周志华 西瓜书 习题3.3
做这道题花费了五天左右的时间,主要是python基础不怎么样,看着别人的代码,主要是参考https://blog.csdn.net/Snoopy_Yuan/article/details/63684219
一行一行地弄懂,然后再自己写。
一、获得以下经验:
1、在使用梯度下降算法求解数值的最优解时,要观察拟合曲线的拟合情况,拟合曲线逼近稳定值才可
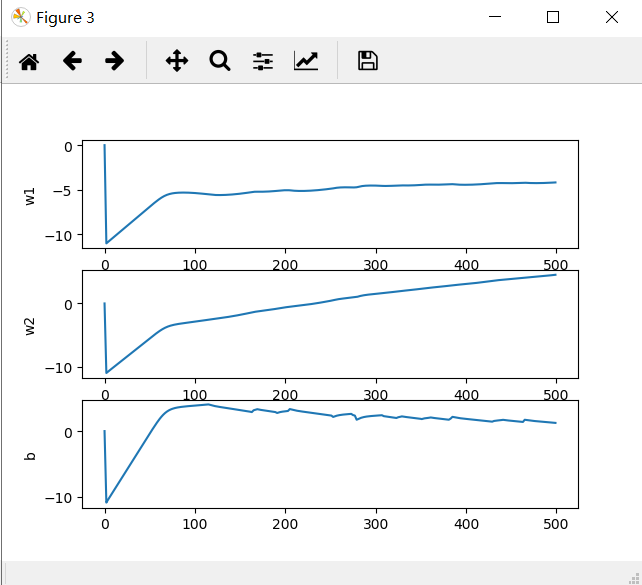
在上图所示的拟合曲线中,曲线没有趋于稳定,应调节梯度下降的步长,或者增加拟合次数,
调节后的拟合结果如下图
拟合曲线趋于稳定值,拟合效果还是比较好的(巧了,在拟合500次的情况下步长比它大,比它小的都不稳定,但增大拟合次数可解决这一问题)
二、源代码
源代码的算法部分是在看懂别人的代码的基础上自己敲的,其余部分直接从https://blog.csdn.net/Snoopy_Yuan/article/details/63684219摘的,希望原作者不要骂我。。。。。。。
1、主程序 main_self.py
1 import numpy as np # for matrix calculation 2 3 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 4 5 # load the CSV file as a numpy matrix 6 7 dataset = np.loadtxt('../watermelon_3a.csv', delimiter=",") #以逗号为分隔符,读取文件数据,读出一个17行四列的数组 8 9 # separate the data from the target attributes 10 11 X = dataset[:, 1:3]#截取第一列,第二列数据 12 13 y = dataset[:, 3]#截取第三列数据 14 15 m, n = np.shape(X)#m反回行数,n反回列数 16 17 # draw scatter diagram to show the raw data 18 19 f1 = plt.figure(1) 20 21 plt.title('watermelon_3a') 22 23 plt.xlabel('density') 24 25 plt.ylabel('ratio_sugar') 26 27 plt.scatter(X[y == 0, 0], X[y == 0, 1], marker='o', color='k', s=100, label='bad') 28 #X[y == 0, 0]是一个一行九列的向量[0.666 0.243 0.245 0.343 0.639 0.657 0.36 0.593 0.719],它取得是X矩阵的第0列中,对y==0为真的行数的数据 29 #scatter函数是用来绘制散点图的 https://blog.csdn.net/fei347795790/article/details/94331112 30 31 plt.scatter(X[y == 1, 0], X[y == 1, 1], marker='o', color='g', s=100, label='good') 32 33 plt.legend(loc='upper right') 34 35 #plt.show()#用来显示图像 #如果不把这一行注释掉,程序执行到此处自动结束 36 37 38 from sklearn import model_selection 39 40 #import self_def 41 import self_def_xdl 42 43 # X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test 44 45 np.ones(n) 46 47 m, n = np.shape(X) 48 49 X_ex = np.c_[X, np.ones(m)] # extend the variable matrix to [x, 1] 为啥要写成X_ex呢,在p59 式3.25下面 50 51 X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = model_selection.train_test_split(X_ex, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=0)#划分训练集和测试集 52 53 # using gradDescent to get the optimal parameter beta = [w, b] in page-59 54 55 beta = self_def_xdl.gradDscent(X_train, y_train)#beta = -4.7 0.3 2.5 56 57 # prediction, beta mapping to the model 58 59 y_pred = self_def_xdl.predict(X_test, beta) 60 61 m_test = np.shape(X_test)[0] 62 63 # calculation of confusion_matrix and prediction accuracy计算混淆矩阵和计算的准确性 64 65 cfmat = np.zeros((2, 2)) 66 67 for i in range(m_test): 68 69 if y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 0: 70 cfmat[0, 0] += 1 71 72 elif y_pred[i] == y_test[i] == 1: 73 cfmat[1, 1] += 1 74 75 elif y_pred[i] == 0: 76 cfmat[1, 0] += 1 77 78 elif y_pred[i] == 1: 79 cfmat[0, 1] += 1 80 81 print(cfmat)
二、自定义函数 self_def_xdl.py
