最近都在巩固JS的基础知识,今天组要看的是有关继承方面的,每次看都会加深自己的理解呢
1.借助构造函数实现继承
原理:在子类中改变父类this的指向
function Parent1() { this.name = 'parent1'; } function Child1() { Parent1.call(this); //也可以使用 apply,改变函数运行的上下文;将父级的构造函数的this指向子类的实例 this.type = 'child1'; } console.log(new Child1());

在控制台打印的信息可以看出,Child1的实例继承了Parent1的name属性
缺点:不能继承父类原型对象上的方法或属性
在原有代码的基础上做如下修改:
function Parent1() { this.name = 'parent1'; } Parent1.prototype.say = function () { console.log('hi'); }; Parent1.prototype.color='red'; function Child1() { Parent1.call(this); this.type = 'child1'; } var s=new Child1();
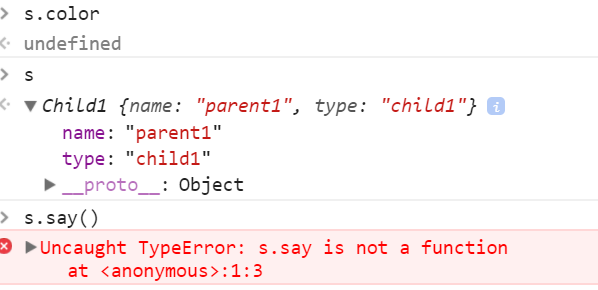 在控制台进行查看,可以看到s并没有继承color属性和say()方法
在控制台进行查看,可以看到s并没有继承color属性和say()方法
2.借助原型链实现继承
function Parent2() { this.name = 'parent2'; } function Child2() { this.type = 'child1'; } /** *原型链继承原理:s1是Child2的实例对象,它的__ptoro__属性指向Child2的原型对象, *即Child2.prototype;代码中Child2.prototype=new Parent2(),等于Parent2的实例对 *象,因此可以继承Parent2 */ Child2.prototype=new Parent2(); //重点 var s1 = new Child2();
缺点:原型链上的对象共享;如果父类Parent2中包含引用类型的属性,不同子类上的该属性是共享的,改变任意一个的值都会影响其他。
function Parent2() { this.name = 'parent2'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function Child2() { this.type = 'child2'; } Child2.prototype = new Parent2(); //重点 var s1 = new Child2(); var s2 = new Child2(); console.log(s1.play, s2.play); s1.play.push(4); console.log(s1.play, s2.play);
 虽然只改变了s1的play属性,但s2的也被改变了
虽然只改变了s1的play属性,但s2的也被改变了
3.组合继承方式;构造函数+原型链相结合
function Parent3() { this.name = 'parent3'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function Child3() { Parent3.call(this); this.type = 'child3'; } Child3.prototype = new Parent3(); var s3 = new Child3(); var s4 = new Child3(); s3.play.push(4); console.log(s3.play, s4.play);
//注意:s3.constructor是Parent3
组合方式虽然解决了共享的问题,即s3的play值得改变不会影响s4的play值;但是这种方式会使父级的构造函数执行两次,因此可以进行优化。
3-1.组合继承方式的优化1
function Parent4() { this.name = 'parent4'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function Child4() { Parent4.call(this); this.type = 'child4'; } Child4.prototype = Parent4.prototype; var s5 = new Child4(); var s6 = new Child4(); s5.play.push(4); console.log(s5, s6);


不足:无法识别实例是由子类直接实例化还是由父类直接实例化的;s5的constructor是Parent4;因为Child4.prototype = Parent4.prototype;
3.2 组合继承的完美写法
function Parent5() { this.name = 'parent5'; this.play = [1, 2, 3]; } function Child5() { Parent5.call(this); this.type = 'child5'; } //Object.create创建一个中间对象,原型对象是父类的原型对象 Child5.prototype = Object.create(Parent5.prototype); Child5.prototype.constructor = Child5 var s7 = new Child5(); var s8 = new Child5(); console.log(s7, s8);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号