优解为:[1, 3, 2, 4, 1]*/
99 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号