实验一 Many Time Pad
实验内容
【时间】 暂定 5 月 23 号(周六)晚上
【编程语言】 Python(推荐)或者 C/C++
【实验目的】
- 了解流密码的结构特点;
- 掌握 One-time Pad 的一般具体实现;
- 通过使用 Python(推荐)或者 C,编程实现一个流密码加密示例的破解,进一步认识在流密码加密中多次使用相同密钥导致的问题。
【实验内容】
在掌握流密码结构的基础上,通过本实验观察使用相同流密码密钥加密多个明文导致的严重后果。
附件 ciphertext.txt 有 11 个十六进制编码的密文,它们是使用流密码加密 11 个明文的结果,所有密文都使用相同的流密码密钥。
实验的目标是解密最后一个密文,并提交明文消息。
提示:
- 对密文进行异或,并考虑当空格与 [a ~ z, A ~ Z] 中的字符进行异或时会发生什么。
- 附件 encrypt.py 是用于生成密文的 Python 示例程序(不影响实验,仅供参考)。
实验分析
首先从生成密文的示例程序 encrypt.py 入手:
def strxor(a, b):
# xor two strings of different lengths
if len(a) > len(b):
return "".join([chr(ord(x) ^ ord(y)) for (x, y) in zip(a[:len(b)], b)])
else:
return "".join([chr(ord(x) ^ ord(y)) for (x, y) in zip(a, b[:len(a)])])
其中 strxor(a, b) 为加密函数,参数 a 为密钥,b 为明文。我们可以看出加密就是对明文和密钥进行异或。从异或入手,我们可以找出一些线索。
线索 1
从提示中我们可以找到“线索”:字母异或空格,相当于转换大小写。
空格 ^ 小写字母 = 大写字母,比如'a' ^ ' ' = 'A'空格 ^ 大写字母 = 小写字母字母 ^ 字母 = 非字母
因此,对于消息 \(m\),对位置 \(i\),\(j\) 上的字符 \(m_i\), \(m_j\) 进行异或,如果异或结果为英文字母,那么 \(i\),\(j\) 两个位置上的字符很可能一个是空格,另一个是英文字母(但也有其他可能,比如 '!' ^ 'B' = 'c',实验最后进行了解释)。
线索 2
对于异或,我们有另外一个性质:\(x = x \oplus y \oplus y\)。
假设密文 \(c\)、消息 \(m\)、密钥 \(k\),有 \(c_1 = m_1 \oplus k\),\(c_2 = m_2 \oplus k\) ……。于是根据上述异或的性质,我们可以得到 \(c_1 \oplus c_2 = m_1 \oplus k \oplus m_2 \oplus k = m_1 \oplus m_2\),此时,\(k\) 被消去了,得到了等式 \(c_1 \oplus c_2 = m_1 \oplus m_2\)。
思路
根据“线索”,我们可以形成大致的解密思路:
先寻找明文中可能存在的空格,位置记为 \(p\),接着有两种思路,
- 一种方法是:将 \(p\) 对应的密文(\(c\))和 space 做异或操作,就可得到对应位置的密钥信息,当获取足够多的密钥信息后,即可对目标密文进行解密
- 解释:因为此时位置 \(p\) 的明文为空格,即 \(m = space\),所以有 \(c \oplus space = m \oplus k \oplus space = space \oplus k \oplus space = k\)
- 另一种方法是:将 \(p\) 对应的密文(\(c_1\))直接和待解密密文(\(c_2\))进行异或,可得出待解密密文对应位置上的明文(大小写相反)
- 解释:\(c_1 \oplus c_2 = m_1 \oplus m_2\),因为 \(m_1\) 为空格,所以 \(c_1 \oplus c_2\) 的结果为 \(m_2\) 转换大小写的结果
如何寻找明文中可能存在的空格呢?
