周志华西瓜书习题5.5
前言
这是第一次自己尝试着把书上的代码去编写成程序,但遗憾的是,没有达到预想的结果
但是,我调了半天,终于调出来了,hahahahahahahaha
主要是犯了两个重大错误:
1,只调eta2,却忘记了调eta1,eta1要比eta2重要的多,
2,自己粗心,测试时居然用数据集X_train进行测试,而用y_test和测试集进行对比,我TM。。。。。。。。。。
第一次
第一次使用3.0a数据集,隐层有三个神经元,代码如下
''' 主要按照图5.8的伪代码进行 使用数据集3.0a,两个输入一个输出,对于数据集3.0,不知道怎么把类别转化为数字 使用的神经网络模型如下 +++++++++++++++++++++++++ + O + 输出层 有一个阈值 theta + / | \ + + / | \ + 隐层到输出层的三个权值 w + / | \ + + O O O + 隐层 有三个阈值 gamma + + + 中间太难画了,直接省略了 + 输入层到隐层有三个权值 v + + + O O + 输入层 +++++++++++++++++++++++++ ''' import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import self_def #读取数据集 data = np.loadtxt('watermelon_3a.csv',delimiter=',') X = data[:,1:3] y = data[:,3] #划分数据集 from sklearn import model_selection X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.4, random_state=0) m,n = np.shape(X_train) #参数初始化 theta = np.random.rand(1) #np.random.rand()可产生0到1内的随机数 w = np.random.rand(3) gamma = np.random.rand(3) v = np.random.rand(3,2) eta1 = 0.1 eta2 = 0.2 #参数的历史数据,用于查看迭代情况 theta_history = np.zeros(m) w_history = np.zeros((m,3)) gamma_history = np.zeros((m,3)) v_history = np.zeros((3*m,2)) #训练 for k in range(m): #计算三个隐层神经元的输出 b = np.zeros(3) for h in range(3): b[h] = self_def.neuron_out1(X_train[k],v[h],gamma[h]) #输出层神经元的输出估计,式5.3 y_esti = self_def.neuron_out1(b,w,theta) #计算g,式5.10 g = y_esti*(1-y_esti)*(y_train[k]-y_esti) #计算e,式5.15 e = np.zeros(3) for h in range(3): e[h] = b[h]*(1-b[h])*(w[h]*g) # j = 1,5.15的求和式不必再计算 #计算5.11-5.14 delta_w = np.zeros(3) for h in range(3): delta_w[h] = eta1*g*b[h] delta_theta = -1*eta1*g #检查一下 delta_v = np.zeros((3,2)) for h in range(3): for i in range(2): delta_v[h,i] = eta2*e[h]*X_train[k,i] delta_gamma = -1*eta2*e #参数更新 theta += delta_theta w += delta_w gamma += delta_gamma v += delta_v #记录历史数据 theta_history[k] = theta w_history[k] = w gamma_history[k] = gamma v_history[3*k:3*k+3] = v #训练 mm = np.shape(X_test)[0] y_pred = np.zeros((mm,1)) for k in range(mm): #计算三个隐层神经元的输出 for h in range(3): b[h] = self_def.neuron_out1(X_train[k],v[h],gamma[h]) #输出层神经元的输出估计,式5.3 y_esti = self_def.neuron_out1(b,w,theta) if y_esti >= 0.5: y_pred[k] = 1 #计算混淆矩阵 cfmat = np.zeros((2, 2)) for i in range(mm): if y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 0: cfmat[0, 0] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 1: cfmat[1, 1] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == 0: cfmat[1, 0] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == 1: cfmat[0, 1] += 1 print(cfmat) #查看迭代情况 t = np.arange(m) p1 = plt.subplot(411) p1.plot(t,theta_history) p2 = plt.subplot(412) w0 = np.ravel(w_history[:,0]) p2.plot(t,w0) w1 = np.ravel(w_history[:,1]) p2.plot(t,w1) w2 = np.ravel(w_history[:,2]) p2.plot(t,w2) p3 = plt.subplot(413) gamma0 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:,0]) p3.plot(t,gamma0) gamma1 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:,1]) p3.plot(t,gamma1) gamma2 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:,2]) p3.plot(t,gamma2) plt.show() print('end')
但是结果不怎么样,我感觉是因为数据量太小,啥也训不出来,于是换数据集
第二次
数据集选用的是UCI数据集iris的一部分,共有100个,正例反例各50个
代码如下
''' 主要按照图5.8的伪代码进行 使用数据集UCI中的iris的一个子数据集,四输入一个输出 使用的神经网络模型如下 +++++++++++++++++++++++++ + O + 输出层 有一个阈值 theta_j 1 + // | \ \ + + / / | \ \ + 隐层到输出层的五个权值 w_hj 5*1 + / / | \ \ + + O O O O O + 隐层 有五个阈值 gamma_h 5 + + + 中间太难画了,直接省略了 + 输入层到隐层有5*4个权值 v_hj 5*4 + + + O O O O + 输入层 +++++++++++++++++++++++++ '''
