Vue3源码分析之 Ref 与 ReactiveEffect
Vue3中的响应式实现原理
完整 js版本简易源码 在最底部
ref 与 reactive 是Vue3中的两个定义响应式对象的API,其中reactive是通过 Proxy 来实现的,它返回对象的响应式副本,而Ref则是返回一个可变的ref对象,只有一个 .value属性指向他内部的值,本文则重点来分析一下 Ref 的实现原理
ref:接受一个内部值并返回一个响应式且可变的 ref 对象。ref 对象仅有一个
.valueproperty,指向该内部值。
-
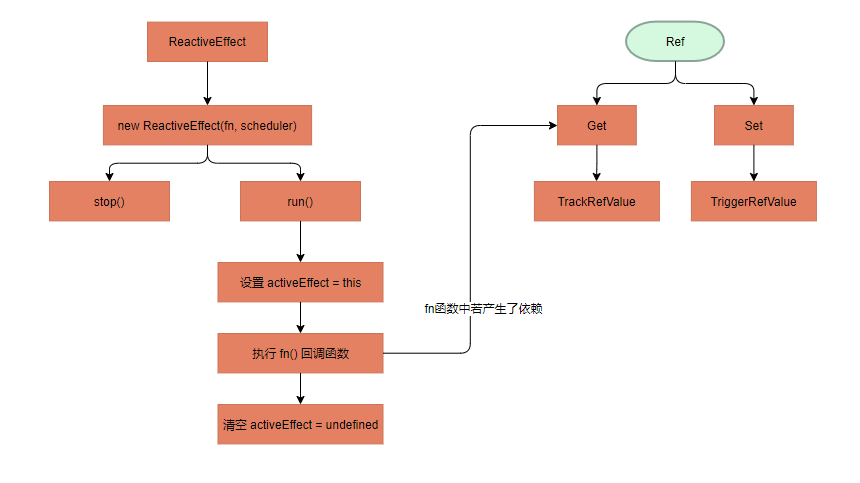
Ref依赖收集
首先我们需要了解 ReactiveEffect 类,创建这个类需要传入一个 副作用函数 和 scheduler,在这个类中有 active、deps 两个重要的属性:
active:是否为激活状态,默认为:true
deps:所有依赖这个 effect 的响应式对象
ReactiveEffect 简易 js 版本源代码:
// 记录当前活跃的对象 let activeEffect // 标记是否追踪 let shouldTrack = false class ReactiveEffect{ active = true // 是否为激活状态 deps = [] // 所有依赖这个 effect 的响应式对象 onStop = null // function constructor(fn, scheduler) { this.fn = fn // 回调函数,如: computed(/* fn */() => { return testRef.value ++ }) // function类型,不为空那么在 TriggerRefValue 函数中会执行 effect.scheduler,否则会执行 effect.run this.scheduler = scheduler } run() { // 如果这个 effect 不需要被响应式对象收集 if(!this.active) { return this.fn() } // 源码这里用了两个工具函数:pauseTracking 和 enableTracking 来改变 shouldTrack的状态 shouldTrack = true activeEffect = this // 在设置完 activeEffect 后执行,在方法中能够对当前活跃的 activeEffect 进行依赖收集 const result = this.fn() shouldTrack = false // 执行完副作用函数后要清空当前活跃的 effect activeEffect = undefined return result } // 暂停追踪 stop() { if (this.active) { // 找到所有依赖这个 effect 的响应式对象 // 从这些响应式对象里面把 effect 给删除掉 cleanupEffect(this) // 执行onStop回调函数 if (this.onStop) { this.onStop(); } this.active = false; } } }了解了 ReactiveEffect 类,再来分析 Ref
ref 简易JS版本源代码
class RefImpl{ // Set格式,存储 effect dep // 存储原始值 _rawValue // 标记这是一个 Ref 对象,isRef API就可以直接通过判断这个内部属性即可 __v_isRef = true // _shallow:这个值是为了实现 shallowRef API 而存在 // 目前这里没有使用到 constructor(value, _shallow) { this._value = value // 存储原始值,用来与新值做对比 this._rawValue = _shallow ? value : toRaw(value) // _value 内部值 // toReactive => isObject(value) ? reactive(value) : value // 对 value 进行包装 this._value = _shallow ? value : toReactive(value) } get value() { // 在获取这个 Ref 内部值时 进行依赖收集 // trackRefValue() 依赖收集 trackRefValue(this) return this._value } }trackRefValue方法实现
/** * activeEffect 当前活跃的 effect 对象 * shouldTrack 是否允许追踪 * const isTracking = () => activeEffect && shouldTrack */ function trackRefValue(ref) { // 若没有活跃的 effect 对象或 不需要进行追踪 if(!isTracking()) { return } // 如果这个 Ref 对象还没有对 dep 进行初始化(Ref 中 dep 属性默认为 undefined) if(!ref.dep) { ref.dep = new Set() } trackEffects(ref.dep) } function trackEffects(dep) { // 若改 effect 对象已经收集,跳过 if(!dep.has(activeEffect)) { // 将 effect 对象添加到 Ref 对象的 dep 中 dep.add(activeEffect) // 将这个Ref的dep存放到这个 effect 的 deps 中 // 目的是为了在停止追踪时,从 响应式对象将 effect 移除掉 activeEffect.deps.push(dep) } }写个 testComputed 函数来回顾 和 测试一下上面的流程