在 ciphertext.txt 中,每两个 16 进制字符代表明文的一个字符(因为 ASCII 的范围为 0 ~ 255)。我们把某条密文与剩余 9 条密文的相同位置进行异或,如果异或出来结果大部分都是字母,则说明了这条密文的这个位置对应的明文极有可能是个空格。
因此,从上述分析得知,在流密码加密中多次使用相同密钥是不安全的。
代码
以下代码片段通过计算出密钥的方法(而非直接对目标密文进行异或)来解密,并对关键部分进行注释。
计算空格的时候,可以把待解密密文也一起放进去异或,增加样本
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 判断空格的门限值,可根据结果进行修改调整
const int THRESHOLD_VALUE = 5;
const int KEY_LENGTH = 400;
// 存储各条密文同一个位置的最大 count 值
static vector<int> countArray(KEY_LENGTH);
// 读取密文
void readText(const string& fileName, vector<string>& cip, string& targetCip)
{
ifstream inFile(fileName);
if(!inFile.is_open())
{
cout << "Can't open the file\n";
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
string temp;
bool flag = false;
while(getline(inFile, temp))
{
string::size_type idx = temp.find("Ciphertext");
if(flag)
{
flag = false;
cip.push_back(temp);
}
if(idx != string::npos)
{
flag = true;
}
}
// 最后一条待解密的密文也放入 cip
cip.push_back(temp);
targetCip = temp;
}
int isAlphabet(int c)
{
if(c >= 65 && c <= 90)
{
return 1;
}
if(c >= 97 && c <= 122)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int hexToDecimal(const string& hexStr)
{
int decimal;
stringstream ss;
ss.str(hexStr);
ss >> hex >> decimal;
return decimal;
}
string decimalToHex(int decimal)
{
stringstream ss;
ss << hex << decimal;
return ss.str();
}
// 计算可能的空格位置
