java算法篇之三:链表
1. 简介
前面已经实现了动态数组、栈、队列三种线性数据结构,但其底层都是依托静态数组,靠resize解决固定容量问题。
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。是一种真正的动态数据结构
-
数据存储在“节点”(Node)中,一个节点包含至少两部分,一部分存储真正的数据,另一部分是指向其他节点的指针。当某个节点的指针指向空节点(NULL)则表明该节点为尾节点
class Node { public E e; public Node next; }
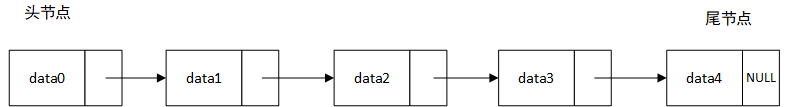
-
优点:真正的动态,不需要处理固定容量的问题
-
缺点:丧失了随机访问的能力,无法像数组一样通过下标或索引直接访问到数据
2. 添加元素
2.1 分析
添加元素分为三种情况,分别为在链表头添加元素、在链表中间添加元素、在链表尾添加元素
-
在链表头添加元素
- 只需要将新添加元素节点的指针指向头节点,然后将头节点设置新添加的元素
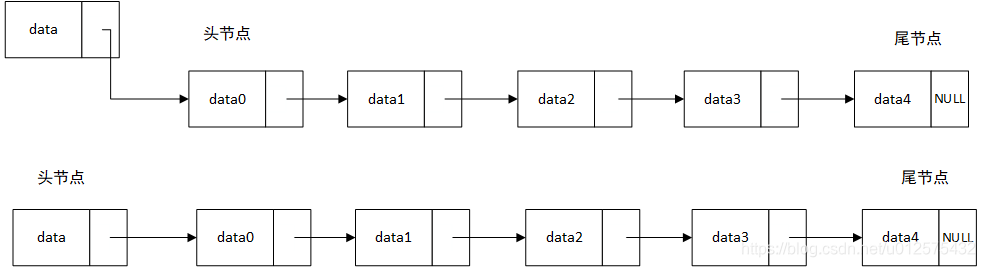
- 只需要将新添加元素节点的指针指向头节点,然后将头节点设置新添加的元素
-
在链表中间添加元素。假设待添加元素为节点A
- 向index位置添加元素时,需要先获取前一个位置index-1节点,记为节点B,然后将节点A的next指针指向节点B的next指针,将节点B的next指针指向节点A。
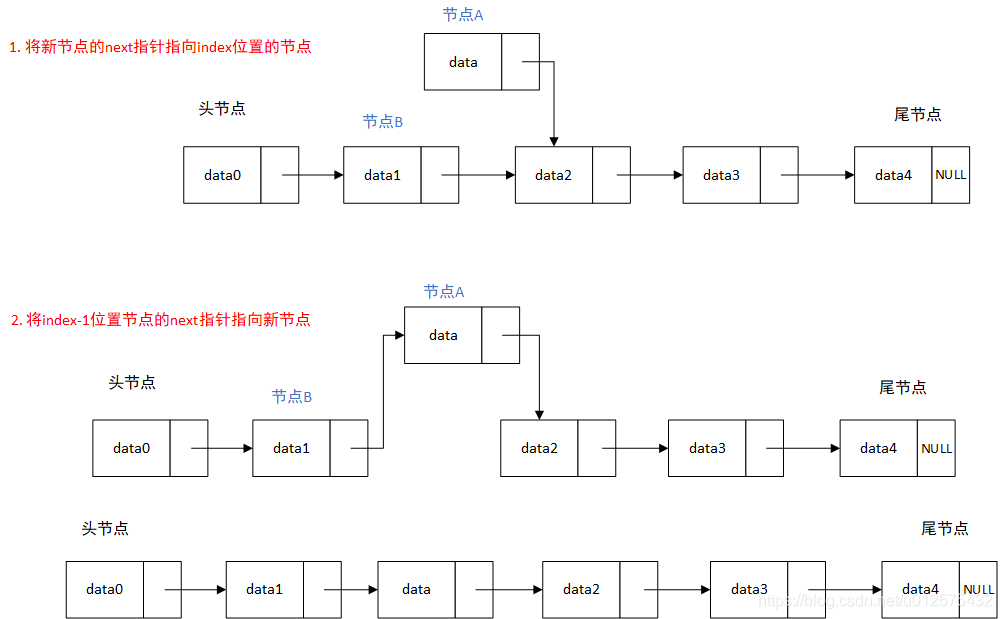
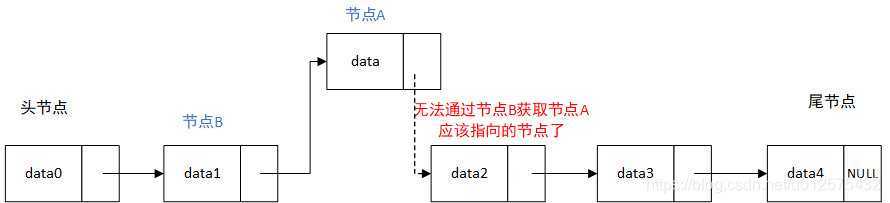
eg: 必须先将节点A的next指针指向节点B的next指针,再将节点B的next指针指向节点A。顺序不可以反过来,否则节点B的next指针指向节点A后,真正的index位置的节点就丢失了,无法根据节点B获取到了
- 向index位置添加元素时,需要先获取前一个位置index-1节点,记为节点B,然后将节点A的next指针指向节点B的next指针,将节点B的next指针指向节点A。
-
在链表尾添加元素
- 跟在链表中间添加元素一致。此时尾节点就是节点B,节点A的next指针指向节点B的next指针即为NULL,然后节点B的next指针指向新元素节点A
2.2 实现
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
public Node() {
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node head;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
this.head = null;
this.size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
this.head = new Node(e, this.head);
this.size++;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index <0 || index > this.size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
if (index == 0)
this.addFirst(e);
else {
Node prev = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index - 1; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
this.size++;
}
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e) {
this.add(this.size, e);
}
}
3. 虚拟头节点
3.1 分析
- 上面已经实现了在链表中新增元素,但在链表头添加元素与其他位置添加元素业务逻辑有差别。此时可以通过虚拟头节点解决该问题
- 虚拟头节点不存储任何数据
- 虚拟头节点的next指针指向的节点才是真正的头节点
3.2 实现
public class LinkedList<E> {
private class Node {
public E e;
public Node next;
public Node(E e, Node next) {
this.e = e;
this.next = next;
}
public Node(E e) {
this(e, null);
}
public Node() {
this(null, null);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return e.toString();
}
}
private Node dummyHead;
private int size;
public LinkedList() {
this.dummyHead = new Node(null, null);
this.size = 0;
}
// 获取链表中的元素个数
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