const testRef = new RefImpl(1) const testComputed = (fn) => { // 创建一个 effect 对象 const testEffect = new ReactiveEffect(fn) // 默认执行 effect.run() 函数(设置 activeEffect=this -> 执行 fn(依赖收集) -> 清空 activeEffect=undefined) return testEffect.run() // 此时,依赖情况: // testRef.dep = [ testEffect:effect ] // testEffect.deps = [ testRef.dep ] } const fn = () => { console.log('textComputed', testRef.value) } testComputed(fn) -
Ref 触发更新
在 RefImpl 类中增加 set value 方法
class RefImpl{ // ...... // 增加 set value () 方法 set value(newVal) { newVal = this._shallow ? newVal : toRaw(newVal) // 对比 新老值 是否相等,这里不能简单的使用 == 或 === // Object.is() 方法判断两个值是否为同一个值。 if (!Object.is(newVal, this._rawValue)) { this._rawValue = newVal this._value = this._shallow ? newVal : toReactive(newVal) // 在内部值被改变的时候会触发依赖更新 triggerRefValue(this) // ,newValue) 在dev环境下使用了 newValue,这里忽略 } } // ...... }triggerRefValue 方法实现
function triggerRefValue(ref) { triggerEffects(ref.dep); } function triggerEffects(dep) { // 执行 Ref.dep 中收集的所有 effect for (const effect of dep) { // 这里做个判断,执行的 effect 不是 当前活跃的 effect if(effect !== activeEffect) { if(effect.scheduler) { // effect.scheduler 文章前面有讲过 /** Vue3中模板更新,就是通过创建了一个 scheduler,然后推入 微任务队列 中去执行的 const effect = new ReactiveEffect(componentUpdateFn,() => queueJob(instance.update)) const update = (instance.update = effect.run.bind(effect) as SchedulerJob) */ effect.scheduler() } else { effect.run() } } } }修改 testComputed 函数进行测试
const testRef = new RefImpl(1) const testComputedWatch = (fn) => { // 创建一个 effect 对象 const testEffect = new ReactiveEffect(fn) // 默认执行 effect.run() 函数(设置 activeEffect=this -> 执行 fn(依赖收集) -> 清空 activeEffect=undefined) return testEffect.run() // 此时,依赖情况: // testRef.dep = [ testEffect:effect ] // testEffect.deps = [ testRef.dep ] } const fn = () => { console.log('textComputed', testRef.value) } testComputed(fn) testRef.value ++ // -> 'textComputed', 2 testRef.value ++ // -> 'textComputed', 3源代码:
effect.js
// 记录当前活跃的对象 let activeEffect // 标记是否追踪 let shouldTrack = false // 存储已经收集的依赖 // const targetMap = new WeakMap() const isTracking = () => activeEffect && shouldTrack function trackEffects(dep) { if(!dep.has(activeEffect)) { dep.add(activeEffect) activeEffect.deps.push(dep) } } function triggerEffects(dep) { for (const effect of dep) { // 这里做个判断,执行的 effect 不是 当前活跃的 effect if(effect !