#以下是自己改进程序的过程 #2、把三个神经元改为五个神经元 #3、调节eta2的值 #4、参数不再随机化赋值,改为赋指定值 #5、初始参数赋指定值,调节eta2 #6、将训练过程和测试过程简化为函数,见main_3 import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import self_def #读取数据集 data = np.loadtxt('iris_2.csv',delimiter=',') X = data[:,0:4] y = data[:,4] #划分数据集 from sklearn import model_selection X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=0) m,n = np.shape(X_train) #参数初始化 theta = np.random.rand(1) #np.random.rand()可产生0到1内的随机数 w = np.random.rand(5) gamma = np.random.rand(5) v = np.random.rand(5,4) #参数赋指定值 theta = 0.5 w = np.arange(0,1,0.2) gamma = np.arange(0,1,0.2) for ii in range(5): v[ii] = np.arange(0,1,0.25) eta1 = 0.4 eta2 = 0.5 delta_w = np.zeros(5) delta_theta = 0 delta_v = np.zeros((5,4)) delta_gamma = 0 #参数的历史数据,用于查看迭代情况 theta_history = np.zeros(m) w_history = np.zeros((m,5)) gamma_history = np.zeros((m,5)) v_history = np.zeros((5*m,4)) #训练 for k in range(m): #计算三个隐层神经元的输出 b = np.zeros(5) for h in range(5): b[h] = self_def.neuron_out1(X_train[k],v[h],gamma[h]) #输出层神经元的输出估计,式5.3 y_esti = self_def.neuron_out1(b,w,theta) #计算g,式5.10 g = y_esti*(1-y_esti)*(y_train[k]-y_esti) #计算e,式5.15 e = np.zeros(5) for h in range(5): e[h] = b[h]*(1-b[h])*(w[h]*g) # j = 1,5.15的求和式不必再计算 #计算5.11-5.14 for h in range(5): delta_w[h] = eta1*g*b[h] delta_theta = -1*eta1*g #检查一下 for h in range(5): for i in range(4): delta_v[h,i] = eta2*e[h]*X_train[k,i] delta_gamma = -1*eta2*e #参数更新 theta += delta_theta w += delta_w gamma += delta_gamma v += delta_v #记录历史数据 theta_history[k] = theta w_history[k] = w gamma_history[k] = gamma v_history[5*k:5*k+5] = v #预测 mm = np.shape(X_test)[0] y_pred = np.zeros((mm,1)) for k in range(mm): #计算三个隐层神经元的输出 for h in range(5): b[h] = self_def.neuron_out1(X_test[k],v[h],gamma[h]) #输出层神经元的输出估计,式5.3 y_esti = self_def.neuron_out1(b,w,theta) #y_pred[k] = y_test[k] if y_esti >= 0.5: y_pred[k] = 1 #计算混淆矩阵 cfmat = np.zeros((2, 2)) for i in range(mm): if y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 0: cfmat[0, 0] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 1: cfmat[1, 1] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == 0: cfmat[1, 0] += 1 elif y_pred[i] == 1: cfmat[0, 1] += 1 print(cfmat) print('end') # 查看迭代情况 t = np.arange(m) p1 = plt.subplot(411) p1.plot(t, theta_history) plt.ylabel('theta') p2 = plt.subplot(412) w0 = np.ravel(w_history[:, 0]) plt.ylabel('w') p2.plot(t, w0) w1 = np.ravel(w_history[:, 1]) p2.plot(t, w1) w2 = np.ravel(w_history[:, 2]) p2.plot(t, w2) p3 = plt.subplot(413) gamma0 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:, 0]) plt.ylabel('gamma') p3.plot(t, gamma0) gamma1 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:, 1]) p3.plot(t, gamma1) gamma2 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:, 2]) p3.plot(t, gamma2) gamma3 = np.ravel(gamma_history[:, 3]) p3.plot(t, gamma3) plt.show()
结果
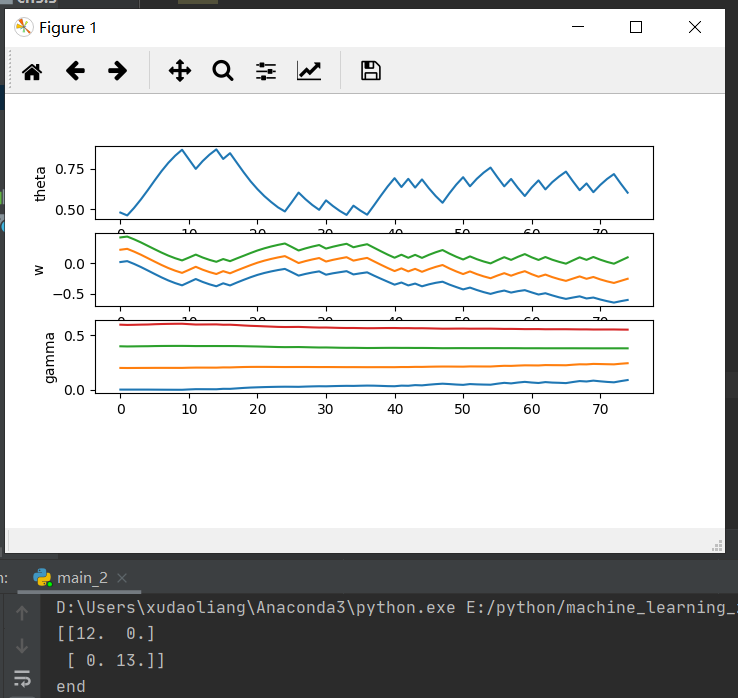
虽然准确率已经达到了100%,但是各个参数没有趋于稳定,这跟标准BP算法自身有很大的关系
心得
以下是自己改进程序的过程
#2、把三个神经元改为五个神经元
#3、调节eta2的值
#4、参数不再随机化赋值,改为赋指定值,每次都使用不同的初值,肯定不方便观察eta2对训练结果的影响
#5、初始参数赋指定值,调节eta2
#6、跟着程序一步一步的走,发现eta1的作用远比eta2大得多
进一步改进:简化函数主体的结构,并作出 precision = f(eta1,eta2)的图像,寻找合适的eta1和eta2






