程序员基本功系列4——跳表
跳表最典型的应用是在 Redis 的有序集合,是通过哈希表+跳表来实现的,因为有序集合中的元素是不重复的,这是通过哈希表来实现的。
今天我们主要看跳表。先来看一张图:
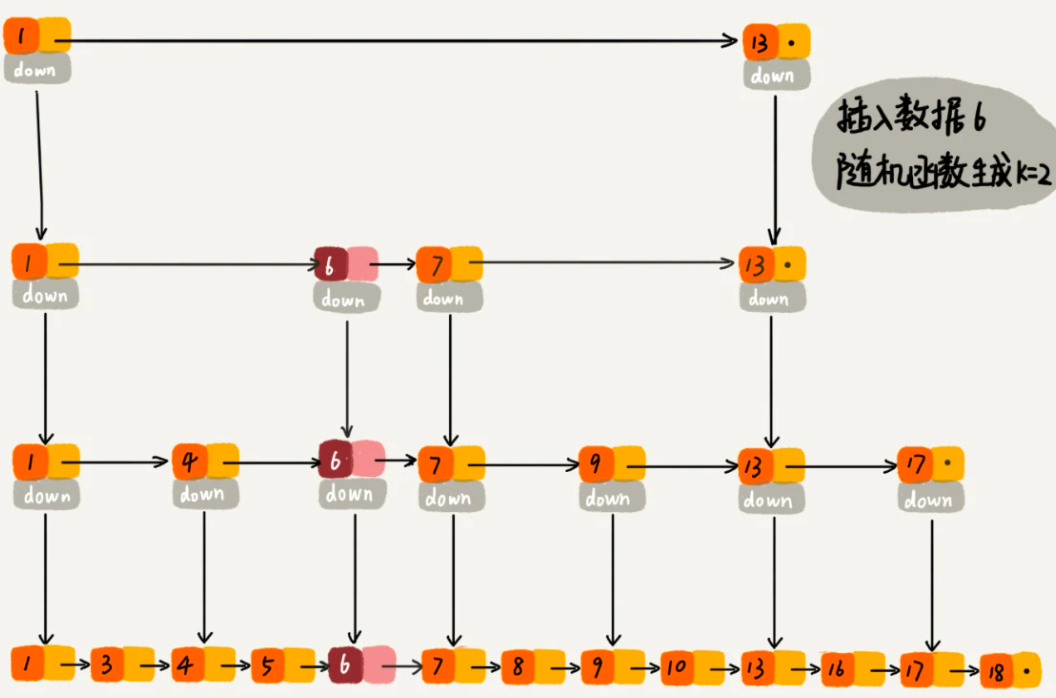
跳表底层是链表来存储节点数据,然后逐层建立索引。它查询数据的时间复杂度是 O(logn),因为底层是链表,所以插入和删除的时间复杂度是 O(1),主要是浪费在位置的查找上,所以插入和删除的时间复杂度也是 O(logn)。
红黑树也可以实现快速的查询、插入和删除,那 Redis为什么不适用红黑树?一个原因是红黑树的代码实现要相对复杂,二是按区间查找数据红黑树效率要比跳表低很多。
最后来看一段Java实现的跳表来更好的理解跳表:
package com.study.skiplist; import java.util.Random; /** * 1,跳表的一种实现方法,用于练习。跳表中存储的是正整数,并且存储的是不重复的。 * 2,看完这个,再看ConcurrentSkipListMap 源码,会有很大收获 */ public class SkipList2 { private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 16; private int levelCount = 1; /** * 带头链表 */ private Node head = new Node(MAX_LEVEL); private Random r = new Random(); public Node find(int value) { Node p = head; // 从最大层开始查找,找到前一节点,通过--i,移动到下层再开始查找 for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) { while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) { // 找到前一节点 p = p.forwards[i]; } } if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) { return p.forwards[0]; } else { return null; } } /** * 插入 */ public void insert(int value) { int level = head.forwards[0] == null ? 1 : randomLevel(); // 每次只增加一层,如果条件满足 if (level > levelCount) { level = ++levelCount; } Node newNode = new Node(level); newNode.data = value; Node update[] = new Node[level]; for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) { update[i] = head; } Node p = head; // 从最大层开始查找,找到前一节点,通过--i,移动到下层再开始查找 for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) { while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) { // 找到前一节点 p = p.forwards[i]; } // levelCount 会 > level,所以加上判断 if (level > i) { update[i] = p; } } for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) { newNode.forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i]; update[i].forwards[i] = newNode; } } /** * 插入方法2 */ public void insert2(int value) { int level = head.forwards[0] == null ? 1 : randomLevel(); // 每次只增加一层,如果条件满足 if (level > levelCount) { level = ++levelCount; } Node newNode = new Node(level); newNode.data = value; Node p = head; // 从最大层开始查找,找到前一节点,通过--i,移动到下层再开始查找 for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) { while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) { // 找到前一节点 p = p.forwards[i]; } // levelCount 会 > level,所以加上判断 if (level > i) { if (p.forwards[i] == null) { p.forwards[i] = newNode; } else { Node next = p.forwards[i]; p.forwards[i] = newNode; newNode.forwards[i] = next; } } } } /** * 未优化前 * @param level 0 表示随机层数,不为0,表示指定层数,指定层数 * 可以让每次打印结果不变动,这里是为了便于学习理解 */ public void insert(int value, int level) { // 随机一个层数 if (level == 0) { level = randomLevel(); } // 创建新节点 Node newNode = new Node(level); newNode.data = value; // 表示从最大层到低层,都要有节点数据 newNode.maxLevel = level; // 记录要更新的层数,表示新节点要更新到哪几层 Node update[] = new Node[level]; for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) { update[i] = head; } /** * * 1,说明:层是从下到上的,这里最下层编号是0,最上层编号是15 * 2,这里没有从已有数据最大层(编号最大)开始找,(而是随机层的最大层)导致有些问题。 * 如果数据量为1亿,随机level=1 ,那么插入时间复杂度为O(n) */ Node p = head; for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; --i) { while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) { p = p.forwards[i]; } // 这里update[i]表示当前层节点的前一节点,因为要找到前一节点,才好插入数据 update[i] = p; } // 将每一层节点和后面节点关联 for (int i = 0; i < level; ++i) { // 记录当前层节点后面节点指针 newNode.forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i]; // 前一个节点的指针,指向当前节点 update[i].forwards[i] = newNode; } // 更新层高 if (levelCount < level) levelCount = level; } public void delete(int value) { Node[] update = new Node[levelCount]; Node p = head; for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) { while (p.forwards[i] != null && p.forwards[i].data < value) { p = p.forwards[i]; } update[i] = p; } if (p.forwards[0] != null && p.forwards[0].data == value) { for (int i = levelCount - 1; i >= 0; --i) { if (update[i].forwards[i] != null && update[i].forwards[i].data == value) { update[i].forwards[i] = update[i].forwards[i].forwards[i]; } } } } /** * 随机 level 次,如果是奇数层数 +1,防止伪随机 */ private int randomLevel() { int level = 1; for (int i = 1; i < MAX_LEVEL; ++i) { if (r.nextInt() % 2 == 1) { level++; } } return level; } /** * 打印每个节点数据和最大层数 */ public void printAll() { Node p = head; while (p.forwards[0] != null) { System.out.print(p.forwards[0] + " "); p = p.forwards[0]; } System.out.println(); } /** * 打印所有数据 */ public void printAll_beautiful() { Node p = head; Node[] c = p.forwards; Node[] d = c; int maxLevel = c.length; for (int i = maxLevel - 1; i >= 0; i--) { do { System.out.print((d[i] != null ? d[i].data : null) + ":" + i + "-------"); } while (d[i] != null && (d = d[i].forwards)[i] != null); System.out.println(); d = c; } } /** * 跳表的节点,每个节点记录了当前节点数据和所在层数数据 */ public class Node { private int data = -1; /** * 表示当前节点位置的下一个节点所有层的数据,从上层切换到下层,就是数组下标-1, * forwards[3]表示当前节点在第三层的下一个节点。 */ private Node forwards[]; /** * 这个值其实可以不用,看优化insert() */ private int maxLevel = 0; public Node(int level) { forwards = new Node[level]; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(); builder.append("{ data: "); builder.append(data); builder.append("; levels: "); builder.append(maxLevel); builder.append(" }"); return builder.toString(); } } public static void main(String[] args) { SkipList2 list = new SkipList2(); list.insert(1, 3); list.insert(2, 3); list.insert(3, 2); list.insert(4, 4); list.insert(5, 10); list.insert(6, 4); list.insert(8, 5); list.insert(7, 4); list.printAll_beautiful(); list.printAll(); /** * 结果如下: * null:15------- * null:14------- * null:13------- * null:12------- * null:11------- * null:10------- * 5:9------- * 5:8------- * 5:7------- * 5:6------- * 5:5------- * 5:4------- 8:4------- * 4:3-------5:3-------6:3-------7:3-------8:3------- * 1:2-------2:2------- 4:2-------5:2-------6:2-------7:2-------8:2------- * 1:1-------2:1-------3:1-------4:1-------5:1-------6:1-------7:1-------8:1------- * 1:0-------2:0-------3:0-------4:0-------5:0-------6:0-------7:0-------8:0------- * { data: 1; levels: 3 } { data: 2; levels: 3 } { data: 3; levels: 2 } { data: 4; levels: 4 } * { data: 5; levels: 10 } { data: 6; levels: 4 } { data: 7; levels: 4 } { data: 8; levels: 5 } */ // 优化后insert() SkipList2 list2 = new SkipList2(); list2.insert2(1); list2.insert2(2); list2.insert2(6); list2.insert2(7); list2.insert2(8); list2.insert2(3); list2.insert2(4); list2.insert2(5); System.out.println(); list2.printAll_beautiful(); } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 一起来玩mcp_server_sqlite,让AI帮你做增删改查!!