== activeEffect) { if(effect.scheduler) { effect.scheduler() } else { effect.run() } } } } class ReactiveEffect{ active = true deps = [] onStop = null constructor(fn, scheduler) { this.fn = fn this.scheduler = scheduler } run() { if(!this.active) { return this.fn() } // 源码这里用了两个工具函数:pauseTracking 和 enableTracking 来改变 shouldTrack的状态 shouldTrack = true activeEffect = this // 在设置完 activeEffect 后执行,在方法中能够对当前活跃的 activeEffect 进行依赖收集 const result = this.fn() shouldTrack = false // 执行完副作用函数后要清空当前活跃的 effect activeEffect = undefined return result } // 暂停追踪 stop() { if (this.active) { // 找到所有依赖这个 effect 的响应式对象 // 从这些响应式对象里面把 effect 给删除掉 cleanupEffect(this) // 执行onStop回调函数 if (this.onStop) { this.onStop(); } this.active = false; } } } function cleanupEffect(effect) { const { deps } = effect if (deps.length) { for (let i = 0; i < deps.length; i++) { deps[i].delete(effect) } deps.length = 0 } } module.exports = { ReactiveEffect, isTracking, trackEffects, triggerEffects }ref.js
// const { toReactive, toRaw } = require('./reactive.js') // start reactive.js 模块 const isObject = (val) => val !== null && typeof val === 'object' const toReactive = val => isObject(val) ? reactive(val) : val function toRaw(observed) { // __v_raw 是一个标志位,表示这个是一个 reactive const raw = observed && observed['__v_raw'] return raw ? toRaw(raw) : observed } // end reactive.js const { ReactiveEffect, isTracking, trackEffects, triggerEffects } = require('./effect.js') function trackRefValue(ref) { if(!isTracking()) { return } if(!ref.dep) { ref.dep = new Set() } trackEffects(ref.dep) } function triggerRefValue(ref) { triggerEffects(ref.dep); } class RefImpl{ dep _rawValue __v_isRef = true constructor(value, _shallow) { this._value = value // 存储原始值,用来与新值做对比 this._rawValue = _shallow ? value : toRaw(value) this._value = _shallow ? value : toReactive(value) } get value() { // 收集依赖 trackRefValue(this) return this._value } set value(newVal) { newVal = this._shallow ? newVal : toRaw(newVal) // Object.is() 方法判断两个值是否为同一个值。 if (!Object.is(newVal, this._rawValue)) { this._rawValue = newVal this._value = this._shallow ? newVal : toReactive(newVal) triggerRefValue(this) // ,newValue) 在dev环境下使用了 newValue,这里忽略 } } } function isRef(r) { return Boolean(r && r.__v_isRef === true) } function createRef(rawValue, _shallow) { if (isRef(rawValue)) { return rawValue } return new RefImpl(rawValue, _shallow) } function ref(val) { return createRef(val, false) } module.exports = { isRef, ref }测试代码
/** ** 测试代码 ***/ const testRef = ref(1) const textComputed = () => { const testEffect = new ReactiveEffect(() => { console.log('textComputed', testRef.value) }) testEffect.run() console.log('testEffect.deps', testEffect.deps) } const textComputed1 = () => { const fn = () => { console.log('textComputed', testRef.value) } const testEffect = new ReactiveEffect(fn) testEffect.run() } textComputed1() textComputed() console.log('testRef', testRef) // testRef.value ++