1 def likelihood_xdl(X,y,beta): 2 ''' 3 对应于实现P59-3.29 4 :param X:(x;1) m行n+1列的数组,n列代表样本有n个维度,m行代表有m个样本,为啥要n+1列呢,见3.25下面的一段话 5 :param y: m行1列的数组 6 :param beta: 1行n+1列的数组beta = (w;b) 7 :return: l_beta,一个数值 8 ''' 9 import numpy as np 10 m,n = np.shape(X) 11 sum = 0 12 for i in range(m): 13 sum += -y[i]*np.dot(beta,X[i].T)+np.math.log(1+np.math.exp(np.dot(beta,X[i].T))) 14 return sum 15 16 def gradDscent(X,y): 17 ''' 18 我使用的是批量梯度下降算法,如果样本的数据量比较大,还可使用随机梯度下降算法,详见https://blog.csdn.net/lilyth_lilyth/article/details/8973972 19 X,y是训练集的数据,对3.27式使用梯度下降算法 20 :param X: (x;1) m行n+1列的数组,n列代表样本有n个维度,m行代表有m个样本,为啥要n+1列呢,见3.25下面的一段话 21 :param y: m行1列的数组 22 :return:经过梯度下降算法一步一步迭代得出的beta 23 ''' 24 import numpy as np 25 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 26 m,n = np.shape(X) 27 h = 0.11#步长 28 beta = np.zeros(n)#1行n列 29 delta_beta = h*np.ones(n) 30 max_times = 1500#迭代次数 31 beta_history = np.zeros((n,max_times))#记录beta的历史数据 #注意,括号中还有括号 #注意n和maxtime的顺序 32 l_beta = 0 33 l_beta_temp = 0 34 35 for i in range(max_times): 36 temp_beta = beta #暂存beta数据 37 beta_history[:, i] = beta.T # 记录下beta的历史,后面去查看拟合情况 38 for j in range(n): 39 beta[j] += delta_beta[j] 40 41 l_beta_temp = likelihood_xdl(X,y,beta) 42 delta_beta[j] = -h*(l_beta_temp-l_beta)/delta_beta[j]#使用式B.16,B.17更新delta_beta 43 44 beta = temp_beta#恢复beta的数据 45 46 beta += delta_beta 47 l_beta = likelihood_xdl(X,y,beta) 48 49 t = np.arange(max_times) 50 f3 = plt.figure(3) 51 p1 = plt.subplot(311) # 311-3行1列第一个 52 p1.plot(t, beta_history[0]) 53 54 plt.ylabel('w1') 55 56 p2 = plt.subplot(312) 57 58 p2.plot(t, beta_history[1]) 59 60 plt.ylabel('w2') 61 62 p3 = plt.subplot(313) 63 64 p3.plot(t, beta_history[2]) 65 66 plt.ylabel('b') 67 68 plt.show() # 显示所有图像 69 70 return beta 71 72 def sigmoid(x, beta): 73 ''' 74 式3.18和3.25下面的一段话 75 @param x: 测试集的一个样本,为一维行向量 76 77 @param beta: 一维行向量 78 79 @return: sigmoid函数预测结果 80 81 ''' 82 import numpy as np 83 return 1.0 / (1 + np.math.exp(- np.dot(beta, x.T))) 84 85 86 def predict(X, beta): 87 ''' 88 89 使用3.16式 90 91 @param X: data sample form like [x, 1] 92 93 @param beta: the parameter of sigmoid form like [w, b] 94 95 @return: the class lable array 96 97 ''' 98 import numpy as np 99 m, n = np.shape(X) 100 101 y = np.zeros(m) 102 103 for i in range(m): 104 105 if sigmoid(X[i], beta) > 0.5: y[i] = 1; 106 107 return y 108 109 return beta
三、原始数据集 watermelon_3a.csv
1,0.697,0.46,1
2,0.774,0.376,1
3,0.634,0.264,1
4,0.608,0.318,1
5,0.556,0.215,1
6,0.403,0.237,1
7,0.481,0.149,1
8,0.437,0.211,1
9,0.666,0.091,0
10,0.243,0.0267,0
11,0.245,0.057,0
12,0.343,0.099,0
13,0.639,0.161,0
14,0.657,0.198,0
15,0.36,0.37,0
16,0.593,0.042,0
17,0.719,0.103,0




