Java String的理解
Java String的理解
在Java中String是一个比较特殊的对象---不可继承,不可变,直接赋值创建
不可继承,不可变
- String 类型被标final关键字修饰,所以不可继承
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
// ....
}
- Sting类中提供了一个final修饰的字符数组,用于存储Sting类型的值,所以一旦初始化则不能修改。
public final class String
implements java.io.Serializable, Comparable<String>, CharSequence {
private final char value[];
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
}
String的创建
Sting类型是Java中最常用的一个对象,可以通过两种方式进行创建
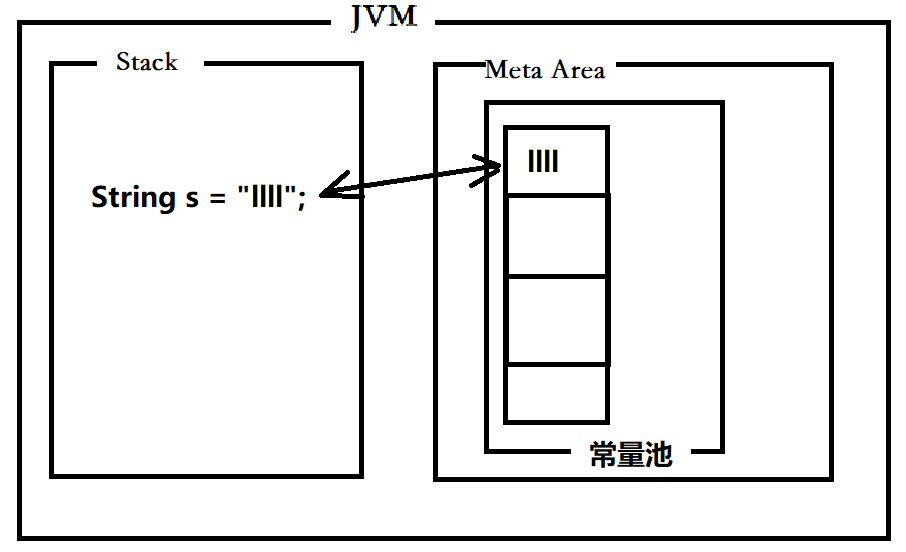
- 直接赋值
因为比较常用,所以 JVM对String类型进行了优化,可以对String类型直接赋值,直接将该String类型创建在常量池中,以方便引用
JVM对直接赋值的String类型,会先从常量池中查询对应的String类型,如果没有则会创建一个存储到常量池中,然后返回该引用。
// 直接赋值
String s = "llll";
-
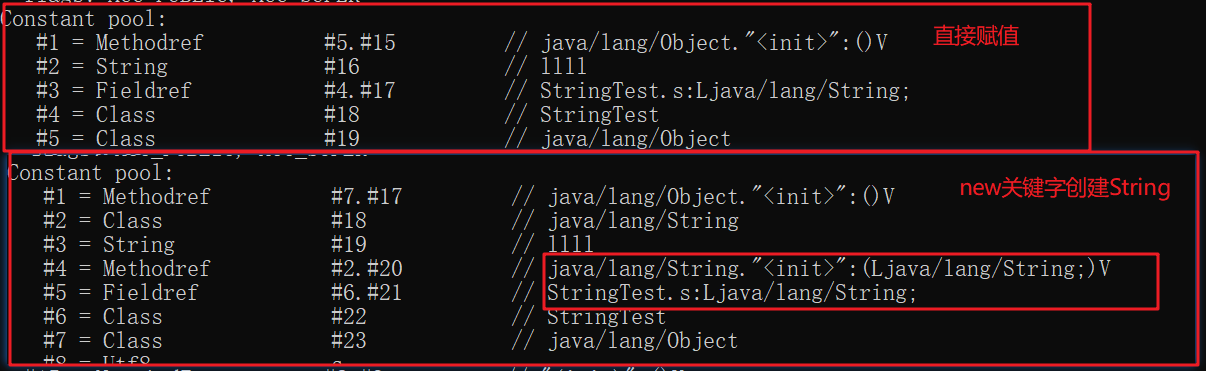
new关键字创建String对象
new关键字创建的String对象的区别在于,会先在堆内存中进行初始化,然后到常量池中加载对应的String类型。返回堆内存中的地址值给引用 -
两种方式的区别
String方法简介
构造方法
- 基础构造方法
public String() {
this.value = "".value;
}
public String(String original) {
this.value = original.value;
this.hash = original.hash;
}
- 字符数组构造方法
// 根据整个字符数组创建字符串
public String(char value[]) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(value, value.length);
}
//截取部分字符数组创建字符串
public String(char value[], int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= value.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > value.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
this.value = Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset+count);
}
- 根据Unicode编码进行创建字符串
// 没有使用过。。。
public String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) {
if (offset < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset);
}
if (count <= 0) {
if (count < 0) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(count);
}
if (offset <= codePoints.length) {
this.value = "".value;
return;
}
}
// Note: offset or count might be near -1>>>1.