vector<vector<int>> findSpace(vector<string>& ciphertext)
{
vector<vector<int>> spacePos;
// 对于给出的 10 条密文,计算对应明文中可能为空格的位置
for(vector<int>::size_type i = 0; i != ciphertext.size(); i++)
{
string& cipher = ciphertext[i];
string::size_type cipherLen = cipher.length();
vector<int> space;
// 每两个 16 进制字符代表明文的一个字符
for(string::size_type j = 0; j < cipherLen; j = j + 2)
{
int tempI = hexToDecimal(cipher.substr(j, 2));
int count = 0;
// 位置 j 和 j + 1 上的字符与其余 10 条密文(包括待解密密文)该位置的字符进行异或
for(vector<string>::size_type k = 0; k != ciphertext.size(); k++)
{
string& residueCipher = ciphertext[k];
if(i == k || j > residueCipher.length())
{
continue;
}
int tempK = hexToDecimal(residueCipher.substr(j, 2));
// 若异或结果为字母,则 count++
count += isAlphabet(tempI ^ tempK);
}
// 若超过 THRESHOLD_VALUE 条的异或结果为字母,那么我们可以认定这个位置对应的明文是空格
if(count > THRESHOLD_VALUE)
{
space.push_back(j);
// count 值越大,空格的可能性越大。存入位置 j 上最大的 count 和对应密文的序号,因为 j + 1
// 位置是空的,刚好可以存密文的序号
if(countArray[j] < count)
{
countArray[j] = count;
countArray[j + 1] = i;
}
}
}
spacePos.push_back(space);
}
return spacePos;
}
// 计算密钥
vector<string> calculateKey(vector<string>& ciphertext)
{
vector<string> key(KEY_LENGTH);
vector<vector<int>> spacePos = findSpace(ciphertext);
for(vector<string>::size_type i = 0; i != ciphertext.size(); i++)
{
string& cipher = ciphertext[i];
