代码:
import bpy #Define which objects to use placement_ob = bpy.context.scene.objects['Sphere'] camera_ob = bpy.context.scene.objects['Camera'] render = bpy.context.scene.render # Set the render path render_path = 'renders\\vertex-{:03d}' # Use backslash for Windows paths for index, vert in enumerate(placement_ob.data.vertices): # Apply the object's world matrix to the vertex's local coordinates to get world coordinates vcoord = placement_ob.matrix_world @ vert.co # Set the render filepath for the current vertex render.filepath = render_path.format(index) # Move the camera to the vertex's world position camera_ob.location = vcoord # Render the scene bpy.ops.render.render(write_still=True) # If you want to render all vertices, remove the break statement # If you only want to test if it works, you can leave the break statement # break # Remove after you see it works print('Done!')
中文注释:
import bpy # 定义要使用的物体 placement_ob = bpy.context.scene.objects['Sphere'] # 'Sphere' 是要渲染的物体名称 camera_ob = bpy.context.scene.objects['Camera'] # 'Camera' 是摄像机的名称 render = bpy.context.scene.render # 获取渲染场景的引用 # 设置渲染路径 render_path = 'renders\\vertex-{:03d}' # 使用反斜杠作为Windows路径分隔符 for index, vert in enumerate(placement_ob.data.vertices): # 遍历所有顶点 # 应用物体的世界矩阵到顶点的局部坐标以获取世界坐标 vcoord = placement_ob.matrix_world @ vert.co # 使用矩阵乘法运算符 # 设置当前顶点的渲染文件路径 render.filepath = render_path.format(index) # 使用顶点索引格式化路径 # 将摄像机移动到顶点的世界位置 camera_ob.location = vcoord # 设置摄像机的位置 # 渲染场景 bpy.ops.render.render(write_still=True) # 执行静态图像渲染操作 # 如果你想要渲染所有顶点,移除下面的break语句 # 如果你只想测试脚本是否工作,可以保留break语句 # break # 一旦看到它工作,就移除这个break语句 print('Done!') # 打印完成信息
物体界面截图
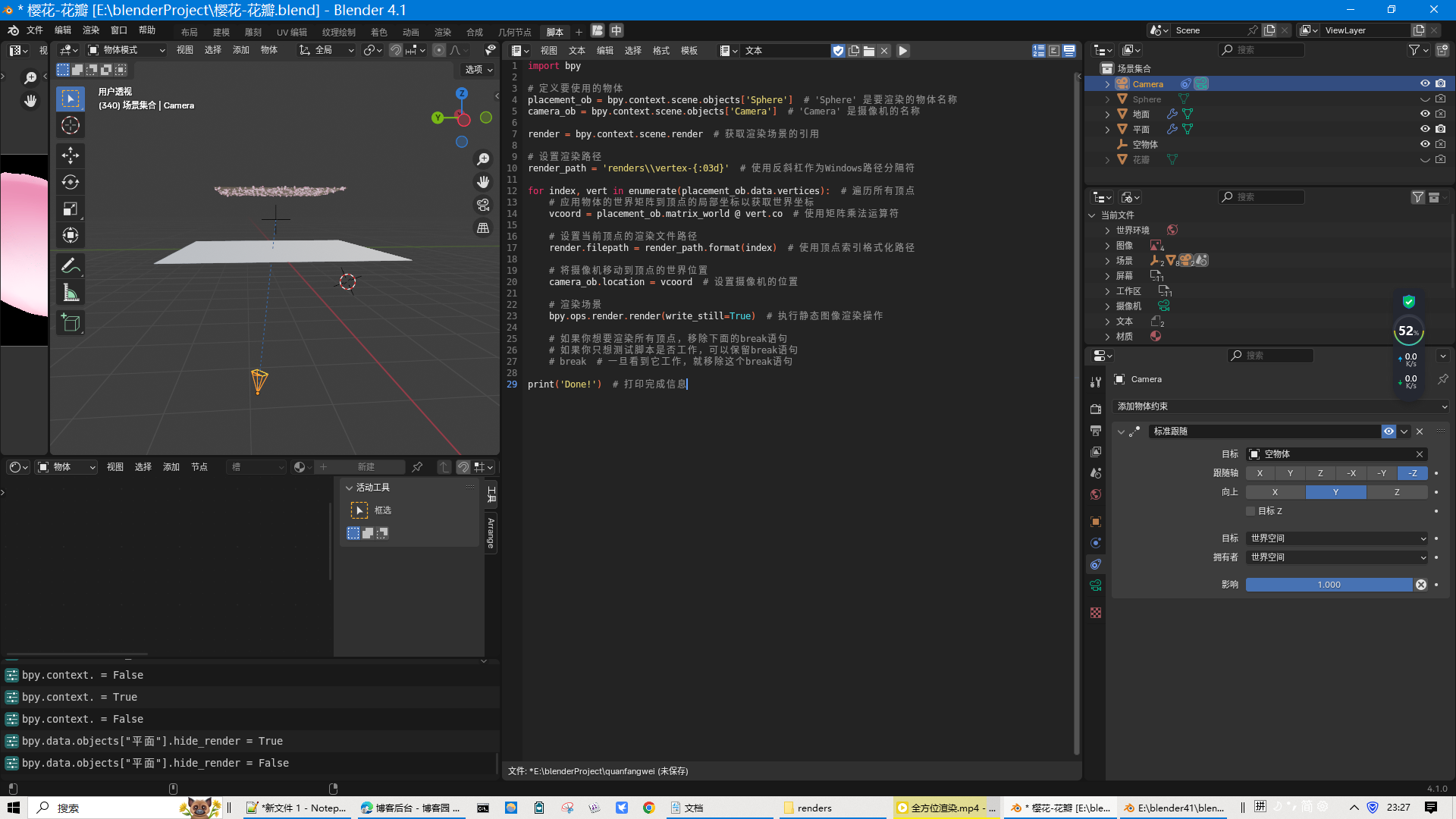
说明:
新建一个空物体,放在平面与地面中间,
新建一个UV球体,放大,覆盖整个要摄像的场景,应用精简修改6级,让球面变为17个点(能围绕一圈,且点数不多),
摄像机添加标准跟随(目标为空物体,保证相机始终对着要拍摄的物体),
运行脚本,就可以渲染出17张当前静帧的图片






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
2020-04-17 django性能优化