if (offset > codePoints.length - count) {
throw new StringIndexOutOfBoundsException(offset + count);
}
final int end = offset + count;
// Pass 1: Compute precise size of char[]
int n = count;
for (int i = offset; i < end; i++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
continue;
else if (Character.isValidCodePoint(c))
n++;
else throw new IllegalArgumentException(Integer.toString(c));
}
// Pass 2: Allocate and fill in char[]
final char[] v = new char[n];
for (int i = offset, j = 0; i < end; i++, j++) {
int c = codePoints[i];
if (Character.isBmpCodePoint(c))
v[j] = (char)c;
else
Character.toSurrogates(c, v, j++);
}
this.value = v;
}
- 根据字节数组创建字符串
// 需要指定编码集,根据传递的编码集解码
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, String charsetName)
throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
if (charsetName == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charsetName");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charsetName, bytes, offset, length);
}
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length, Charset charset) {
if (charset == null)
throw new NullPointerException("charset");
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(charset, bytes, offset, length);
}
// 根据传入的字节数组和其长度创建字符串
public String(byte bytes[], int offset, int length) {
checkBounds(bytes, offset, length);
this.value = StringCoding.decode(bytes, offset, length);
}
public String(byte bytes[]) {
this(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
}
- 使用StringBuffer和StringBuilder创建字符串,不过不常用,可以使用这两个对象的toString方法创建字符串,更有效率
public String(StringBuffer buffer) {
synchronized(buffer) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(buffer.getValue(), buffer.length());
}
}
public String(StringBuilder builder) {
this.value = Arrays.copyOf(builder.getValue(), builder.length());
}
- 预留方法,默认访问类型,通过直接赋值创建字符串
// 预留方法,默认访问类型,通过直接赋值创建字符串
String(char[] value, boolean share) {
// assert share : "unshared not supported";
this.value = value;
}
静态方法
- valueOf()
调用toString()方法
public static String valueOf(Object obj) {
return (obj == null) ? "null" : obj.toString();
}
public static String valueOf(int i) {
return Integer.toString(i);
}
public static String valueOf(long l) {
return Long.toString(l);
}
public static String valueOf(float f) {
return Float.toString(f);
}
public static String valueOf(double d) {
return Double.toString(d);
}
调用构造
public static String valueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
public static String valueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
public static String valueOf(char c) {
char data[] = {c};
return new String(data, true);
}
public static String copyValueOf(char data[], int offset, int count) {
return new String(data, offset, count);
}
public static String copyValueOf(char data[]) {
return new String(data);
}
boolean
public static String valueOf(boolean b) {
return b ? "true" : "false";
}
- 格式化
public static String format(String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter().format(format, args).toString();
}
public static String format(Locale l, String format, Object... args) {
return new Formatter(l).format(format, args).toString();
}
普通方法
intern()方法
可以通过调用该方法指向常量池中的对象
public native String intern();
参考源码
第一要有志,第二要有识,第三要有恒。