// 返回链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
// 在链表的index(0-based)位置添加新元素e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
public void add(int index, E e) {
if (index <0 || index > this.size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Add failed. Illegal index.");
Node prev = dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
prev = prev.next;
}
prev.next = new Node(e, prev.next);
this.size++;
}
// 在链表头添加新的元素e
public void addFirst(E e) {
this.add(0, e);
}
// 在链表末尾添加新的元素e
public void addLast(E e) {
this.add(this.size, e);
}
}
4. 链表的遍历、查询、修改
// 获得链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
public E get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Get failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = this.dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
cur = cur.next;
return cur.e;
}
// 获得链表的第一个元素
public E getFirst() {
return this.get(0);
}
// 获取链表的最后一个元素
public E getLast() {
return this.get(this.size - 1);
}
// 修改链表的第index(0-based)个位置的元素为e
// 在链表中不是一个常用的操作,练习用
public void set(int index, E e) {
if (index < 0 || index > this.size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Set failed. Illegal index.");
Node cur = this.dummyHead.next;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
cur = cur.next;
cur.e = e;
}
// 查找链表中是否存在元素e
public boolean contains(E e) {
Node cur = this.dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null) {
if (cur.e.equals(e))
return true;
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("LinkedList: ");
Node cur = this.dummyHead.next;
while (cur != null) {
res.append(cur + " -> ");
cur = cur.next;
}
res.append("NULL");
return res.toString();
}
5. 从链表中删除元素
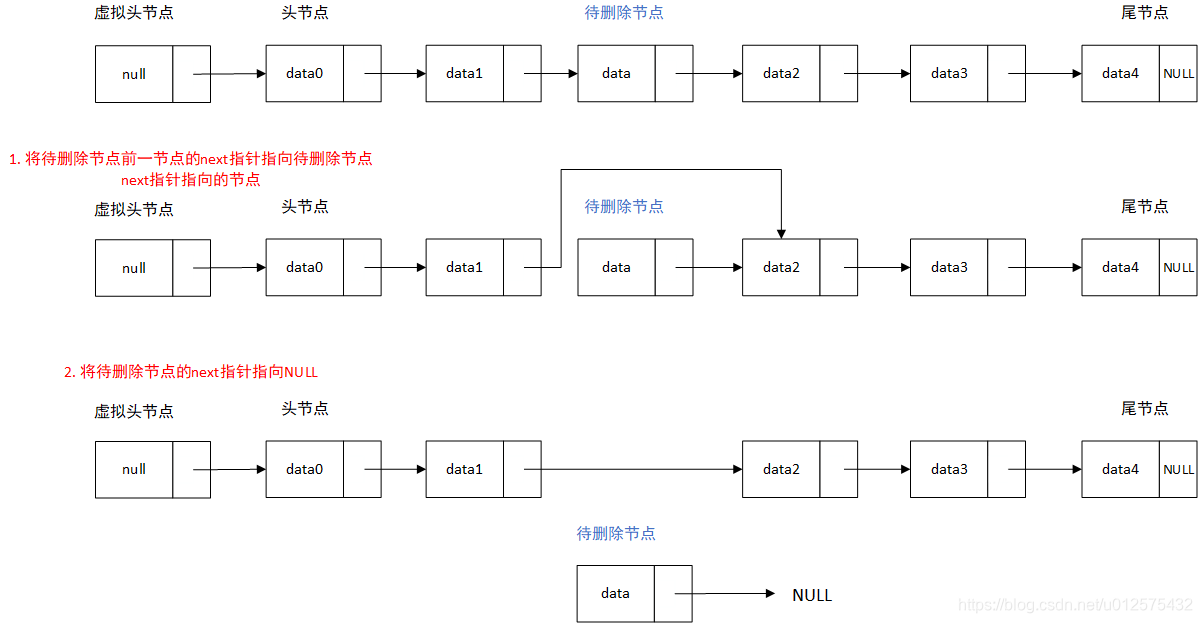
// 从链表中删除index(0-based)位置的元素,返回删除的元素
// 从链表中删除元素不是一个常用操作,练习用
public E remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Remove failed. Index is illegal.");
Node prev = this.dummyHead;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
prev = prev.next;
Node retNode = prev.next;
prev.next = retNode.next;
retNode.next = null;
this.size--;
return retNode.e;
}
// 从链表中删除第一个元素,返回删除的元素
public E removeFirst() {
return this.remove(0);
}
// 从链表中删除最后一个元素,返回删除的元素
public E removeLast() {
return this.remove(this.size - 1);
}
© 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请注明出处



