https原理、http连接池、HttpClient和OkHttp的区别
1、https原理
2、http连接池
3、HttpClient和OkHttp的区别
从二者的使用,超时设置,性能方面看下它们的不同之处。
3.1、二者的使用
HttpClient的使用
使用HttpClient发送请求主要分为一下几步骤:
- 创建 CloseableHttpClient对象或CloseableHttpAsyncClient对象,前者同步,后者为异步
- 创建Http请求对象
- 调用execute方法执行请求,如果是异步请求在执行之前需调用start方法
创建连接:
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build();
该连接为同步连接,如果要使用异步连接(文件上传也是)需要引入额外依赖:
<!---文件上传-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpmime</artifactId>
<version>4.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--异步请求-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpasyncclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.3</version>
</dependency>
Get请求:
@Test public void testGet() throws IOException { String api = "/api/files/1"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); }
Post请求:
@Test public void testPost() throws IOException { String api = "/api/user"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url); UserVO userVO = UserVO.builder().name("h2t2").build(); httpPost.setHeader("Content-Type", "application/json;charset=utf8"); httpPost.setEntity(new StringEntity(JSONObject.toJSONString(userVO), "UTF-8")); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); }
文件上传:
@Test public void testUpload1() throws IOException { String api = "/api/files/1"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url); File file = new File("/Users/hetiantian/Desktop/test.pdf"); FileBody fileBody = new FileBody(file); MultipartEntityBuilder builder = MultipartEntityBuilder.create(); builder.setMode(HttpMultipartMode.BROWSER_COMPATIBLE); builder.addPart("file", fileBody); //addPart上传文件 HttpEntity entity = builder.build(); httpPost.setEntity(entity); CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); System.out.println(EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity())); }
OkHttp的使用
使用OkHttp发送请求主要分为一下几步骤:
- 创建OkHttpClient对象
- 创建Request对象
- 将Request 对象封装为Call
- 通过Call 来执行同步或异步请求,调用execute方法同步执行,调用enqueue方法异步执行
创建连接:
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Get请求:
@Test public void testGet() throws IOException { String api = "/api/files/1"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); Request request = new Request.Builder() .url(url) .get() .build(); final Call call = client.newCall(request); Response response = call.execute(); System.out.println(response.body().string()); }
Post请求:
@Test public void testPost() throws IOException { String api = "/api/user"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); //请求参数 JSONObject json = new JSONObject(); json.put("name", "hetiantian"); RequestBody requestBody = RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("application/json; charset=utf-8"), String.valueOf(json)); Request request = new Request.Builder() .url(url) .post(requestBody) //post请求 .build(); final Call call = client.newCall(request); Response response = call.execute(); System.out.println(response.body().string()); }
文件上传:
@Test public void testUpload() throws IOException { String api = "/api/files/1"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); RequestBody requestBody = new MultipartBody.Builder() .setType(MultipartBody.FORM) .addFormDataPart("file", "docker_practice.pdf", RequestBody.create(MediaType.parse("multipart/form-data"), new File("C:/Users/hetiantian/Desktop/学习/docker_practice.pdf"))) .build(); Request request = new Request.Builder() .url(url) .post(requestBody) //默认为GET请求,可以不写 .build(); final Call call = client.newCall(request); Response response = call.execute(); System.out.println(response.body().string()); }
总结:从使用上来看,OkHttp的build模式创建对象更简洁一些
3.2、超时设置
HttpClient超时设置:
在HttpClient4.3+版本以上,超时设置通过RequestConfig进行设置
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClientBuilder.create().build(); private RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom() .setSocketTimeout(60 * 1000) .setConnectTimeout(60 * 1000).build(); String api = "/api/files/1"; String url = String.format("%s%s", BASE_URL, api); HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url); httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig); //设置超时时间
OkHttp超时设置:
直接在OkHttp上进行设置
private OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient.Builder() .connectTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//设置连接超时时间 .readTimeout(60, TimeUnit.SECONDS)//设置读取超时时间 .build();
总结:如果client是单例模式,HttpClient在设置超时方面来的更灵活,针对不同请求类型设置不同的超时时间,OkHttp一旦设置了超时时间,所有请求类型的超时时间也就确定。
3.3、性能比较
测试环境:
- CPU 六核
- 内存 8G
- windows10
每种测试用例都测试五次,排除偶然性
client连接为单例:
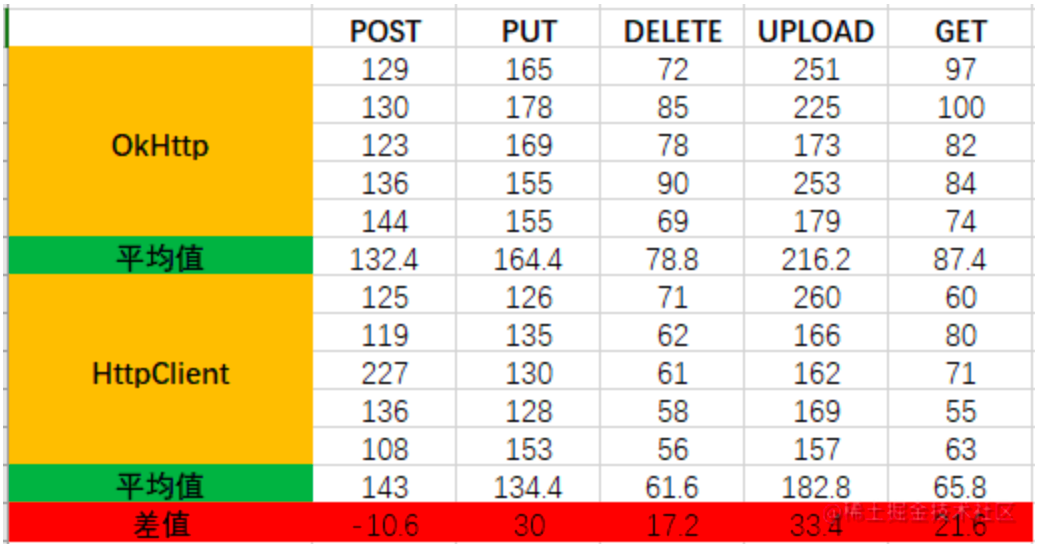
client连接不为单例:
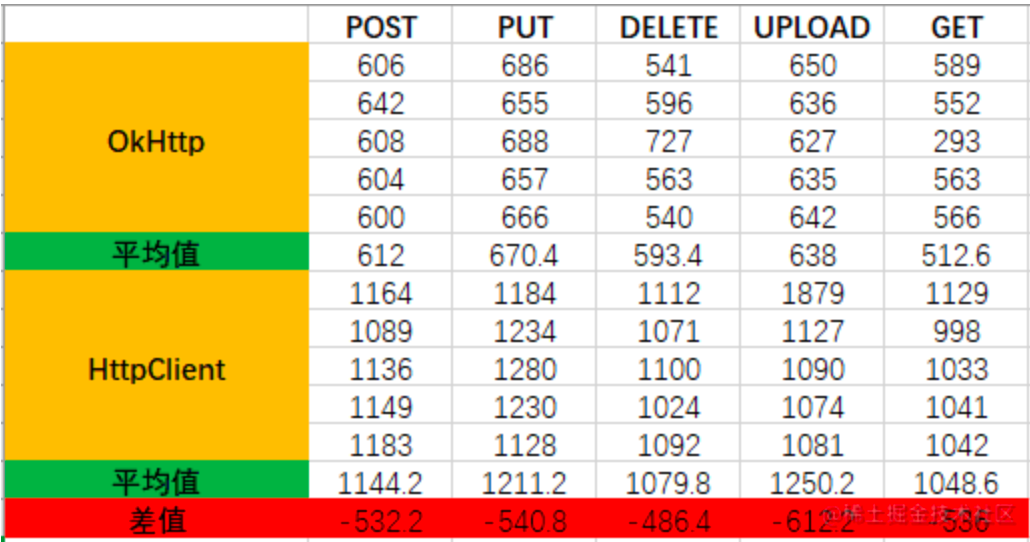
总结:二者在单例模式时都会使用到线程池,所以比非单例模式性能要高。单例模式下,HttpClient的响应速度要更快一些,单位为毫秒,性能差异相差不大,非单例模式下,OkHttp的性能更好,HttpClient创建连接比较耗时。
4、OKhttp原理
OKHttp的主要特性包括:
-
连接池:OKHttp维护一个连接池,可复用活动的HTTP和HTTP/2连接。
-
GZIP压缩:通过GZIP压缩下载的数据,可以减少传输数据量。
-
缓存机制:对请求的响应进行缓存,减少服务器的负载和带宽消耗。
-
支持SPDY和HTTP/2:在支持的服务器上使用,可以使用同一个连接发送多个请求。
-
请求构建和同步:OKHttp提供构建请求的构建器模式,支持同步和异步请求。
OKhttp对TCP的复用:利用连接池,缓存所有的有效连接对象。(默认最大5个连接)
清理机制:垃圾连接
1.超过5分钟没有用过的链接
2.超过5个闲置链接后,从最久闲置的链接开始执行清理(LRU)