vector<int>& space = spacePos[i];
for(auto pos : space)
{
if(countArray[pos + 1] == (int)i)
{
// 该位置密文与空格进行异或,计算该位置的密钥
// 32 是空格的 ASCII 码
int k = 32 ^ hexToDecimal(cipher.substr(pos, 2));
key[pos] = decimalToHex(k);
}
}
}
return key;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
vector<string> ciphertext;
string targetCiphertext;
readText("./ciphertext.txt", ciphertext, targetCiphertext);
vector<string> key = calculateKey(ciphertext);
string message;
// 解密目标密文
for(string::size_type i = 0; i < targetCiphertext.length(); i = i + 2)
{
// 若对应位置上无密钥,则该位置统一放置 '0'
if(key[i].empty())
{
message.push_back('0');
}
else
{
char m = hexToDecimal(targetCiphertext.substr(i, 2)) ^ hexToDecimal(key[i]);
message.push_back(m);
}
}
cout << message << endl;
return 0;
}
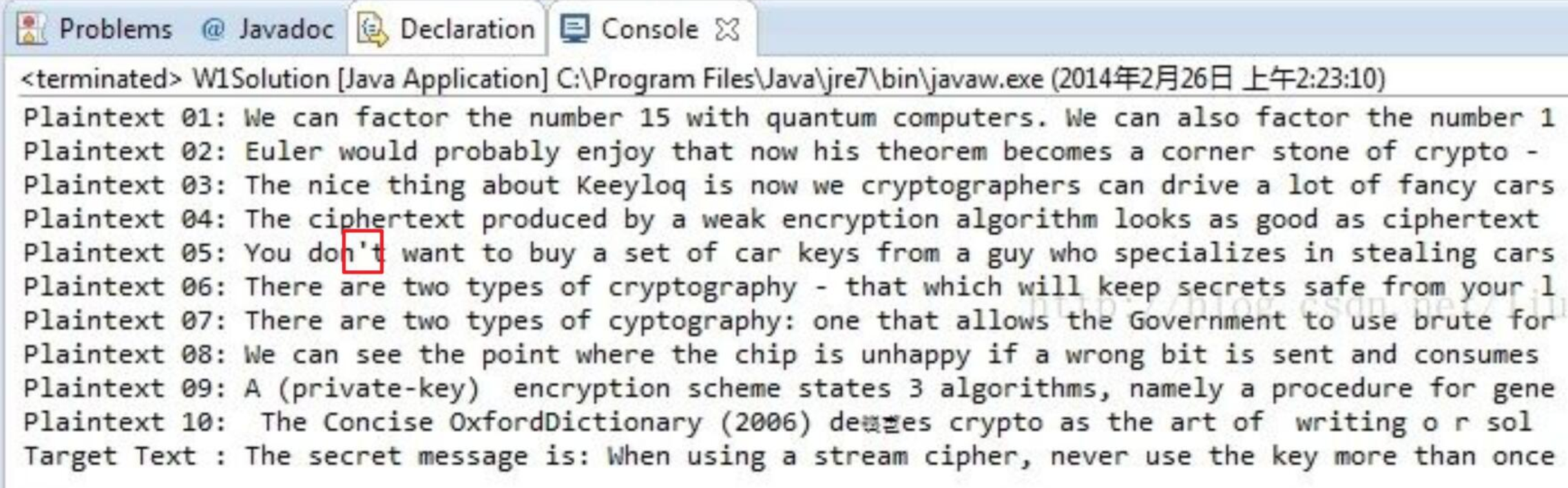
实验结果
运行上述代码,输出:
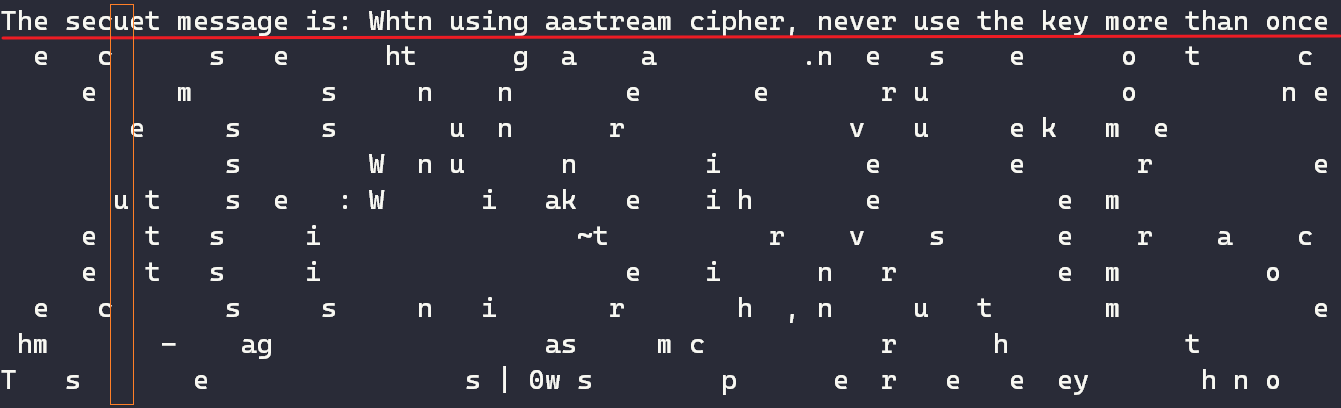
The secuet message is: Whtn using aastream cipher, never use the key more than once
可以猜出,原文为:The secret message is: When using a stream cipher, never use the key more than once
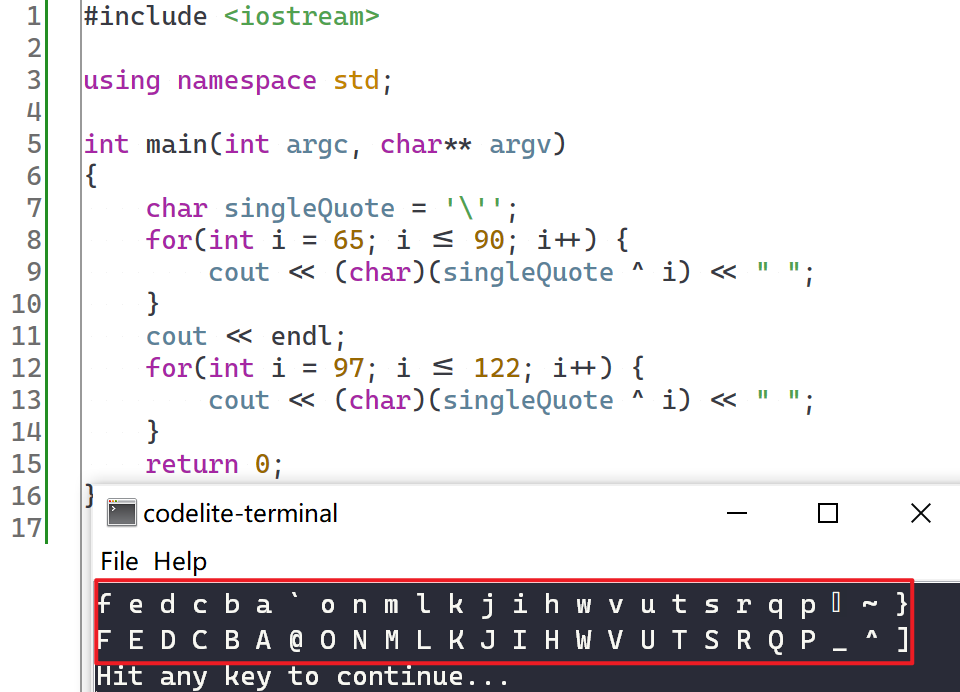
我们发现,第 8 个字符
r(secret)被解析成了u。
从上图可以看出,只有第 5 条密文的第 8 个位置被假定为空格,但是最终第 8 个字符却解错了,由此说明第 5 条密文的第 8 个位置实际上并不是空格,它被误判了。那这个位置的正确明文是什么呢?这篇文章给出了正确率较高的明文,下图:
可以看到该位置是一个单引号
',把单引号和所有字母进行异或:
大多数都是字母,所以单引号被误判为空格(因为判断空格的依据是:异或出来的结果是否为字母)。